diff options
Diffstat (limited to 'python-apiflask.spec')
| -rw-r--r-- | python-apiflask.spec | 966 |
1 files changed, 966 insertions, 0 deletions
diff --git a/python-apiflask.spec b/python-apiflask.spec new file mode 100644 index 0000000..4b1ec2f --- /dev/null +++ b/python-apiflask.spec @@ -0,0 +1,966 @@ +%global _empty_manifest_terminate_build 0 +Name: python-APIFlask +Version: 1.3.1 +Release: 1 +Summary: A lightweight web API framework based on Flask and marshmallow-code projects. +License: MIT +URL: https://apiflask.com +Source0: https://mirrors.nju.edu.cn/pypi/web/packages/b3/0f/447d605b7b4d290c4418eaea2a3663d09599fee6373b1f56514961480a77/APIFlask-1.3.1.tar.gz +BuildArch: noarch + +Requires: python3-apispec +Requires: python3-flask-httpauth +Requires: python3-flask-marshmallow +Requires: python3-flask +Requires: python3-webargs +Requires: python3-typing-extensions +Requires: python3-asgiref +Requires: python3-dotenv +Requires: python3-pyyaml + +%description + + + +# APIFlask + +[](https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask/actions) [](https://codecov.io/gh/apiflask/apiflask) + +APIFlask is a lightweight Python web API framework based on [Flask](https://github.com/pallets/flask) and [marshmallow-code](https://github.com/marshmallow-code) projects. It's easy to use, highly customizable, ORM/ODM-agnostic, and 100% compatible with the Flask ecosystem. + +With APIFlask, you will have: + +- More sugars for view function (`@app.input()`, `@app.output()`, `@app.get()`, `@app.post()` and more) +- Automatic request validation and deserialization +- Automatic response formatting and serialization +- Automatic [OpenAPI Specification](https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification) (OAS, formerly Swagger Specification) document generation +- Automatic interactive API documentation +- API authentication support (with [Flask-HTTPAuth](https://github.com/miguelgrinberg/flask-httpauth)) +- Automatic JSON response for HTTP errors + + +## Requirements + +- Python 3.7+ +- Flask 1.1.0+ + + +## Installation + +For Linux and macOS: + +```bash +$ pip3 install apiflask +``` + +For Windows: + +```bash +> pip install apiflask +``` + + +## Links + +- Website: <https://apiflask.com> +- Documentation: <https://apiflask.com/docs> +- PyPI Releases: <https://pypi.python.org/pypi/APIFlask> +- Change Log: <https://apiflask.com/changelog> +- Source Code: <https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask> +- Issue Tracker: <https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask/issues> +- Discussion: <https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask/discussions> +- Twitter: <https://twitter.com/apiflask> + + +## Example + +```python +from apiflask import APIFlask, Schema, abort +from apiflask.fields import Integer, String +from apiflask.validators import Length, OneOf + +app = APIFlask(__name__) + +pets = [ + {'id': 0, 'name': 'Kitty', 'category': 'cat'}, + {'id': 1, 'name': 'Coco', 'category': 'dog'} +] + + +class PetIn(Schema): + name = String(required=True, validate=Length(0, 10)) + category = String(required=True, validate=OneOf(['dog', 'cat'])) + + +class PetOut(Schema): + id = Integer() + name = String() + category = String() + + +@app.get('/') +def say_hello(): + # returning a dict or list equals to use jsonify() + return {'message': 'Hello!'} + + +@app.get('/pets/<int:pet_id>') +@app.output(PetOut) +def get_pet(pet_id): + if pet_id > len(pets) - 1: + abort(404) + # you can also return an ORM/ODM model class instance directly + # APIFlask will serialize the object into JSON format + return pets[pet_id] + + +@app.patch('/pets/<int:pet_id>') +@app.input(PetIn(partial=True)) +@app.output(PetOut) +def update_pet(pet_id, data): + # the validated and parsed input data will + # be injected into the view function as a dict + if pet_id > len(pets) - 1: + abort(404) + for attr, value in data.items(): + pets[pet_id][attr] = value + return pets[pet_id] +``` + +<details> +<summary>You can also use class-based views based on <code>MethodView</code></summary> + +```python +from apiflask import APIFlask, Schema, abort +from apiflask.fields import Integer, String +from apiflask.validators import Length, OneOf +from apiflask.views import MethodView + +app = APIFlask(__name__) + +pets = [ + {'id': 0, 'name': 'Kitty', 'category': 'cat'}, + {'id': 1, 'name': 'Coco', 'category': 'dog'} +] + + +class PetIn(Schema): + name = String(required=True, validate=Length(0, 10)) + category = String(required=True, validate=OneOf(['dog', 'cat'])) + + +class PetOut(Schema): + id = Integer() + name = String() + category = String() + + +class Hello(MethodView): + + # use HTTP method name as class method name + def get(self): + return {'message': 'Hello!'} + + +class Pet(MethodView): + + @app.output(PetOut) + def get(self, pet_id): + """Get a pet""" + if pet_id > len(pets) - 1: + abort(404) + return pets[pet_id] + + @app.input(PetIn(partial=True)) + @app.output(PetOut) + def patch(self, pet_id, data): + """Update a pet""" + if pet_id > len(pets) - 1: + abort(404) + for attr, value in data.items(): + pets[pet_id][attr] = value + return pets[pet_id] + + +app.add_url_rule('/', view_func=Hello.as_view('hello')) +app.add_url_rule('/pets/<int:pet_id>', view_func=Pet.as_view('pet')) +``` +</details> + +<details> +<summary>Or use <code>async def</code> with Flask 2.0</summary> + +```bash +$ pip install -U "apiflask[async]" +``` + +```python +import asyncio + +from apiflask import APIFlask + +app = APIFlask(__name__) + + +@app.get('/') +async def say_hello(): + await asyncio.sleep(1) + return {'message': 'Hello!'} +``` + +See <em><a href="https://flask.palletsprojects.com/async-await">Using async and await</a></em> for the details of the async support in Flask 2.0. + +</details> + +Save this as `app.py`, then run it with: + +```bash +$ flask run --reload +``` + +Or run in debug mode: + +```bash +$ flask run --debug +``` + +Now visit the interactive API documentation (Swagger UI) at <http://localhost:5000/docs>: + +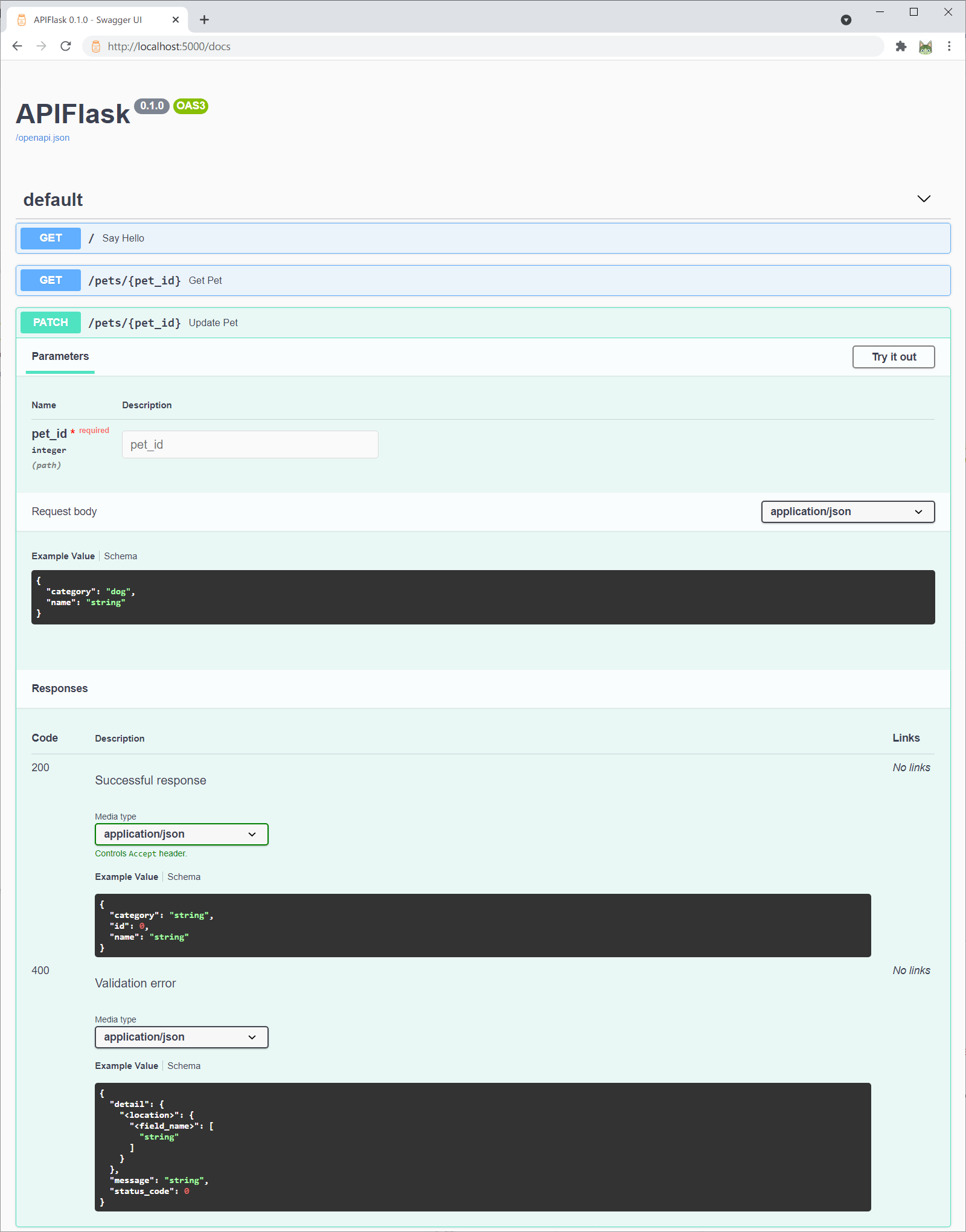 + +Or you can change the API documentation UI when creating the APIFlask instance with the `docs_ui` parameter: + +```py +app = APIFlask(__name__, docs_ui='redoc') +``` + +Now <http://localhost:5000/docs> will render the API documentation with Redoc. + +Supported `docs_ui` values (UI libraries) include: + +- `swagger-ui` (default value): [Swagger UI](https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui) +- `redoc`: [Redoc](https://github.com/Redocly/redoc) +- `elements`: [Elements](https://github.com/stoplightio/elements) +- `rapidoc`: [RapiDoc](https://github.com/rapi-doc/RapiDoc) +- `rapipdf`: [RapiPDF](https://github.com/mrin9/RapiPdf) + +The auto-generated OpenAPI spec file is available at <http://localhost:5000/openapi.json>. You can also get the spec with [the `flask spec` command](https://apiflask.com/openapi/#the-flask-spec-command): + +```bash +$ flask spec +``` + +For some complete examples, see [/examples](https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask/tree/main/examples). + + +## Relationship with Flask + +APIFlask is a thin wrapper on top of Flask. You only need to remember the following differences (see *[Migrating from Flask](https://apiflask.com/migrating)* for more details): + +- When creating an application instance, use `APIFlask` instead of `Flask`. +- When creating a blueprint instance, use `APIBlueprint` instead of `Blueprint`. +- When creating a class-based view, use `apiflask.views.MethodView` instead of `flask.views.MethodView`. +- The `abort()` function from APIFlask (`apiflask.abort`) returns JSON error response. + +For a minimal Flask application: + +```python +from flask import Flask, request, escape + +app = Flask(__name__) + +@app.route('/') +def hello(): + name = request.args.get('name', 'Human') + return f'Hello, {escape(name)}' +``` + +Now change to APIFlask: + +```python +from apiflask import APIFlask # step one +from flask import request, escape + +app = APIFlask(__name__) # step two + +@app.route('/') +def hello(): + name = request.args.get('name', 'Human') + return f'Hello, {escape(name)}' +``` + +In a word, to make Web API development in Flask more easily, APIFlask provides `APIFlask` and `APIBlueprint` to extend Flask's `Flask` and `Blueprint` objects and it also ships with some helpful utilities. Other than that, you are actually using Flask. + + +## Relationship with marshmallow + +APIFlask accepts marshmallow schema as data schema, uses webargs to validate the request data against the schema, and uses apispec to generate the OpenAPI representation from the schema. + +You can build marshmallow schemas just like before, but APIFlask also exposes some marshmallow APIs for convenience: + +- `apiflask.Schema`: The base marshmallow schema class. Notice it sets the `set_class` to `OrderedSet` by default. +- `apiflask.fields`: The marshmallow fields, contain the fields from both marshmallow and Flask-Marshmallow. Beware that the aliases (`Url`, `Str`, `Int`, `Bool`, etc.) were removed. +- `apiflask.validators`: The marshmallow validators. + +```python +from apiflask import Schema +from apiflask.fields import Integer, String +from apiflask.validators import Length, OneOf +from marshmallow import pre_load, post_dump, ValidationError +``` + +## Credits + +APIFlask starts as a fork of [APIFairy](https://github.com/miguelgrinberg/APIFairy) and is inspired by [flask-smorest](https://github.com/marshmallow-code/flask-smorest) and [FastAPI](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi) (see *[Comparison and Motivations](https://apiflask.com/comparison)* for the comparison between these projects). + + + + +%package -n python3-APIFlask +Summary: A lightweight web API framework based on Flask and marshmallow-code projects. +Provides: python-APIFlask +BuildRequires: python3-devel +BuildRequires: python3-setuptools +BuildRequires: python3-pip +%description -n python3-APIFlask + + + +# APIFlask + +[](https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask/actions) [](https://codecov.io/gh/apiflask/apiflask) + +APIFlask is a lightweight Python web API framework based on [Flask](https://github.com/pallets/flask) and [marshmallow-code](https://github.com/marshmallow-code) projects. It's easy to use, highly customizable, ORM/ODM-agnostic, and 100% compatible with the Flask ecosystem. + +With APIFlask, you will have: + +- More sugars for view function (`@app.input()`, `@app.output()`, `@app.get()`, `@app.post()` and more) +- Automatic request validation and deserialization +- Automatic response formatting and serialization +- Automatic [OpenAPI Specification](https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification) (OAS, formerly Swagger Specification) document generation +- Automatic interactive API documentation +- API authentication support (with [Flask-HTTPAuth](https://github.com/miguelgrinberg/flask-httpauth)) +- Automatic JSON response for HTTP errors + + +## Requirements + +- Python 3.7+ +- Flask 1.1.0+ + + +## Installation + +For Linux and macOS: + +```bash +$ pip3 install apiflask +``` + +For Windows: + +```bash +> pip install apiflask +``` + + +## Links + +- Website: <https://apiflask.com> +- Documentation: <https://apiflask.com/docs> +- PyPI Releases: <https://pypi.python.org/pypi/APIFlask> +- Change Log: <https://apiflask.com/changelog> +- Source Code: <https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask> +- Issue Tracker: <https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask/issues> +- Discussion: <https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask/discussions> +- Twitter: <https://twitter.com/apiflask> + + +## Example + +```python +from apiflask import APIFlask, Schema, abort +from apiflask.fields import Integer, String +from apiflask.validators import Length, OneOf + +app = APIFlask(__name__) + +pets = [ + {'id': 0, 'name': 'Kitty', 'category': 'cat'}, + {'id': 1, 'name': 'Coco', 'category': 'dog'} +] + + +class PetIn(Schema): + name = String(required=True, validate=Length(0, 10)) + category = String(required=True, validate=OneOf(['dog', 'cat'])) + + +class PetOut(Schema): + id = Integer() + name = String() + category = String() + + +@app.get('/') +def say_hello(): + # returning a dict or list equals to use jsonify() + return {'message': 'Hello!'} + + +@app.get('/pets/<int:pet_id>') +@app.output(PetOut) +def get_pet(pet_id): + if pet_id > len(pets) - 1: + abort(404) + # you can also return an ORM/ODM model class instance directly + # APIFlask will serialize the object into JSON format + return pets[pet_id] + + +@app.patch('/pets/<int:pet_id>') +@app.input(PetIn(partial=True)) +@app.output(PetOut) +def update_pet(pet_id, data): + # the validated and parsed input data will + # be injected into the view function as a dict + if pet_id > len(pets) - 1: + abort(404) + for attr, value in data.items(): + pets[pet_id][attr] = value + return pets[pet_id] +``` + +<details> +<summary>You can also use class-based views based on <code>MethodView</code></summary> + +```python +from apiflask import APIFlask, Schema, abort +from apiflask.fields import Integer, String +from apiflask.validators import Length, OneOf +from apiflask.views import MethodView + +app = APIFlask(__name__) + +pets = [ + {'id': 0, 'name': 'Kitty', 'category': 'cat'}, + {'id': 1, 'name': 'Coco', 'category': 'dog'} +] + + +class PetIn(Schema): + name = String(required=True, validate=Length(0, 10)) + category = String(required=True, validate=OneOf(['dog', 'cat'])) + + +class PetOut(Schema): + id = Integer() + name = String() + category = String() + + +class Hello(MethodView): + + # use HTTP method name as class method name + def get(self): + return {'message': 'Hello!'} + + +class Pet(MethodView): + + @app.output(PetOut) + def get(self, pet_id): + """Get a pet""" + if pet_id > len(pets) - 1: + abort(404) + return pets[pet_id] + + @app.input(PetIn(partial=True)) + @app.output(PetOut) + def patch(self, pet_id, data): + """Update a pet""" + if pet_id > len(pets) - 1: + abort(404) + for attr, value in data.items(): + pets[pet_id][attr] = value + return pets[pet_id] + + +app.add_url_rule('/', view_func=Hello.as_view('hello')) +app.add_url_rule('/pets/<int:pet_id>', view_func=Pet.as_view('pet')) +``` +</details> + +<details> +<summary>Or use <code>async def</code> with Flask 2.0</summary> + +```bash +$ pip install -U "apiflask[async]" +``` + +```python +import asyncio + +from apiflask import APIFlask + +app = APIFlask(__name__) + + +@app.get('/') +async def say_hello(): + await asyncio.sleep(1) + return {'message': 'Hello!'} +``` + +See <em><a href="https://flask.palletsprojects.com/async-await">Using async and await</a></em> for the details of the async support in Flask 2.0. + +</details> + +Save this as `app.py`, then run it with: + +```bash +$ flask run --reload +``` + +Or run in debug mode: + +```bash +$ flask run --debug +``` + +Now visit the interactive API documentation (Swagger UI) at <http://localhost:5000/docs>: + + + +Or you can change the API documentation UI when creating the APIFlask instance with the `docs_ui` parameter: + +```py +app = APIFlask(__name__, docs_ui='redoc') +``` + +Now <http://localhost:5000/docs> will render the API documentation with Redoc. + +Supported `docs_ui` values (UI libraries) include: + +- `swagger-ui` (default value): [Swagger UI](https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui) +- `redoc`: [Redoc](https://github.com/Redocly/redoc) +- `elements`: [Elements](https://github.com/stoplightio/elements) +- `rapidoc`: [RapiDoc](https://github.com/rapi-doc/RapiDoc) +- `rapipdf`: [RapiPDF](https://github.com/mrin9/RapiPdf) + +The auto-generated OpenAPI spec file is available at <http://localhost:5000/openapi.json>. You can also get the spec with [the `flask spec` command](https://apiflask.com/openapi/#the-flask-spec-command): + +```bash +$ flask spec +``` + +For some complete examples, see [/examples](https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask/tree/main/examples). + + +## Relationship with Flask + +APIFlask is a thin wrapper on top of Flask. You only need to remember the following differences (see *[Migrating from Flask](https://apiflask.com/migrating)* for more details): + +- When creating an application instance, use `APIFlask` instead of `Flask`. +- When creating a blueprint instance, use `APIBlueprint` instead of `Blueprint`. +- When creating a class-based view, use `apiflask.views.MethodView` instead of `flask.views.MethodView`. +- The `abort()` function from APIFlask (`apiflask.abort`) returns JSON error response. + +For a minimal Flask application: + +```python +from flask import Flask, request, escape + +app = Flask(__name__) + +@app.route('/') +def hello(): + name = request.args.get('name', 'Human') + return f'Hello, {escape(name)}' +``` + +Now change to APIFlask: + +```python +from apiflask import APIFlask # step one +from flask import request, escape + +app = APIFlask(__name__) # step two + +@app.route('/') +def hello(): + name = request.args.get('name', 'Human') + return f'Hello, {escape(name)}' +``` + +In a word, to make Web API development in Flask more easily, APIFlask provides `APIFlask` and `APIBlueprint` to extend Flask's `Flask` and `Blueprint` objects and it also ships with some helpful utilities. Other than that, you are actually using Flask. + + +## Relationship with marshmallow + +APIFlask accepts marshmallow schema as data schema, uses webargs to validate the request data against the schema, and uses apispec to generate the OpenAPI representation from the schema. + +You can build marshmallow schemas just like before, but APIFlask also exposes some marshmallow APIs for convenience: + +- `apiflask.Schema`: The base marshmallow schema class. Notice it sets the `set_class` to `OrderedSet` by default. +- `apiflask.fields`: The marshmallow fields, contain the fields from both marshmallow and Flask-Marshmallow. Beware that the aliases (`Url`, `Str`, `Int`, `Bool`, etc.) were removed. +- `apiflask.validators`: The marshmallow validators. + +```python +from apiflask import Schema +from apiflask.fields import Integer, String +from apiflask.validators import Length, OneOf +from marshmallow import pre_load, post_dump, ValidationError +``` + +## Credits + +APIFlask starts as a fork of [APIFairy](https://github.com/miguelgrinberg/APIFairy) and is inspired by [flask-smorest](https://github.com/marshmallow-code/flask-smorest) and [FastAPI](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi) (see *[Comparison and Motivations](https://apiflask.com/comparison)* for the comparison between these projects). + + + + +%package help +Summary: Development documents and examples for APIFlask +Provides: python3-APIFlask-doc +%description help + + + +# APIFlask + +[](https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask/actions) [](https://codecov.io/gh/apiflask/apiflask) + +APIFlask is a lightweight Python web API framework based on [Flask](https://github.com/pallets/flask) and [marshmallow-code](https://github.com/marshmallow-code) projects. It's easy to use, highly customizable, ORM/ODM-agnostic, and 100% compatible with the Flask ecosystem. + +With APIFlask, you will have: + +- More sugars for view function (`@app.input()`, `@app.output()`, `@app.get()`, `@app.post()` and more) +- Automatic request validation and deserialization +- Automatic response formatting and serialization +- Automatic [OpenAPI Specification](https://github.com/OAI/OpenAPI-Specification) (OAS, formerly Swagger Specification) document generation +- Automatic interactive API documentation +- API authentication support (with [Flask-HTTPAuth](https://github.com/miguelgrinberg/flask-httpauth)) +- Automatic JSON response for HTTP errors + + +## Requirements + +- Python 3.7+ +- Flask 1.1.0+ + + +## Installation + +For Linux and macOS: + +```bash +$ pip3 install apiflask +``` + +For Windows: + +```bash +> pip install apiflask +``` + + +## Links + +- Website: <https://apiflask.com> +- Documentation: <https://apiflask.com/docs> +- PyPI Releases: <https://pypi.python.org/pypi/APIFlask> +- Change Log: <https://apiflask.com/changelog> +- Source Code: <https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask> +- Issue Tracker: <https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask/issues> +- Discussion: <https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask/discussions> +- Twitter: <https://twitter.com/apiflask> + + +## Example + +```python +from apiflask import APIFlask, Schema, abort +from apiflask.fields import Integer, String +from apiflask.validators import Length, OneOf + +app = APIFlask(__name__) + +pets = [ + {'id': 0, 'name': 'Kitty', 'category': 'cat'}, + {'id': 1, 'name': 'Coco', 'category': 'dog'} +] + + +class PetIn(Schema): + name = String(required=True, validate=Length(0, 10)) + category = String(required=True, validate=OneOf(['dog', 'cat'])) + + +class PetOut(Schema): + id = Integer() + name = String() + category = String() + + +@app.get('/') +def say_hello(): + # returning a dict or list equals to use jsonify() + return {'message': 'Hello!'} + + +@app.get('/pets/<int:pet_id>') +@app.output(PetOut) +def get_pet(pet_id): + if pet_id > len(pets) - 1: + abort(404) + # you can also return an ORM/ODM model class instance directly + # APIFlask will serialize the object into JSON format + return pets[pet_id] + + +@app.patch('/pets/<int:pet_id>') +@app.input(PetIn(partial=True)) +@app.output(PetOut) +def update_pet(pet_id, data): + # the validated and parsed input data will + # be injected into the view function as a dict + if pet_id > len(pets) - 1: + abort(404) + for attr, value in data.items(): + pets[pet_id][attr] = value + return pets[pet_id] +``` + +<details> +<summary>You can also use class-based views based on <code>MethodView</code></summary> + +```python +from apiflask import APIFlask, Schema, abort +from apiflask.fields import Integer, String +from apiflask.validators import Length, OneOf +from apiflask.views import MethodView + +app = APIFlask(__name__) + +pets = [ + {'id': 0, 'name': 'Kitty', 'category': 'cat'}, + {'id': 1, 'name': 'Coco', 'category': 'dog'} +] + + +class PetIn(Schema): + name = String(required=True, validate=Length(0, 10)) + category = String(required=True, validate=OneOf(['dog', 'cat'])) + + +class PetOut(Schema): + id = Integer() + name = String() + category = String() + + +class Hello(MethodView): + + # use HTTP method name as class method name + def get(self): + return {'message': 'Hello!'} + + +class Pet(MethodView): + + @app.output(PetOut) + def get(self, pet_id): + """Get a pet""" + if pet_id > len(pets) - 1: + abort(404) + return pets[pet_id] + + @app.input(PetIn(partial=True)) + @app.output(PetOut) + def patch(self, pet_id, data): + """Update a pet""" + if pet_id > len(pets) - 1: + abort(404) + for attr, value in data.items(): + pets[pet_id][attr] = value + return pets[pet_id] + + +app.add_url_rule('/', view_func=Hello.as_view('hello')) +app.add_url_rule('/pets/<int:pet_id>', view_func=Pet.as_view('pet')) +``` +</details> + +<details> +<summary>Or use <code>async def</code> with Flask 2.0</summary> + +```bash +$ pip install -U "apiflask[async]" +``` + +```python +import asyncio + +from apiflask import APIFlask + +app = APIFlask(__name__) + + +@app.get('/') +async def say_hello(): + await asyncio.sleep(1) + return {'message': 'Hello!'} +``` + +See <em><a href="https://flask.palletsprojects.com/async-await">Using async and await</a></em> for the details of the async support in Flask 2.0. + +</details> + +Save this as `app.py`, then run it with: + +```bash +$ flask run --reload +``` + +Or run in debug mode: + +```bash +$ flask run --debug +``` + +Now visit the interactive API documentation (Swagger UI) at <http://localhost:5000/docs>: + + + +Or you can change the API documentation UI when creating the APIFlask instance with the `docs_ui` parameter: + +```py +app = APIFlask(__name__, docs_ui='redoc') +``` + +Now <http://localhost:5000/docs> will render the API documentation with Redoc. + +Supported `docs_ui` values (UI libraries) include: + +- `swagger-ui` (default value): [Swagger UI](https://github.com/swagger-api/swagger-ui) +- `redoc`: [Redoc](https://github.com/Redocly/redoc) +- `elements`: [Elements](https://github.com/stoplightio/elements) +- `rapidoc`: [RapiDoc](https://github.com/rapi-doc/RapiDoc) +- `rapipdf`: [RapiPDF](https://github.com/mrin9/RapiPdf) + +The auto-generated OpenAPI spec file is available at <http://localhost:5000/openapi.json>. You can also get the spec with [the `flask spec` command](https://apiflask.com/openapi/#the-flask-spec-command): + +```bash +$ flask spec +``` + +For some complete examples, see [/examples](https://github.com/apiflask/apiflask/tree/main/examples). + + +## Relationship with Flask + +APIFlask is a thin wrapper on top of Flask. You only need to remember the following differences (see *[Migrating from Flask](https://apiflask.com/migrating)* for more details): + +- When creating an application instance, use `APIFlask` instead of `Flask`. +- When creating a blueprint instance, use `APIBlueprint` instead of `Blueprint`. +- When creating a class-based view, use `apiflask.views.MethodView` instead of `flask.views.MethodView`. +- The `abort()` function from APIFlask (`apiflask.abort`) returns JSON error response. + +For a minimal Flask application: + +```python +from flask import Flask, request, escape + +app = Flask(__name__) + +@app.route('/') +def hello(): + name = request.args.get('name', 'Human') + return f'Hello, {escape(name)}' +``` + +Now change to APIFlask: + +```python +from apiflask import APIFlask # step one +from flask import request, escape + +app = APIFlask(__name__) # step two + +@app.route('/') +def hello(): + name = request.args.get('name', 'Human') + return f'Hello, {escape(name)}' +``` + +In a word, to make Web API development in Flask more easily, APIFlask provides `APIFlask` and `APIBlueprint` to extend Flask's `Flask` and `Blueprint` objects and it also ships with some helpful utilities. Other than that, you are actually using Flask. + + +## Relationship with marshmallow + +APIFlask accepts marshmallow schema as data schema, uses webargs to validate the request data against the schema, and uses apispec to generate the OpenAPI representation from the schema. + +You can build marshmallow schemas just like before, but APIFlask also exposes some marshmallow APIs for convenience: + +- `apiflask.Schema`: The base marshmallow schema class. Notice it sets the `set_class` to `OrderedSet` by default. +- `apiflask.fields`: The marshmallow fields, contain the fields from both marshmallow and Flask-Marshmallow. Beware that the aliases (`Url`, `Str`, `Int`, `Bool`, etc.) were removed. +- `apiflask.validators`: The marshmallow validators. + +```python +from apiflask import Schema +from apiflask.fields import Integer, String +from apiflask.validators import Length, OneOf +from marshmallow import pre_load, post_dump, ValidationError +``` + +## Credits + +APIFlask starts as a fork of [APIFairy](https://github.com/miguelgrinberg/APIFairy) and is inspired by [flask-smorest](https://github.com/marshmallow-code/flask-smorest) and [FastAPI](https://github.com/tiangolo/fastapi) (see *[Comparison and Motivations](https://apiflask.com/comparison)* for the comparison between these projects). + + + + +%prep +%autosetup -n APIFlask-1.3.1 + +%build +%py3_build + +%install +%py3_install +install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir} +if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +pushd %{buildroot} +if [ -d usr/lib ]; then + find usr/lib -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then + find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +if [ -d usr/bin ]; then + find usr/bin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then + find usr/sbin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +touch doclist.lst +if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then + find usr/share/man -type f -printf "/%h/%f.gz\n" >> doclist.lst +fi +popd +mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst . +mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst . + +%files -n python3-APIFlask -f filelist.lst +%dir %{python3_sitelib}/* + +%files help -f doclist.lst +%{_docdir}/* + +%changelog +* Fri May 05 2023 Python_Bot <Python_Bot@openeuler.org> - 1.3.1-1 +- Package Spec generated |
