%global _empty_manifest_terminate_build 0
Name: python-cron-converter
Version: 1.0.2
Release: 1
Summary: Cron string parser and scheduler for Python
License: MIT License
URL: https://github.com/Sonic0/cron-converter
Source0: https://mirrors.nju.edu.cn/pypi/web/packages/ae/4c/91cf59eb9f2ff37aab7daf5d35db1c4452340be44945d33660b794798f41/cron-converter-1.0.2.tar.gz
BuildArch: noarch
Requires: python3-dateutil
Requires: python3-unittest
%description
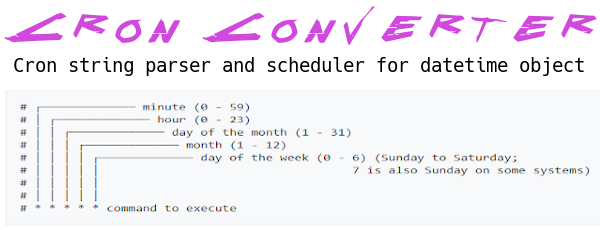
Cron-converter provides a Cron string parser ( from string/lists to string/lists ) and iteration for the datetime object with a cron like format.
This project would be a transposition in Python of JS [cron-converter](https://github.com/roccivic/cron-converter) by [roccivic](https://github.com/roccivic).
[](https://github.com/Sonic0/cron-converter/blob/master/LICENCE)

[](https://codebeat.co/projects/github-com-sonic0-cron-converter-main)
## Install
#### Pip
```bash
pip install cron-converter
```
## Use
```python
from cron_converter import Cron
```
### Create a new instance
```python
cron_instance = Cron()
```
or
```python
cron_instance = Cron('*/10 9-17 1 * *')
```
or (with constructor options)
```python
cron_instance = Cron('*/10 9-17 1 * *', {
'output_weekday_names': True,
'output_month_names': True
})
```
### Parse a cron string
```python
# Every 10 mins between 9am and 5pm on the 1st of every month
# In the case of the second or third creation method this step is not required
cron_instance.from_string('*/10 9-17 1 * *')
# Prints: '*/10 9-17 1 * *'
print(cron_instance.to_string())
# Alternatively, you could print directly the object obtaining the same result:
# print(cron_instance) # Prints: '*/10 9-17 1 * *'
# Prints:
# [
# [ 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 ],
# [ 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 ],
# [ 1 ],
# [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 ],
# [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ]
# ]
print(cron_instance.to_list())
```
### Parse an Array
```python
cron_instance.from_list([[0], [1], [1], [5], [0,2,4,6]])
# Prints: '0 1 1 5 */2'
print(cron_instance.to_string())
```
### Constructor options
Possible options:
- output_weekday_names: false (default)
- output_month_names: false (default)
- output_hashes: false (default)
#### output_weekday_names and output_month_names
```python
cron_instance = Cron(None, {
'output_weekday_names': True,
'output_month_names': True
})
cron_instance.from_string('*/5 9-17/2 * 1-3 1-5')
# Prints: '*/5 9-17/2 * JAN-MAR MON-FRI'
print(cron_instance)
```
or
```python
cron_instance = Cron('*/5 9-17/2 * 1-3 1-5', {
'output_weekday_names': True,
'output_month_names': True
})
# Prints: '*/5 9-17/2 * JAN-MAR MON-FRI'
print(cron_instance)
```
#### output_hashes
```python
cron_instance = Cron('*/5 9-17/2 * 1-3 1-5', {
'output_hashes': True
})
# Prints: 'H/5 H(9-17)/2 H 1-3 1-5'
print(cron_instance.to_string())
```
### Get the schedule execution times. Example with raw Datetime
```python
# Parse a string to init a schedule
cron_instance.from_string('*/5 * * * *')
# Raw datetime without timezone info (not aware)
reference = datetime.now()
# Get the iterator, initialised to now
schedule = cron_instance.schedule(reference)
# Calls to .next() and .prev()
# return a Datetime object
# Examples with time now: '2021-01-01T09:32:00
# Prints: '2021-01-01T09:35:00'
print(schedule.next().isoformat())
# Prints: '2021-01-01T09:40:00'
print(schedule.next().isoformat())
# Reset
schedule.reset()
# Prints: '2021-01-01T09:30:00'
print(schedule.prev().isoformat())
# Prints: '2021-01-01T09:25:00'
print(schedule.prev().isoformat())
```
## About DST
Be sure to init your cron-converter instance with a TZ aware datetime for this to work!
A Scheduler has two optional mutually exclusive arguments: `start_date` or `timezone_str`.
By default (no parameters), a Scheduler start count with a UTC datetime ( _utcnow()_ ) if you not specify any `start_date` datetime object.
If you provide `timezone_str` the Scheduler will start count from a localized now datetime ( _datetime.now(tz_object)_ ).
Example starting from localized now datetime
```python
from cron_converter import Cron
cron = Cron('0 0 * * *')
schedule = cron.schedule(timezone_str='Europe/Rome')
# Prints: result datetime + utc offset
print(schedule.next())
```
Example using pytz:
```python
from pytz import timezone
from datetime import datetime
from cron_converter import Cron
tz = timezone('Europe/Rome')
local_date = tz.localize(datetime(2021, 1, 1))
cron = Cron('0 0 * * *')
schedule = cron.schedule(start_date=local_date)
next_schedule = schedule.next()
next_next_schedule = schedule.next()
# Prints: '2021-01-01T00:00:00+01:00'
print(next_schedule.isoformat())
# Prints: '2021-01-02T00:00:00+01:00'
print(next_next_schedule.isoformat())
```
Example using python_dateutil:
```python
import dateutil.tz
from datetime import datetime
from cron_converter import Cron
tz = dateutil.tz.gettz('Asia/Tokyo')
local_date = datetime(2021, 1, 1, tzinfo=tz)
cron = Cron('0 0 * * *')
schedule = cron.schedule(start_date=local_date)
next_schedule = schedule.next()
next_next_schedule = schedule.next()
# Prints: '2021-01-01T00:00:00+09:00'
print(next_schedule.isoformat())
# Prints: '2021-01-02T00:00:00+09:00'
print(next_next_schedule.isoformat())
```
## About Cron schedule times frequency
It's possible to compare the Cron object schedules frequency. Thanks [@zevaverbach](https://github.com/zevaverbach).
```python
# Hours
Cron('0 1 * * 1-5') == Cron('0 2 * * 1-5') # True
Cron('0 1,2,3 * * 1-5') > Cron('0 1,23 * * 1-5') # True
# Minutes
Cron('* 1 * * 1-5') == Cron('0-59 1 * * 1-5') # True
Cron('1-30 1 * * 1-5') > Cron('1-29 1 * * 1-5') # True
# Days
Cron('* 1 1 * 1-5') == Cron('0-59 1 2 * 1-5') # True
Cron('* 1 1,2 * 1-5') > Cron('* 1 6 * 1-5') # True
# Month
Cron('* 1 1 11 1-5') == Cron('* 1 1 1 1-5') # True
Cron('* 1 6 * 1-5') > Cron('* 1 6 1 1-5') # True
# WeekDay
Cron('* 1 1 11 *') == Cron('* 1 1 11 0-6') # True
Cron('* 1 6 * 1-5') > Cron('* 1 6 * 1-4') # True
```
## About seconds repeats
Cron-converter is NOT able to do second repetition crontabs form.
## Develop & Tests
```bash
git clone https://github.com/Sonic0/cron-converter
cd cron-converter
...
python -m unittest discover -s tests/unit
python -m unittest discover -s tests/integration
```
## Project info
This repo is part of a projects group, called _Cron-Converter_.
Its related repositories:
- [local-crontab](https://github.com/Sonic0/local-crontab)
- [local-crontab-ansible-filter](https://github.com/Sonic0/local-crontab-ansible-filter)
- [local-crontab-serverless-infrastructure](https://github.com/Sonic0/local-crontab-serverless-infrastructure)
- [local-crontab-web-converter](https://github.com/Sonic0/local-crontab-web-converter)
%package -n python3-cron-converter
Summary: Cron string parser and scheduler for Python
Provides: python-cron-converter
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3-setuptools
BuildRequires: python3-pip
%description -n python3-cron-converter

Cron-converter provides a Cron string parser ( from string/lists to string/lists ) and iteration for the datetime object with a cron like format.
This project would be a transposition in Python of JS [cron-converter](https://github.com/roccivic/cron-converter) by [roccivic](https://github.com/roccivic).
[](https://github.com/Sonic0/cron-converter/blob/master/LICENCE)

[](https://codebeat.co/projects/github-com-sonic0-cron-converter-main)
## Install
#### Pip
```bash
pip install cron-converter
```
## Use
```python
from cron_converter import Cron
```
### Create a new instance
```python
cron_instance = Cron()
```
or
```python
cron_instance = Cron('*/10 9-17 1 * *')
```
or (with constructor options)
```python
cron_instance = Cron('*/10 9-17 1 * *', {
'output_weekday_names': True,
'output_month_names': True
})
```
### Parse a cron string
```python
# Every 10 mins between 9am and 5pm on the 1st of every month
# In the case of the second or third creation method this step is not required
cron_instance.from_string('*/10 9-17 1 * *')
# Prints: '*/10 9-17 1 * *'
print(cron_instance.to_string())
# Alternatively, you could print directly the object obtaining the same result:
# print(cron_instance) # Prints: '*/10 9-17 1 * *'
# Prints:
# [
# [ 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 ],
# [ 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 ],
# [ 1 ],
# [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 ],
# [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ]
# ]
print(cron_instance.to_list())
```
### Parse an Array
```python
cron_instance.from_list([[0], [1], [1], [5], [0,2,4,6]])
# Prints: '0 1 1 5 */2'
print(cron_instance.to_string())
```
### Constructor options
Possible options:
- output_weekday_names: false (default)
- output_month_names: false (default)
- output_hashes: false (default)
#### output_weekday_names and output_month_names
```python
cron_instance = Cron(None, {
'output_weekday_names': True,
'output_month_names': True
})
cron_instance.from_string('*/5 9-17/2 * 1-3 1-5')
# Prints: '*/5 9-17/2 * JAN-MAR MON-FRI'
print(cron_instance)
```
or
```python
cron_instance = Cron('*/5 9-17/2 * 1-3 1-5', {
'output_weekday_names': True,
'output_month_names': True
})
# Prints: '*/5 9-17/2 * JAN-MAR MON-FRI'
print(cron_instance)
```
#### output_hashes
```python
cron_instance = Cron('*/5 9-17/2 * 1-3 1-5', {
'output_hashes': True
})
# Prints: 'H/5 H(9-17)/2 H 1-3 1-5'
print(cron_instance.to_string())
```
### Get the schedule execution times. Example with raw Datetime
```python
# Parse a string to init a schedule
cron_instance.from_string('*/5 * * * *')
# Raw datetime without timezone info (not aware)
reference = datetime.now()
# Get the iterator, initialised to now
schedule = cron_instance.schedule(reference)
# Calls to .next() and .prev()
# return a Datetime object
# Examples with time now: '2021-01-01T09:32:00
# Prints: '2021-01-01T09:35:00'
print(schedule.next().isoformat())
# Prints: '2021-01-01T09:40:00'
print(schedule.next().isoformat())
# Reset
schedule.reset()
# Prints: '2021-01-01T09:30:00'
print(schedule.prev().isoformat())
# Prints: '2021-01-01T09:25:00'
print(schedule.prev().isoformat())
```
## About DST
Be sure to init your cron-converter instance with a TZ aware datetime for this to work!
A Scheduler has two optional mutually exclusive arguments: `start_date` or `timezone_str`.
By default (no parameters), a Scheduler start count with a UTC datetime ( _utcnow()_ ) if you not specify any `start_date` datetime object.
If you provide `timezone_str` the Scheduler will start count from a localized now datetime ( _datetime.now(tz_object)_ ).
Example starting from localized now datetime
```python
from cron_converter import Cron
cron = Cron('0 0 * * *')
schedule = cron.schedule(timezone_str='Europe/Rome')
# Prints: result datetime + utc offset
print(schedule.next())
```
Example using pytz:
```python
from pytz import timezone
from datetime import datetime
from cron_converter import Cron
tz = timezone('Europe/Rome')
local_date = tz.localize(datetime(2021, 1, 1))
cron = Cron('0 0 * * *')
schedule = cron.schedule(start_date=local_date)
next_schedule = schedule.next()
next_next_schedule = schedule.next()
# Prints: '2021-01-01T00:00:00+01:00'
print(next_schedule.isoformat())
# Prints: '2021-01-02T00:00:00+01:00'
print(next_next_schedule.isoformat())
```
Example using python_dateutil:
```python
import dateutil.tz
from datetime import datetime
from cron_converter import Cron
tz = dateutil.tz.gettz('Asia/Tokyo')
local_date = datetime(2021, 1, 1, tzinfo=tz)
cron = Cron('0 0 * * *')
schedule = cron.schedule(start_date=local_date)
next_schedule = schedule.next()
next_next_schedule = schedule.next()
# Prints: '2021-01-01T00:00:00+09:00'
print(next_schedule.isoformat())
# Prints: '2021-01-02T00:00:00+09:00'
print(next_next_schedule.isoformat())
```
## About Cron schedule times frequency
It's possible to compare the Cron object schedules frequency. Thanks [@zevaverbach](https://github.com/zevaverbach).
```python
# Hours
Cron('0 1 * * 1-5') == Cron('0 2 * * 1-5') # True
Cron('0 1,2,3 * * 1-5') > Cron('0 1,23 * * 1-5') # True
# Minutes
Cron('* 1 * * 1-5') == Cron('0-59 1 * * 1-5') # True
Cron('1-30 1 * * 1-5') > Cron('1-29 1 * * 1-5') # True
# Days
Cron('* 1 1 * 1-5') == Cron('0-59 1 2 * 1-5') # True
Cron('* 1 1,2 * 1-5') > Cron('* 1 6 * 1-5') # True
# Month
Cron('* 1 1 11 1-5') == Cron('* 1 1 1 1-5') # True
Cron('* 1 6 * 1-5') > Cron('* 1 6 1 1-5') # True
# WeekDay
Cron('* 1 1 11 *') == Cron('* 1 1 11 0-6') # True
Cron('* 1 6 * 1-5') > Cron('* 1 6 * 1-4') # True
```
## About seconds repeats
Cron-converter is NOT able to do second repetition crontabs form.
## Develop & Tests
```bash
git clone https://github.com/Sonic0/cron-converter
cd cron-converter
...
python -m unittest discover -s tests/unit
python -m unittest discover -s tests/integration
```
## Project info
This repo is part of a projects group, called _Cron-Converter_.
Its related repositories:
- [local-crontab](https://github.com/Sonic0/local-crontab)
- [local-crontab-ansible-filter](https://github.com/Sonic0/local-crontab-ansible-filter)
- [local-crontab-serverless-infrastructure](https://github.com/Sonic0/local-crontab-serverless-infrastructure)
- [local-crontab-web-converter](https://github.com/Sonic0/local-crontab-web-converter)
%package help
Summary: Development documents and examples for cron-converter
Provides: python3-cron-converter-doc
%description help

Cron-converter provides a Cron string parser ( from string/lists to string/lists ) and iteration for the datetime object with a cron like format.
This project would be a transposition in Python of JS [cron-converter](https://github.com/roccivic/cron-converter) by [roccivic](https://github.com/roccivic).
[](https://github.com/Sonic0/cron-converter/blob/master/LICENCE)

[](https://codebeat.co/projects/github-com-sonic0-cron-converter-main)
## Install
#### Pip
```bash
pip install cron-converter
```
## Use
```python
from cron_converter import Cron
```
### Create a new instance
```python
cron_instance = Cron()
```
or
```python
cron_instance = Cron('*/10 9-17 1 * *')
```
or (with constructor options)
```python
cron_instance = Cron('*/10 9-17 1 * *', {
'output_weekday_names': True,
'output_month_names': True
})
```
### Parse a cron string
```python
# Every 10 mins between 9am and 5pm on the 1st of every month
# In the case of the second or third creation method this step is not required
cron_instance.from_string('*/10 9-17 1 * *')
# Prints: '*/10 9-17 1 * *'
print(cron_instance.to_string())
# Alternatively, you could print directly the object obtaining the same result:
# print(cron_instance) # Prints: '*/10 9-17 1 * *'
# Prints:
# [
# [ 0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50 ],
# [ 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17 ],
# [ 1 ],
# [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12 ],
# [ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 ]
# ]
print(cron_instance.to_list())
```
### Parse an Array
```python
cron_instance.from_list([[0], [1], [1], [5], [0,2,4,6]])
# Prints: '0 1 1 5 */2'
print(cron_instance.to_string())
```
### Constructor options
Possible options:
- output_weekday_names: false (default)
- output_month_names: false (default)
- output_hashes: false (default)
#### output_weekday_names and output_month_names
```python
cron_instance = Cron(None, {
'output_weekday_names': True,
'output_month_names': True
})
cron_instance.from_string('*/5 9-17/2 * 1-3 1-5')
# Prints: '*/5 9-17/2 * JAN-MAR MON-FRI'
print(cron_instance)
```
or
```python
cron_instance = Cron('*/5 9-17/2 * 1-3 1-5', {
'output_weekday_names': True,
'output_month_names': True
})
# Prints: '*/5 9-17/2 * JAN-MAR MON-FRI'
print(cron_instance)
```
#### output_hashes
```python
cron_instance = Cron('*/5 9-17/2 * 1-3 1-5', {
'output_hashes': True
})
# Prints: 'H/5 H(9-17)/2 H 1-3 1-5'
print(cron_instance.to_string())
```
### Get the schedule execution times. Example with raw Datetime
```python
# Parse a string to init a schedule
cron_instance.from_string('*/5 * * * *')
# Raw datetime without timezone info (not aware)
reference = datetime.now()
# Get the iterator, initialised to now
schedule = cron_instance.schedule(reference)
# Calls to .next() and .prev()
# return a Datetime object
# Examples with time now: '2021-01-01T09:32:00
# Prints: '2021-01-01T09:35:00'
print(schedule.next().isoformat())
# Prints: '2021-01-01T09:40:00'
print(schedule.next().isoformat())
# Reset
schedule.reset()
# Prints: '2021-01-01T09:30:00'
print(schedule.prev().isoformat())
# Prints: '2021-01-01T09:25:00'
print(schedule.prev().isoformat())
```
## About DST
Be sure to init your cron-converter instance with a TZ aware datetime for this to work!
A Scheduler has two optional mutually exclusive arguments: `start_date` or `timezone_str`.
By default (no parameters), a Scheduler start count with a UTC datetime ( _utcnow()_ ) if you not specify any `start_date` datetime object.
If you provide `timezone_str` the Scheduler will start count from a localized now datetime ( _datetime.now(tz_object)_ ).
Example starting from localized now datetime
```python
from cron_converter import Cron
cron = Cron('0 0 * * *')
schedule = cron.schedule(timezone_str='Europe/Rome')
# Prints: result datetime + utc offset
print(schedule.next())
```
Example using pytz:
```python
from pytz import timezone
from datetime import datetime
from cron_converter import Cron
tz = timezone('Europe/Rome')
local_date = tz.localize(datetime(2021, 1, 1))
cron = Cron('0 0 * * *')
schedule = cron.schedule(start_date=local_date)
next_schedule = schedule.next()
next_next_schedule = schedule.next()
# Prints: '2021-01-01T00:00:00+01:00'
print(next_schedule.isoformat())
# Prints: '2021-01-02T00:00:00+01:00'
print(next_next_schedule.isoformat())
```
Example using python_dateutil:
```python
import dateutil.tz
from datetime import datetime
from cron_converter import Cron
tz = dateutil.tz.gettz('Asia/Tokyo')
local_date = datetime(2021, 1, 1, tzinfo=tz)
cron = Cron('0 0 * * *')
schedule = cron.schedule(start_date=local_date)
next_schedule = schedule.next()
next_next_schedule = schedule.next()
# Prints: '2021-01-01T00:00:00+09:00'
print(next_schedule.isoformat())
# Prints: '2021-01-02T00:00:00+09:00'
print(next_next_schedule.isoformat())
```
## About Cron schedule times frequency
It's possible to compare the Cron object schedules frequency. Thanks [@zevaverbach](https://github.com/zevaverbach).
```python
# Hours
Cron('0 1 * * 1-5') == Cron('0 2 * * 1-5') # True
Cron('0 1,2,3 * * 1-5') > Cron('0 1,23 * * 1-5') # True
# Minutes
Cron('* 1 * * 1-5') == Cron('0-59 1 * * 1-5') # True
Cron('1-30 1 * * 1-5') > Cron('1-29 1 * * 1-5') # True
# Days
Cron('* 1 1 * 1-5') == Cron('0-59 1 2 * 1-5') # True
Cron('* 1 1,2 * 1-5') > Cron('* 1 6 * 1-5') # True
# Month
Cron('* 1 1 11 1-5') == Cron('* 1 1 1 1-5') # True
Cron('* 1 6 * 1-5') > Cron('* 1 6 1 1-5') # True
# WeekDay
Cron('* 1 1 11 *') == Cron('* 1 1 11 0-6') # True
Cron('* 1 6 * 1-5') > Cron('* 1 6 * 1-4') # True
```
## About seconds repeats
Cron-converter is NOT able to do second repetition crontabs form.
## Develop & Tests
```bash
git clone https://github.com/Sonic0/cron-converter
cd cron-converter
...
python -m unittest discover -s tests/unit
python -m unittest discover -s tests/integration
```
## Project info
This repo is part of a projects group, called _Cron-Converter_.
Its related repositories:
- [local-crontab](https://github.com/Sonic0/local-crontab)
- [local-crontab-ansible-filter](https://github.com/Sonic0/local-crontab-ansible-filter)
- [local-crontab-serverless-infrastructure](https://github.com/Sonic0/local-crontab-serverless-infrastructure)
- [local-crontab-web-converter](https://github.com/Sonic0/local-crontab-web-converter)
%prep
%autosetup -n cron-converter-1.0.2
%build
%py3_build
%install
%py3_install
install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}
if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
pushd %{buildroot}
if [ -d usr/lib ]; then
find usr/lib -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then
find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/bin ]; then
find usr/bin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then
find usr/sbin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
touch doclist.lst
if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then
find usr/share/man -type f -printf "/%h/%f.gz\n" >> doclist.lst
fi
popd
mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst .
mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst .
%files -n python3-cron-converter -f filelist.lst
%dir %{python3_sitelib}/*
%files help -f doclist.lst
%{_docdir}/*
%changelog
* Fri May 05 2023 Python_Bot - 1.0.2-1
- Package Spec generated



