diff options
| -rw-r--r-- | .gitignore | 1 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | python-flask-tileserver.spec | 862 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | sources | 1 |
3 files changed, 864 insertions, 0 deletions
@@ -0,0 +1 @@ +/flask-tileserver-0.2.3.tar.gz diff --git a/python-flask-tileserver.spec b/python-flask-tileserver.spec new file mode 100644 index 0000000..b49804f --- /dev/null +++ b/python-flask-tileserver.spec @@ -0,0 +1,862 @@ +%global _empty_manifest_terminate_build 0 +Name: python-flask-tileserver +Version: 0.2.3 +Release: 1 +Summary: Locally serve geospatial raster tiles in the Slippy Map standard. +License: MIT License +URL: https://github.com/banesullivan/flask-tileserver +Source0: https://mirrors.nju.edu.cn/pypi/web/packages/1e/86/93ea16d71c89319c0fe03cdf643b5b514973e3e0b254e2399becadcb8dc3/flask-tileserver-0.2.3.tar.gz +BuildArch: noarch + +Requires: python3-click +Requires: python3-flask +Requires: python3-Flask-Caching +Requires: python3-furl +Requires: python3-GDAL +Requires: python3-large-image +Requires: python3-large-image-source-gdal +Requires: python3-requests +Requires: python3-scooby +Requires: python3-ipyleaflet + +%description +# 🌐 Local Tile Server for Geospatial Rasters + +[](https://codecov.io/gh/banesullivan/flask-tileserver) +[](https://pypi.org/project/flask-tileserver/) +[](https://pypi.org/project/flask-tileserver/) + +*Need to visualize a rather large (gigabytes) raster you have locally?* **This is for you.** + +A Flask application for serving tiles from large raster files in +the [Slippy Maps standard](https://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/Slippy_map_tilenames) +(i.e., `/zoom/x/y.png`) + +**Disclaimer**: I put this together over a weekend and I'm definitely going to +change a few things moving forward to make it more stable/robust. This means +that things will most likely break between minor releases (I use the +`major.minor.patch` versioning scheme). + + + + + +## 🌟 Highlights + +- Create a local tile server for large geospatial images +- View local raster files with `ipyleaflet` +- Extract regions of interest (ROIs) interactively + +Under the hood, this uses [`large_image`](https://github.com/girder/large_image) +to launch a tile server in a background thread which will serve raster imagery +to a tile viewer (see `ipyleaflet` examples below). +This tile server can efficiently deliver varying levels of detail of your +raster imagery to your viewer; it helps to have pre-tiled, Cloud Optimized +GeoTIFFs (COG), but no wories if not as `large_image` will tile and cache for +you when opening the raster. + +There is an included, standalone web viewer leveraging +[CesiumJS](https://cesium.com/platform/cesiumjs/) and [GeoJS](https://opengeoscience.github.io/geojs/). +You can use the web viewer to select and extract regions of interest from rasters. + +## ⬇️ Installation + +Install from PyPI: https://pypi.org/project/flask-tileserver/ + +``` +pip install flask-tileserver +``` + +### 📝 A Brief Note on Installing GDAL + +GDAL can be a pain in the 🍑 to install, and you may want to handle GDAL +before installing `flask-tileserver`. + +If on linux, I highly recommend using the [large_image_wheels](https://github.com/girder/large_image_wheels) from Kitware. + +``` +pip install --find-links=https://girder.github.io/large_image_wheels --no-cache GDAL +``` + +Otherwise, I recommend using `conda`: + +``` +conda install -c conda-forge GDAL +``` + +## 💭 Feedback + +Please share your thoughts and questions on the [Discussions](https://github.com/banesullivan/flask-tileserver/discussions) board. +If you would like to report any bugs or make feature requests, please open an issue. + +If filing a bug report, please share a scooby `Report`: + +```py +import tileserver +print(tileserver.Report()) +``` + +## 🚀 Usage + +### 🍃 `ipyleaflet` Tile Layers + +The `TileClient` class is a nifty tool to launch a tile server as a background +thread to serve image tiles from any raster file on your local file system. +Additionally, it can be used in conjunction with the `get_leaflet_tile_layer` +utility to create an `ipyleaflet.TileLayer` for interactive visualization in +a Jupyter notebook. Here is an example: + + +```py +from tileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer, TileClient +from ipyleaflet import Map + +# First, create a tile server from local raster file +tile_client = TileClient('~/Desktop/TC_NG_SFBay_US_Geo.tif') + +# Create ipyleaflet tile layer from that server +t = get_leaflet_tile_layer(tile_client) + +# Create ipyleaflet map, add tile layer, and display +m = Map(center=tile_client.center()) +m.add_layer(t) +m +``` + +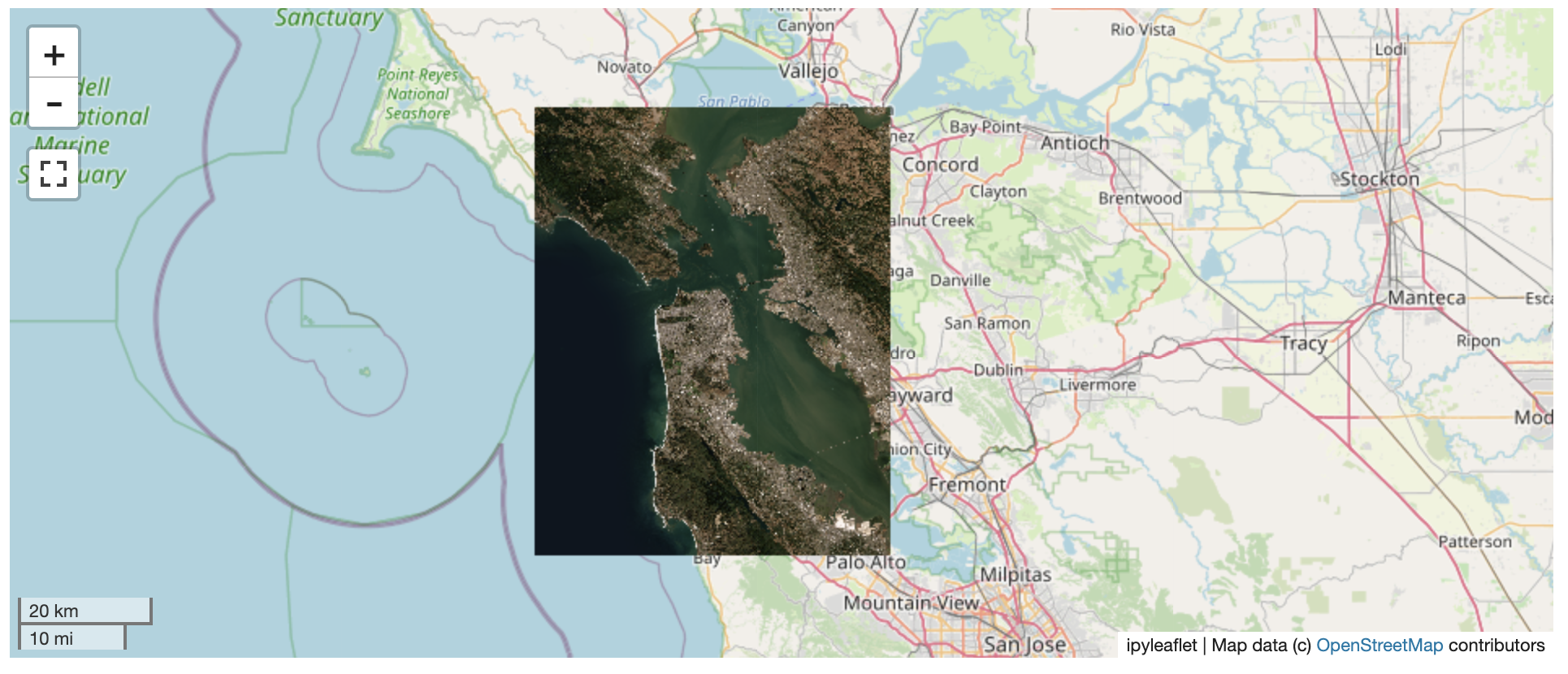 + +#### 🥓 Two Rasters at Once + +```py +from tileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer +from ipyleaflet import Map, ScaleControl, FullScreenControl, SplitMapControl + +# Create 2 tile layers from 2 separate raster files +l = get_leaflet_tile_layer('~/Desktop/TC_NG_SFBay_US_Geo.tif', + band=1, palette='matplotlib.Viridis_20', vmin=50, vmax=200) +r = get_leaflet_tile_layer('~/Desktop/small.tif', + band=2, palette='matplotlib.Plasma_6', vmin=0, vmax=150) + +# Make the ipyleaflet map +m = Map(center=(37.7249511580583, -122.27230466902257), zoom=9) +control = SplitMapControl(left_layer=l, right_layer=r) +m.add_control(control) +m.add_control(ScaleControl(position='bottomleft')) +m.add_control(FullScreenControl()) +m +``` + +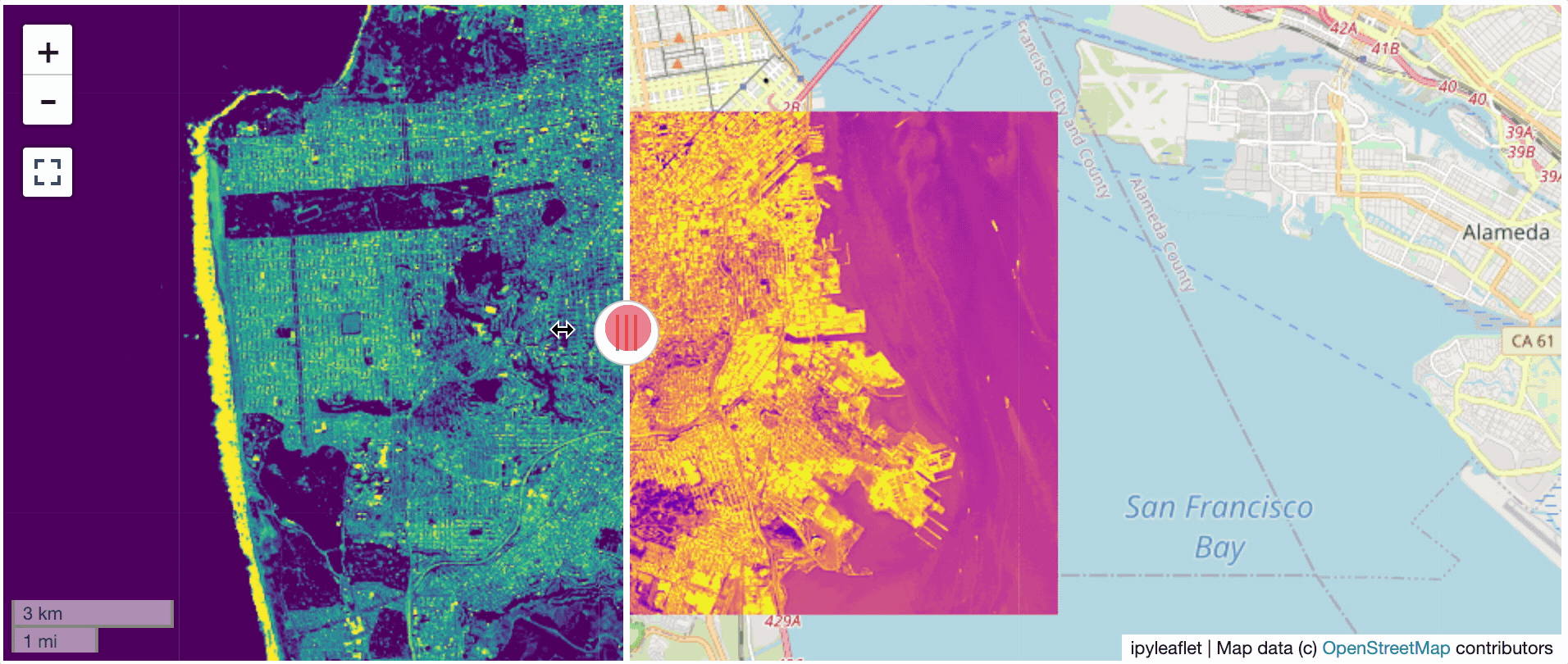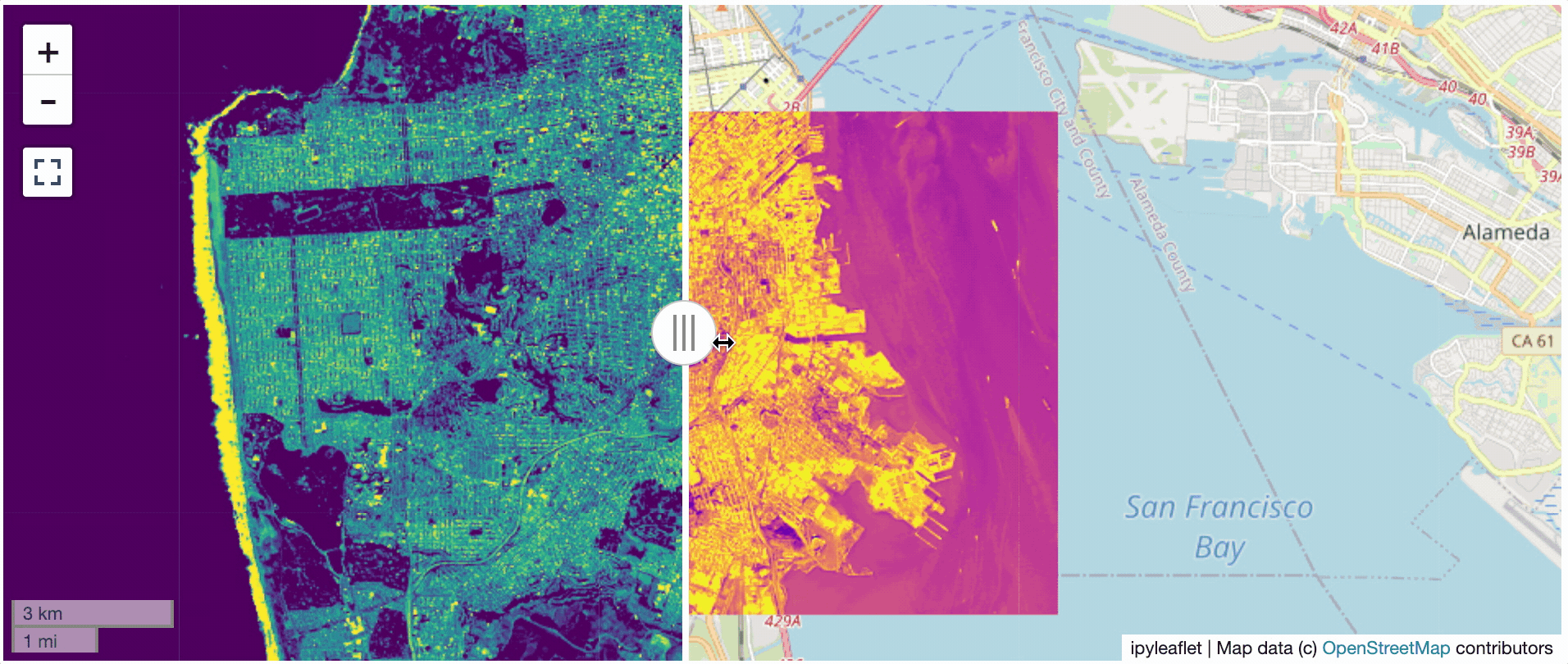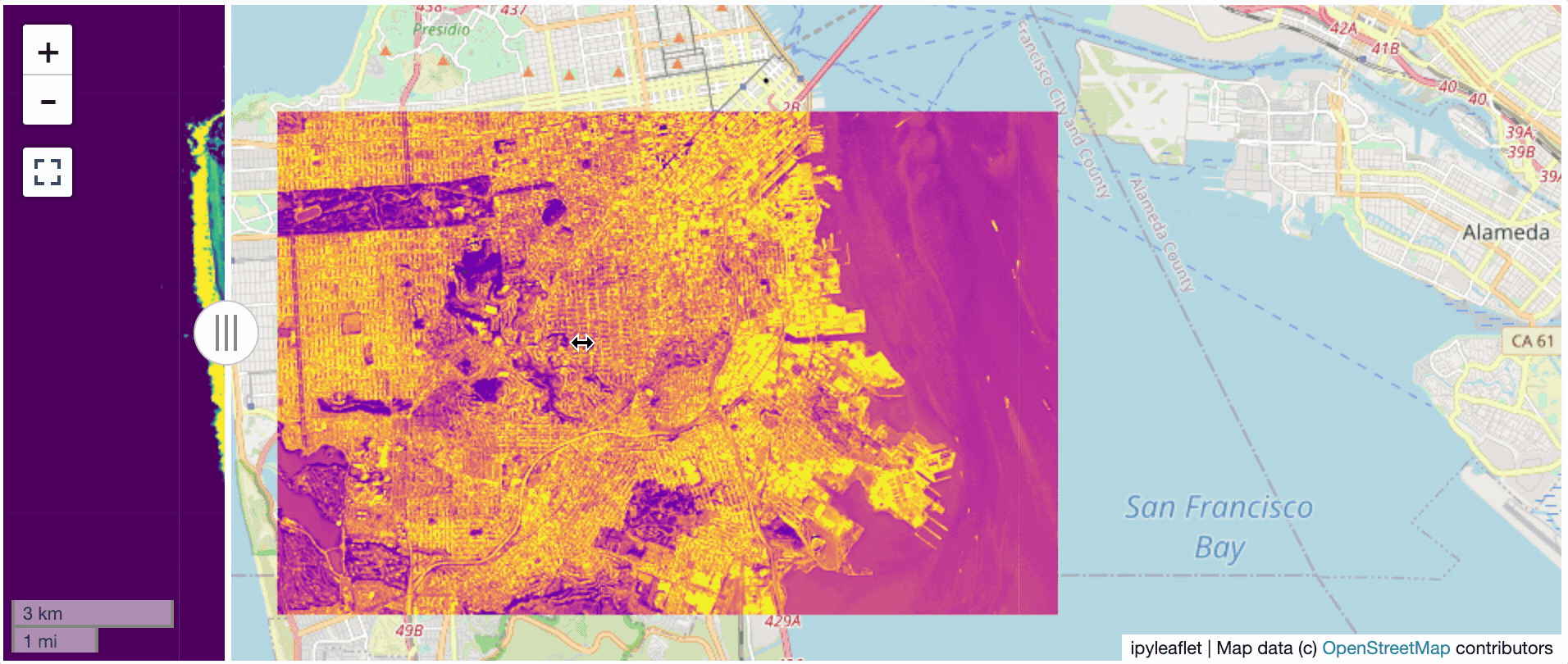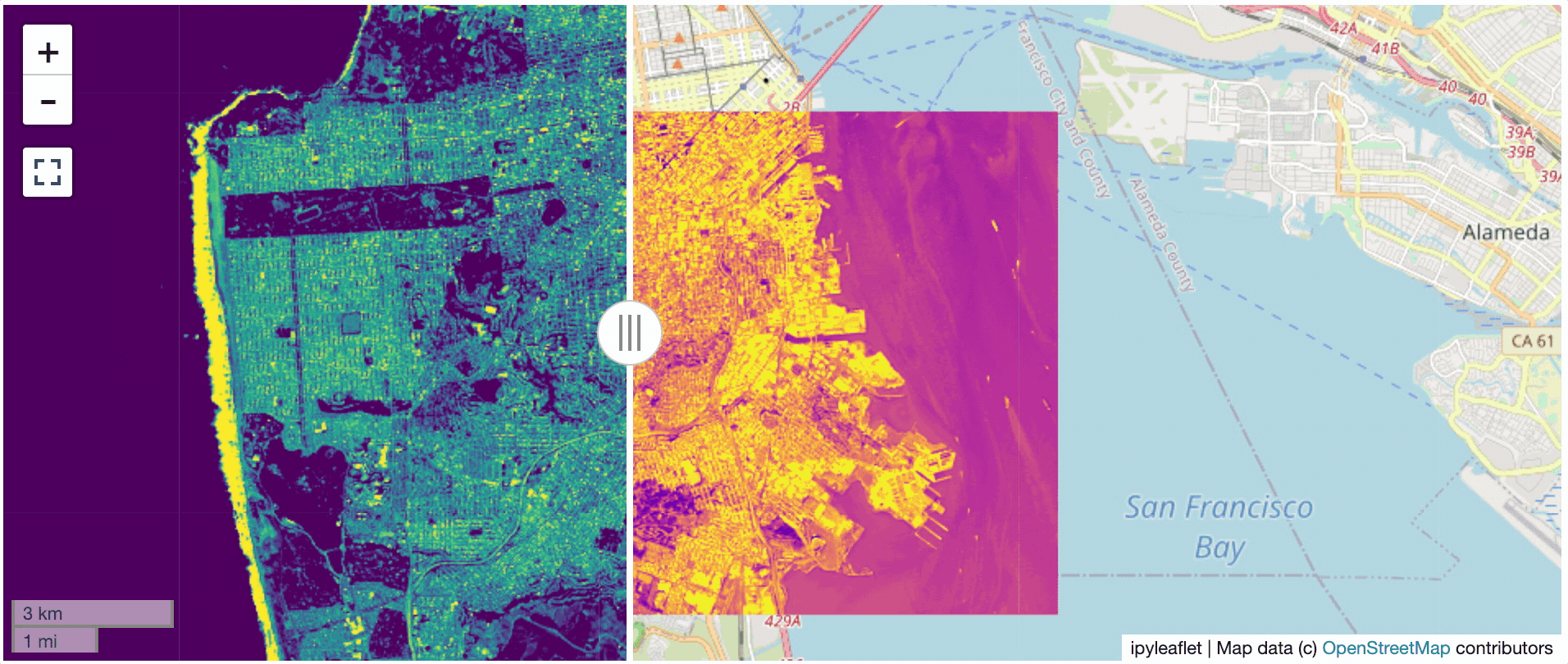 + + +#### 🎯 Using `ipyleaflet` for ROI Extraction + +I have included the `get_leaflet_roi_controls` utility to create some leaflet +UI controls for extracting regions of interest from a tile client. You can +use it as follows and then draw a polygon and click the "Extract ROI" button. + +The outputs are save in your working directory by default (next to the Jupyter notebook). + +```py +from tileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer, get_leaflet_roi_controls +from tileserver import TileClient +from ipyleaflet import Map + +# First, create a tile server from local raster file +tile_client = TileClient('~/Desktop/TC_NG_SFBay_US_Geo.tif') + +# Create ipyleaflet tile layer from that server +t = get_leaflet_tile_layer(tile_client) + +# Create ipyleaflet controls to extract an ROI +draw_control, roi_control = get_leaflet_roi_controls(tile_client) + +# Create ipyleaflet map, add layers, add controls, and display +m = Map(center=(37.7249511580583, -122.27230466902257), zoom=9) +m.add_layer(t) +m.add_control(draw_control) +m.add_control(roi_control) +m +``` + +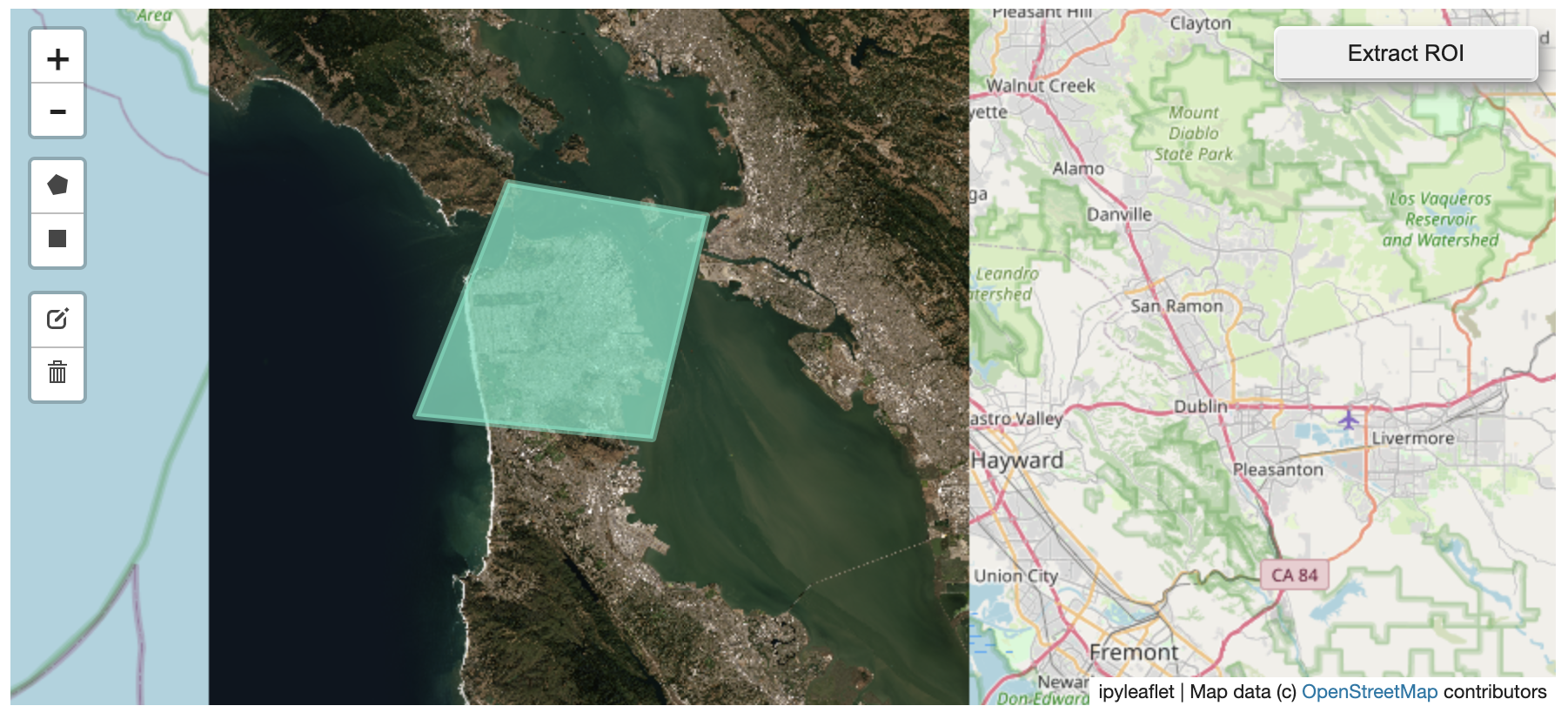 + + +#### 🗺️ Example Datasets + +A few example datasets are included with `tileserver`. A particularly +useful one has global elevation data which you can use to create high resolution Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) of a local region. + +```py +from tileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer, get_leaflet_roi_controls, examples +from ipyleaflet import Map + +# Load example tile layer from publicly available DEM source +tile_client = examples.get_elevation() + +# Create ipyleaflet tile layer from that server +t = get_leaflet_tile_layer(tile_client, + band=1, vmin=-500, vmax=5000, + palette='matplotlib.Plasma_6', + opacity=0.75) + +# Create ipyleaflet controls to extract an ROI +draw_control, roi_control = get_leaflet_roi_controls(tile_client) + +m = Map(zoom=2) +m.add_layer(t) +m.add_control(draw_control) +m.add_control(roi_control) +m +``` + +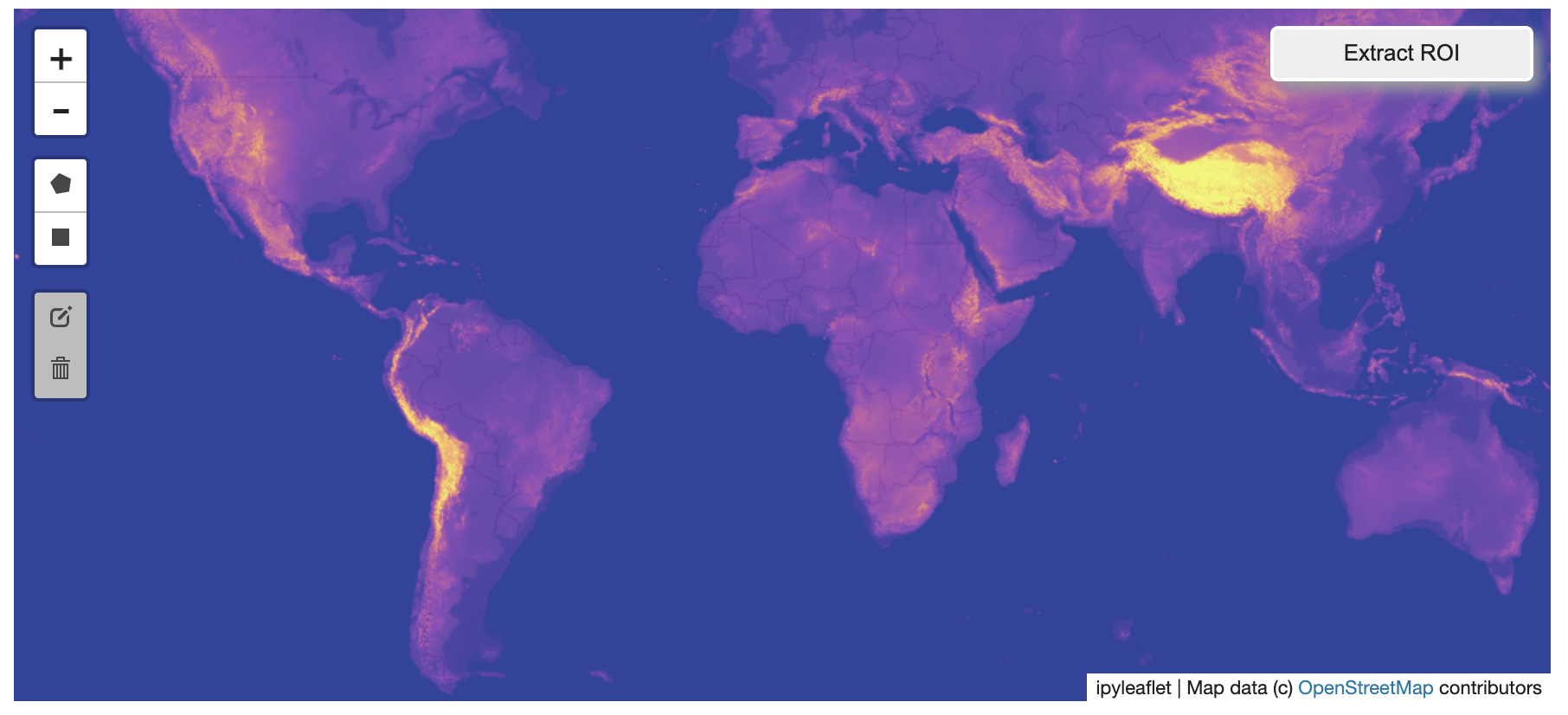 + + +Then you can follow the same routine as described above to extract an ROI. + +I zoomed in over Golden, Colorado and drew a polygon of the extent of the DEM I would like to create: + +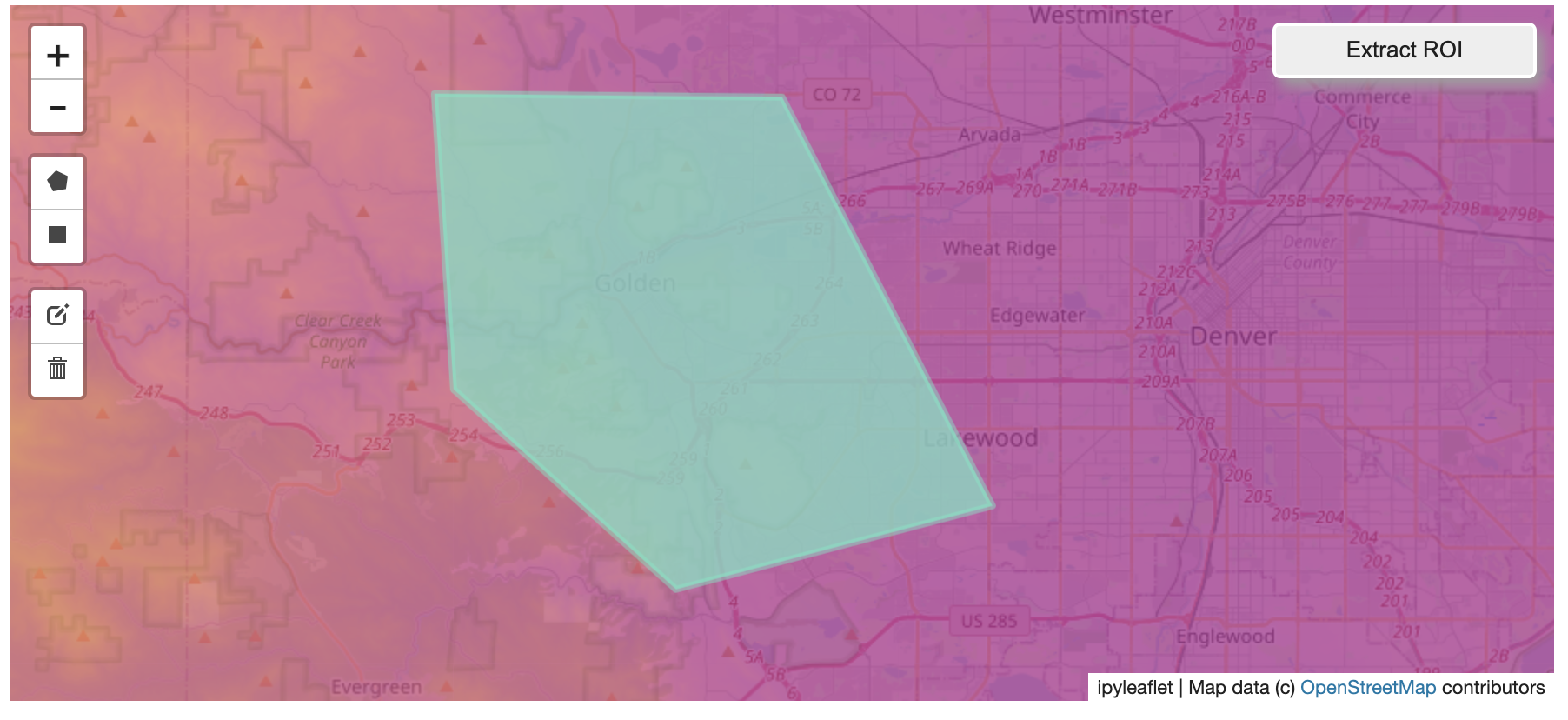 + +And perform the extraction: + +```py + +roi_path = '...' # Look in your working directory + +r = get_leaflet_tile_layer(roi_path, band=1, + palette='matplotlib.Plasma_6', opacity=0.75) + +m2 = Map( + center=(39.763427033262175, -105.20614908076823), + zoom=12, + ) +m2.add_layer(r) +m2 +``` + +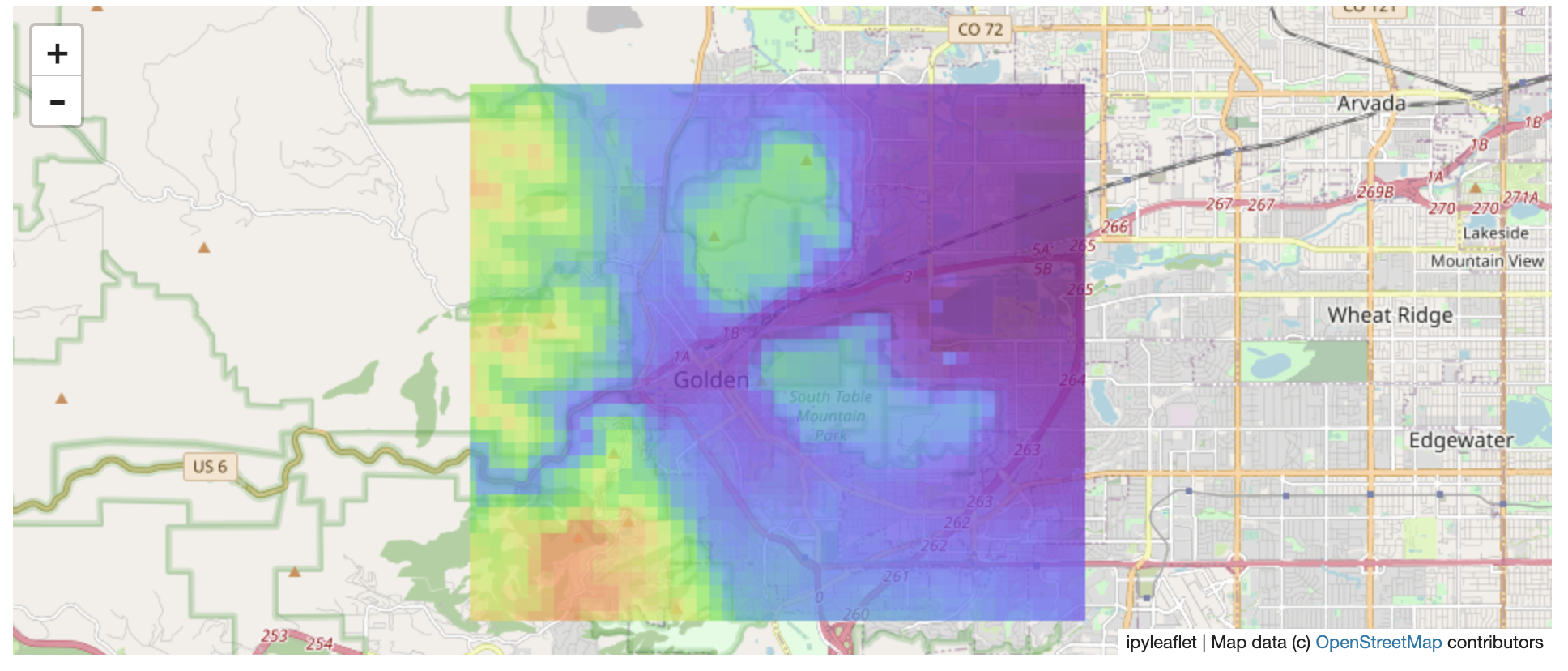 + +Here is another example with the Virtual Earth satellite imagery + +```py +from tileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer, examples +from ipyleaflet import Map + +# Load example tile layer from publicly available imagery +tile_client = examples.get_virtual_earth() + +# Create ipyleaflet tile layer from that server +t = get_leaflet_tile_layer(tile_client, opacity=1) + +m = Map(center=(39.751343612695145, -105.22181306125279), zoom=18) +m.add_layer(t) +m +``` + +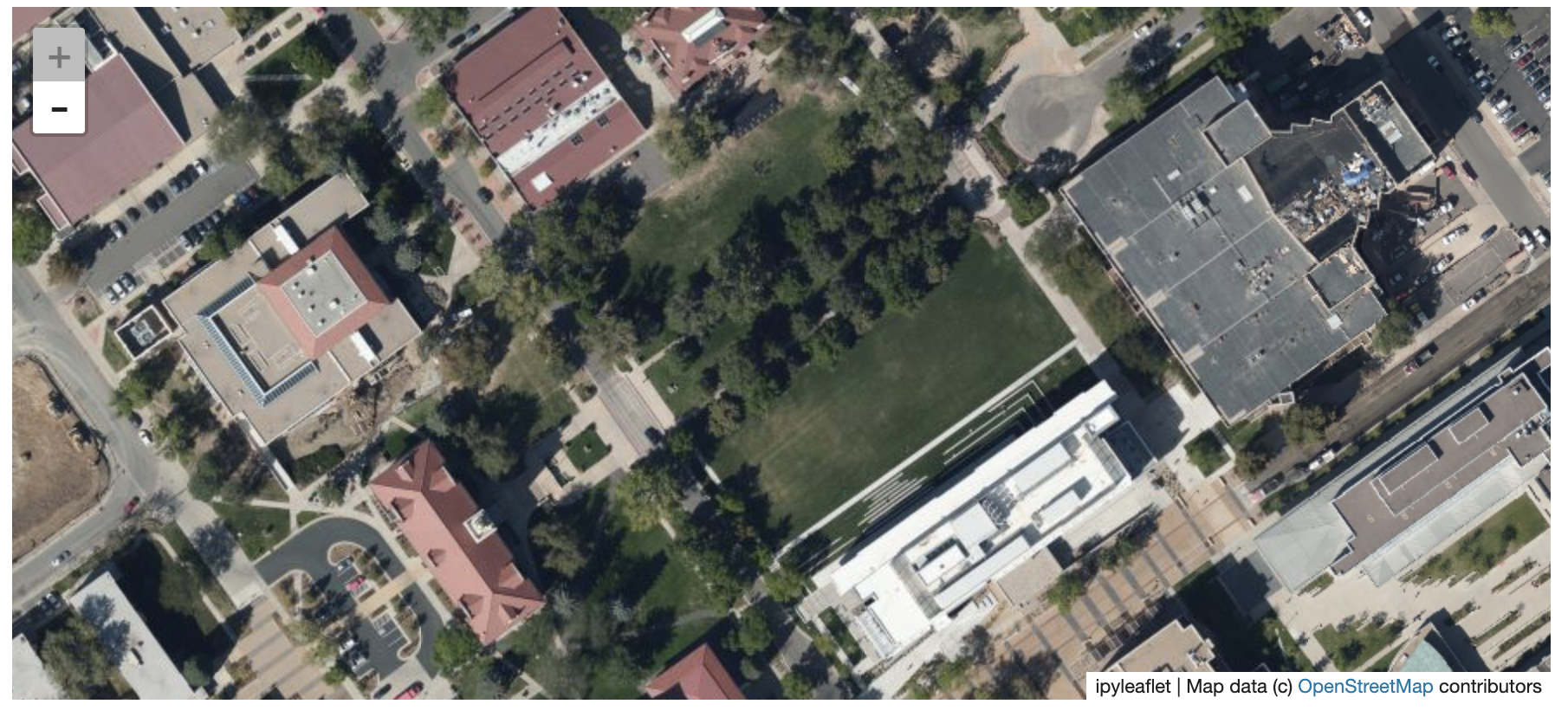 + + +### 🖥️ Local Web Application + +Launch the tileserver from the commandline to use the included web application where you can view the raster and extract regions of interest. + +```bash +python -m tileserver path/to/raster.tif +``` + + + +You can use the web viewer to extract regions of interest: + +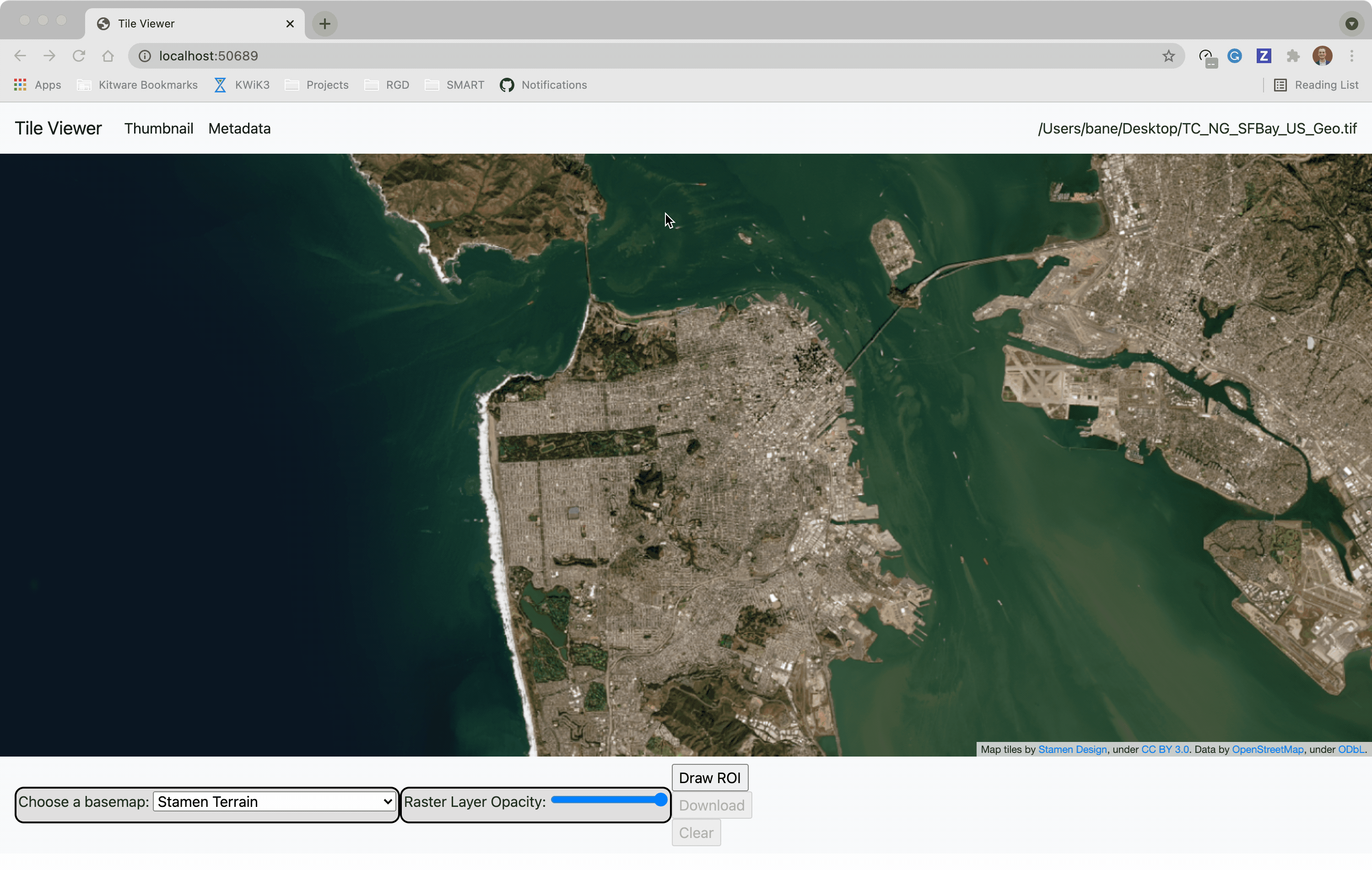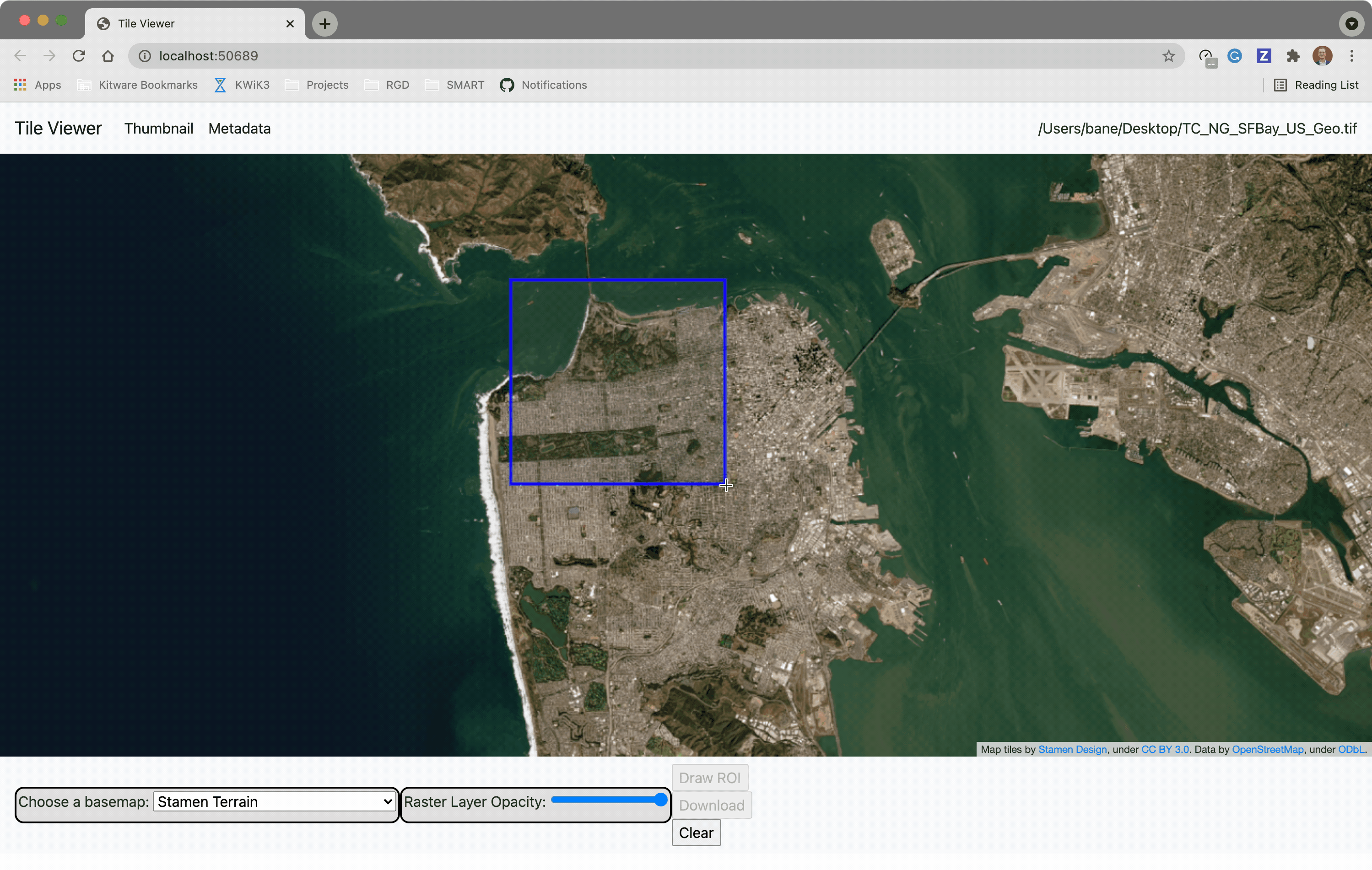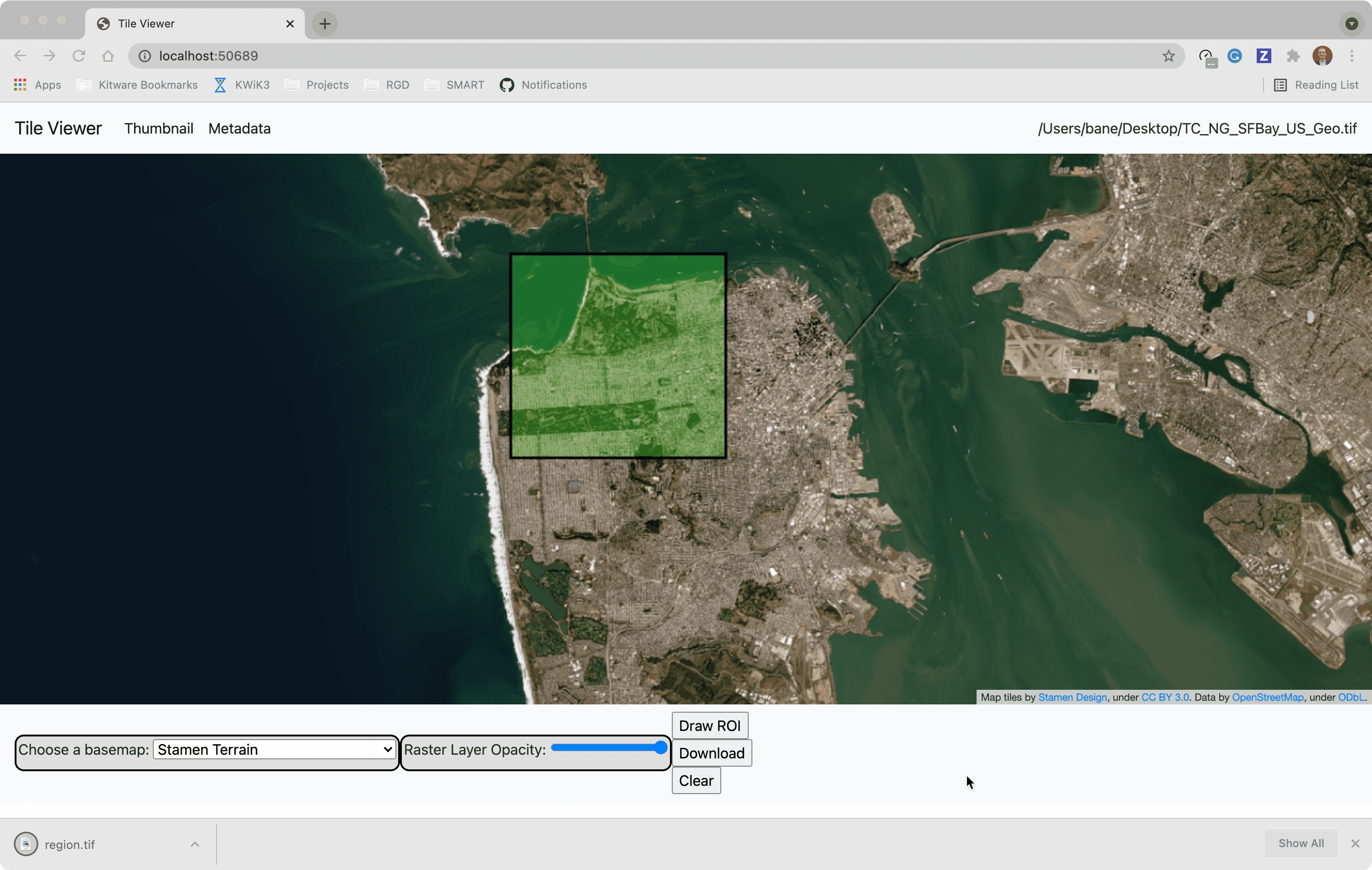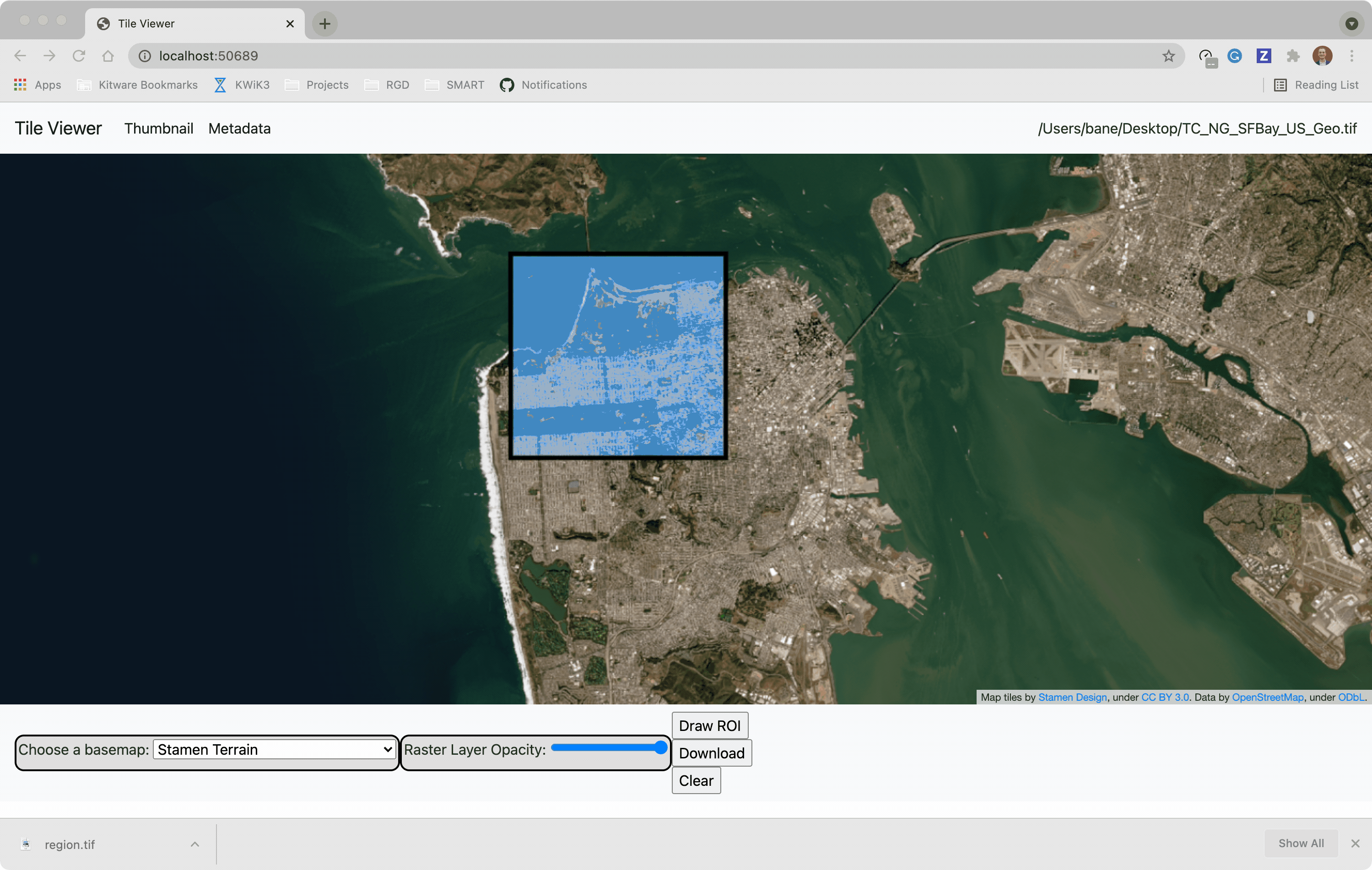 + + +### Usage Notes + +- `get_leaflet_tile_layer` accepts either an existing `TileClient` or a +path from which to create a `TileClient` under the hood. +- The color palette choices come from [`palettable`](https://jiffyclub.github.io/palettable/). + + + + +%package -n python3-flask-tileserver +Summary: Locally serve geospatial raster tiles in the Slippy Map standard. +Provides: python-flask-tileserver +BuildRequires: python3-devel +BuildRequires: python3-setuptools +BuildRequires: python3-pip +%description -n python3-flask-tileserver +# 🌐 Local Tile Server for Geospatial Rasters + +[](https://codecov.io/gh/banesullivan/flask-tileserver) +[](https://pypi.org/project/flask-tileserver/) +[](https://pypi.org/project/flask-tileserver/) + +*Need to visualize a rather large (gigabytes) raster you have locally?* **This is for you.** + +A Flask application for serving tiles from large raster files in +the [Slippy Maps standard](https://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/Slippy_map_tilenames) +(i.e., `/zoom/x/y.png`) + +**Disclaimer**: I put this together over a weekend and I'm definitely going to +change a few things moving forward to make it more stable/robust. This means +that things will most likely break between minor releases (I use the +`major.minor.patch` versioning scheme). + + + + + +## 🌟 Highlights + +- Create a local tile server for large geospatial images +- View local raster files with `ipyleaflet` +- Extract regions of interest (ROIs) interactively + +Under the hood, this uses [`large_image`](https://github.com/girder/large_image) +to launch a tile server in a background thread which will serve raster imagery +to a tile viewer (see `ipyleaflet` examples below). +This tile server can efficiently deliver varying levels of detail of your +raster imagery to your viewer; it helps to have pre-tiled, Cloud Optimized +GeoTIFFs (COG), but no wories if not as `large_image` will tile and cache for +you when opening the raster. + +There is an included, standalone web viewer leveraging +[CesiumJS](https://cesium.com/platform/cesiumjs/) and [GeoJS](https://opengeoscience.github.io/geojs/). +You can use the web viewer to select and extract regions of interest from rasters. + +## ⬇️ Installation + +Install from PyPI: https://pypi.org/project/flask-tileserver/ + +``` +pip install flask-tileserver +``` + +### 📝 A Brief Note on Installing GDAL + +GDAL can be a pain in the 🍑 to install, and you may want to handle GDAL +before installing `flask-tileserver`. + +If on linux, I highly recommend using the [large_image_wheels](https://github.com/girder/large_image_wheels) from Kitware. + +``` +pip install --find-links=https://girder.github.io/large_image_wheels --no-cache GDAL +``` + +Otherwise, I recommend using `conda`: + +``` +conda install -c conda-forge GDAL +``` + +## 💭 Feedback + +Please share your thoughts and questions on the [Discussions](https://github.com/banesullivan/flask-tileserver/discussions) board. +If you would like to report any bugs or make feature requests, please open an issue. + +If filing a bug report, please share a scooby `Report`: + +```py +import tileserver +print(tileserver.Report()) +``` + +## 🚀 Usage + +### 🍃 `ipyleaflet` Tile Layers + +The `TileClient` class is a nifty tool to launch a tile server as a background +thread to serve image tiles from any raster file on your local file system. +Additionally, it can be used in conjunction with the `get_leaflet_tile_layer` +utility to create an `ipyleaflet.TileLayer` for interactive visualization in +a Jupyter notebook. Here is an example: + + +```py +from tileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer, TileClient +from ipyleaflet import Map + +# First, create a tile server from local raster file +tile_client = TileClient('~/Desktop/TC_NG_SFBay_US_Geo.tif') + +# Create ipyleaflet tile layer from that server +t = get_leaflet_tile_layer(tile_client) + +# Create ipyleaflet map, add tile layer, and display +m = Map(center=tile_client.center()) +m.add_layer(t) +m +``` + + + +#### 🥓 Two Rasters at Once + +```py +from tileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer +from ipyleaflet import Map, ScaleControl, FullScreenControl, SplitMapControl + +# Create 2 tile layers from 2 separate raster files +l = get_leaflet_tile_layer('~/Desktop/TC_NG_SFBay_US_Geo.tif', + band=1, palette='matplotlib.Viridis_20', vmin=50, vmax=200) +r = get_leaflet_tile_layer('~/Desktop/small.tif', + band=2, palette='matplotlib.Plasma_6', vmin=0, vmax=150) + +# Make the ipyleaflet map +m = Map(center=(37.7249511580583, -122.27230466902257), zoom=9) +control = SplitMapControl(left_layer=l, right_layer=r) +m.add_control(control) +m.add_control(ScaleControl(position='bottomleft')) +m.add_control(FullScreenControl()) +m +``` + + + + +#### 🎯 Using `ipyleaflet` for ROI Extraction + +I have included the `get_leaflet_roi_controls` utility to create some leaflet +UI controls for extracting regions of interest from a tile client. You can +use it as follows and then draw a polygon and click the "Extract ROI" button. + +The outputs are save in your working directory by default (next to the Jupyter notebook). + +```py +from tileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer, get_leaflet_roi_controls +from tileserver import TileClient +from ipyleaflet import Map + +# First, create a tile server from local raster file +tile_client = TileClient('~/Desktop/TC_NG_SFBay_US_Geo.tif') + +# Create ipyleaflet tile layer from that server +t = get_leaflet_tile_layer(tile_client) + +# Create ipyleaflet controls to extract an ROI +draw_control, roi_control = get_leaflet_roi_controls(tile_client) + +# Create ipyleaflet map, add layers, add controls, and display +m = Map(center=(37.7249511580583, -122.27230466902257), zoom=9) +m.add_layer(t) +m.add_control(draw_control) +m.add_control(roi_control) +m +``` + + + + +#### 🗺️ Example Datasets + +A few example datasets are included with `tileserver`. A particularly +useful one has global elevation data which you can use to create high resolution Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) of a local region. + +```py +from tileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer, get_leaflet_roi_controls, examples +from ipyleaflet import Map + +# Load example tile layer from publicly available DEM source +tile_client = examples.get_elevation() + +# Create ipyleaflet tile layer from that server +t = get_leaflet_tile_layer(tile_client, + band=1, vmin=-500, vmax=5000, + palette='matplotlib.Plasma_6', + opacity=0.75) + +# Create ipyleaflet controls to extract an ROI +draw_control, roi_control = get_leaflet_roi_controls(tile_client) + +m = Map(zoom=2) +m.add_layer(t) +m.add_control(draw_control) +m.add_control(roi_control) +m +``` + + + + +Then you can follow the same routine as described above to extract an ROI. + +I zoomed in over Golden, Colorado and drew a polygon of the extent of the DEM I would like to create: + + + +And perform the extraction: + +```py + +roi_path = '...' # Look in your working directory + +r = get_leaflet_tile_layer(roi_path, band=1, + palette='matplotlib.Plasma_6', opacity=0.75) + +m2 = Map( + center=(39.763427033262175, -105.20614908076823), + zoom=12, + ) +m2.add_layer(r) +m2 +``` + + + +Here is another example with the Virtual Earth satellite imagery + +```py +from tileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer, examples +from ipyleaflet import Map + +# Load example tile layer from publicly available imagery +tile_client = examples.get_virtual_earth() + +# Create ipyleaflet tile layer from that server +t = get_leaflet_tile_layer(tile_client, opacity=1) + +m = Map(center=(39.751343612695145, -105.22181306125279), zoom=18) +m.add_layer(t) +m +``` + + + + +### 🖥️ Local Web Application + +Launch the tileserver from the commandline to use the included web application where you can view the raster and extract regions of interest. + +```bash +python -m tileserver path/to/raster.tif +``` + + + +You can use the web viewer to extract regions of interest: + + + + +### Usage Notes + +- `get_leaflet_tile_layer` accepts either an existing `TileClient` or a +path from which to create a `TileClient` under the hood. +- The color palette choices come from [`palettable`](https://jiffyclub.github.io/palettable/). + + + + +%package help +Summary: Development documents and examples for flask-tileserver +Provides: python3-flask-tileserver-doc +%description help +# 🌐 Local Tile Server for Geospatial Rasters + +[](https://codecov.io/gh/banesullivan/flask-tileserver) +[](https://pypi.org/project/flask-tileserver/) +[](https://pypi.org/project/flask-tileserver/) + +*Need to visualize a rather large (gigabytes) raster you have locally?* **This is for you.** + +A Flask application for serving tiles from large raster files in +the [Slippy Maps standard](https://wiki.openstreetmap.org/wiki/Slippy_map_tilenames) +(i.e., `/zoom/x/y.png`) + +**Disclaimer**: I put this together over a weekend and I'm definitely going to +change a few things moving forward to make it more stable/robust. This means +that things will most likely break between minor releases (I use the +`major.minor.patch` versioning scheme). + + + + + +## 🌟 Highlights + +- Create a local tile server for large geospatial images +- View local raster files with `ipyleaflet` +- Extract regions of interest (ROIs) interactively + +Under the hood, this uses [`large_image`](https://github.com/girder/large_image) +to launch a tile server in a background thread which will serve raster imagery +to a tile viewer (see `ipyleaflet` examples below). +This tile server can efficiently deliver varying levels of detail of your +raster imagery to your viewer; it helps to have pre-tiled, Cloud Optimized +GeoTIFFs (COG), but no wories if not as `large_image` will tile and cache for +you when opening the raster. + +There is an included, standalone web viewer leveraging +[CesiumJS](https://cesium.com/platform/cesiumjs/) and [GeoJS](https://opengeoscience.github.io/geojs/). +You can use the web viewer to select and extract regions of interest from rasters. + +## ⬇️ Installation + +Install from PyPI: https://pypi.org/project/flask-tileserver/ + +``` +pip install flask-tileserver +``` + +### 📝 A Brief Note on Installing GDAL + +GDAL can be a pain in the 🍑 to install, and you may want to handle GDAL +before installing `flask-tileserver`. + +If on linux, I highly recommend using the [large_image_wheels](https://github.com/girder/large_image_wheels) from Kitware. + +``` +pip install --find-links=https://girder.github.io/large_image_wheels --no-cache GDAL +``` + +Otherwise, I recommend using `conda`: + +``` +conda install -c conda-forge GDAL +``` + +## 💭 Feedback + +Please share your thoughts and questions on the [Discussions](https://github.com/banesullivan/flask-tileserver/discussions) board. +If you would like to report any bugs or make feature requests, please open an issue. + +If filing a bug report, please share a scooby `Report`: + +```py +import tileserver +print(tileserver.Report()) +``` + +## 🚀 Usage + +### 🍃 `ipyleaflet` Tile Layers + +The `TileClient` class is a nifty tool to launch a tile server as a background +thread to serve image tiles from any raster file on your local file system. +Additionally, it can be used in conjunction with the `get_leaflet_tile_layer` +utility to create an `ipyleaflet.TileLayer` for interactive visualization in +a Jupyter notebook. Here is an example: + + +```py +from tileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer, TileClient +from ipyleaflet import Map + +# First, create a tile server from local raster file +tile_client = TileClient('~/Desktop/TC_NG_SFBay_US_Geo.tif') + +# Create ipyleaflet tile layer from that server +t = get_leaflet_tile_layer(tile_client) + +# Create ipyleaflet map, add tile layer, and display +m = Map(center=tile_client.center()) +m.add_layer(t) +m +``` + + + +#### 🥓 Two Rasters at Once + +```py +from tileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer +from ipyleaflet import Map, ScaleControl, FullScreenControl, SplitMapControl + +# Create 2 tile layers from 2 separate raster files +l = get_leaflet_tile_layer('~/Desktop/TC_NG_SFBay_US_Geo.tif', + band=1, palette='matplotlib.Viridis_20', vmin=50, vmax=200) +r = get_leaflet_tile_layer('~/Desktop/small.tif', + band=2, palette='matplotlib.Plasma_6', vmin=0, vmax=150) + +# Make the ipyleaflet map +m = Map(center=(37.7249511580583, -122.27230466902257), zoom=9) +control = SplitMapControl(left_layer=l, right_layer=r) +m.add_control(control) +m.add_control(ScaleControl(position='bottomleft')) +m.add_control(FullScreenControl()) +m +``` + + + + +#### 🎯 Using `ipyleaflet` for ROI Extraction + +I have included the `get_leaflet_roi_controls` utility to create some leaflet +UI controls for extracting regions of interest from a tile client. You can +use it as follows and then draw a polygon and click the "Extract ROI" button. + +The outputs are save in your working directory by default (next to the Jupyter notebook). + +```py +from tileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer, get_leaflet_roi_controls +from tileserver import TileClient +from ipyleaflet import Map + +# First, create a tile server from local raster file +tile_client = TileClient('~/Desktop/TC_NG_SFBay_US_Geo.tif') + +# Create ipyleaflet tile layer from that server +t = get_leaflet_tile_layer(tile_client) + +# Create ipyleaflet controls to extract an ROI +draw_control, roi_control = get_leaflet_roi_controls(tile_client) + +# Create ipyleaflet map, add layers, add controls, and display +m = Map(center=(37.7249511580583, -122.27230466902257), zoom=9) +m.add_layer(t) +m.add_control(draw_control) +m.add_control(roi_control) +m +``` + + + + +#### 🗺️ Example Datasets + +A few example datasets are included with `tileserver`. A particularly +useful one has global elevation data which you can use to create high resolution Digital Elevation Models (DEMs) of a local region. + +```py +from tileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer, get_leaflet_roi_controls, examples +from ipyleaflet import Map + +# Load example tile layer from publicly available DEM source +tile_client = examples.get_elevation() + +# Create ipyleaflet tile layer from that server +t = get_leaflet_tile_layer(tile_client, + band=1, vmin=-500, vmax=5000, + palette='matplotlib.Plasma_6', + opacity=0.75) + +# Create ipyleaflet controls to extract an ROI +draw_control, roi_control = get_leaflet_roi_controls(tile_client) + +m = Map(zoom=2) +m.add_layer(t) +m.add_control(draw_control) +m.add_control(roi_control) +m +``` + + + + +Then you can follow the same routine as described above to extract an ROI. + +I zoomed in over Golden, Colorado and drew a polygon of the extent of the DEM I would like to create: + + + +And perform the extraction: + +```py + +roi_path = '...' # Look in your working directory + +r = get_leaflet_tile_layer(roi_path, band=1, + palette='matplotlib.Plasma_6', opacity=0.75) + +m2 = Map( + center=(39.763427033262175, -105.20614908076823), + zoom=12, + ) +m2.add_layer(r) +m2 +``` + + + +Here is another example with the Virtual Earth satellite imagery + +```py +from tileserver import get_leaflet_tile_layer, examples +from ipyleaflet import Map + +# Load example tile layer from publicly available imagery +tile_client = examples.get_virtual_earth() + +# Create ipyleaflet tile layer from that server +t = get_leaflet_tile_layer(tile_client, opacity=1) + +m = Map(center=(39.751343612695145, -105.22181306125279), zoom=18) +m.add_layer(t) +m +``` + + + + +### 🖥️ Local Web Application + +Launch the tileserver from the commandline to use the included web application where you can view the raster and extract regions of interest. + +```bash +python -m tileserver path/to/raster.tif +``` + + + +You can use the web viewer to extract regions of interest: + + + + +### Usage Notes + +- `get_leaflet_tile_layer` accepts either an existing `TileClient` or a +path from which to create a `TileClient` under the hood. +- The color palette choices come from [`palettable`](https://jiffyclub.github.io/palettable/). + + + + +%prep +%autosetup -n flask-tileserver-0.2.3 + +%build +%py3_build + +%install +%py3_install +install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir} +if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +pushd %{buildroot} +if [ -d usr/lib ]; then + find usr/lib -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then + find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +if [ -d usr/bin ]; then + find usr/bin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then + find usr/sbin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +touch doclist.lst +if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then + find usr/share/man -type f -printf "/%h/%f.gz\n" >> doclist.lst +fi +popd +mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst . +mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst . + +%files -n python3-flask-tileserver -f filelist.lst +%dir %{python3_sitelib}/* + +%files help -f doclist.lst +%{_docdir}/* + +%changelog +* Thu May 18 2023 Python_Bot <Python_Bot@openeuler.org> - 0.2.3-1 +- Package Spec generated @@ -0,0 +1 @@ +70d14b8cbe81d9108cc7e33b40696b49 flask-tileserver-0.2.3.tar.gz |
