diff options
| author | CoprDistGit <infra@openeuler.org> | 2023-05-18 04:47:25 +0000 |
|---|---|---|
| committer | CoprDistGit <infra@openeuler.org> | 2023-05-18 04:47:25 +0000 |
| commit | e3addbc43d36c855312166abf57df0c62187ea15 (patch) | |
| tree | a4714397592a2e7fd3e22a678823d8805cab198a /python-pterasoftware.spec | |
| parent | 69c26cef105365f63c4841e3eec48d78ba7a7cda (diff) | |
automatic import of python-pterasoftware
Diffstat (limited to 'python-pterasoftware.spec')
| -rw-r--r-- | python-pterasoftware.spec | 1040 |
1 files changed, 1040 insertions, 0 deletions
diff --git a/python-pterasoftware.spec b/python-pterasoftware.spec new file mode 100644 index 0000000..5c06769 --- /dev/null +++ b/python-pterasoftware.spec @@ -0,0 +1,1040 @@ +%global _empty_manifest_terminate_build 0 +Name: python-PteraSoftware +Version: 2.2.1 +Release: 1 +Summary: This is an open-source, unsteady aerodynamics solver for analyzing flapping-wing flight. +License: MIT +URL: https://github.com/camurban/pterasoftware +Source0: https://mirrors.nju.edu.cn/pypi/web/packages/44/67/106aae9a437b95c6ab4407b3206ed8affd9faeff3cc09b7b8898047824dd/PteraSoftware-2.2.1.tar.gz +BuildArch: noarch + +Requires: python3-matplotlib +Requires: python3-numpy +Requires: python3-pyvista +Requires: python3-scipy +Requires: python3-numba +Requires: python3-cmocean +Requires: python3-tqdm +Requires: python3-webp + +%description + + +*** + + + + + + + + +*** + + + +This is Ptera Software: a fast, easy-to-use, and open-source package for analyzing +flapping-wing flight. + +## Motivation + +In late 2018, I became curious about biological flight. To sate this curiosity, I +wanted to computationally simulate some flapping-wing fliers. I quickly realized I had +two options: + +1. Spend thousands of dollars on a closed-source CFD program, which would take hours to +solve a simple case. +2. Try to learn someone else's open-source, unsteady solver written in a language I +didn't know, or using a framework that is overly complicated for my use case. + +Neither of these seemed like the right choice. + +Thankfully, my friend, Peter Sharpe, had just released his own open-source aerodynamics +solver: AeroSandbox. With his support, I have used AeroSandbox as a jumping-off point +to develop a solver package capable of unsteady simulations. + +Through the combined efforts of Peter Sharpe, Suhas Kodali, and me, Ptera Software was +born. It is an easy-to-use, open-source, and actively-maintained UVLM package capable +of analyzing flapping-wing flight. Moreover, it's written in Python, is well +documented, tested, and validated. + +With your help, I hope we will increase the open-source community's interest and +understanding of biological flight. + +## Features + +1. Various Aerodynamic Simulation Methods + * Steady simulations can be run with a standard horseshoe vortex-lattice method + (VLM) or a ring VLM. + * Unsteady simulations use a ring unsteady VLM (UVLM) solver. + * Unsteady simulations support both fixed and free wakes. + * Unsteady simulations implement vortex aging to reduce numerical instabilities. +2. Customizable Aircraft Geometry + * Aircraft can be defined as a collection of one or more wings of any dimensions and + positions. + * Wings can be defined as a collection of two or more wing cross sections of any + dimensions and positions. + * Wing cross sections can be specified to match the mean camber line of an airfoil. + * The package comes with a massive database of airfoil to chose from. + * Wings are automatically discretized into panels with customizable sizes and + spacings. +3. Customizable Aircraft Motion + * The relative motion of wings and wing cross sections can be defined using any + time-dependent functions of sweep, pitch, and heave angles. +4. Customizable Operating Points + * Parameters such as the free-stream velocity, density, angle of attack, angle of + sideslip, etc. can be changed by the user. +5. High-Speed Simulations + * Using Just-In-Time compilation, Ptera Software can solve many unsteady + flapping-wing simulations in less than a minute! + * Steady simulations take only seconds! +6. Simulations of Formation Flight + * Since v2.0.0, Ptera Software has supported simulations with more than one + airplane. + * This feature can be used to analyze the aerodynamics of flapping-wing formation + flight! +7. Features for Flapping-Wing Vehicle Design + * Ptera Software is focused on developing features to facilitate designing + flapping-wing vehicles. + * For example, use the functions in the trim module to automatically search for a + trim operating point for steady and unsteady simulations of aircraft. + +## Installation and Use + +First things first, you will need a copy of Python 3.8. Python 3.9 is not yet supported +due to a dependency issue in VTK. Download Python 3.8 from the official Python website. +At this time, I do not recommend using a version from the Anaconda distribution as it +could introduce compatibility issues with PyPI. + +There are two ways to use Ptera Software. The first is by downloading GitHub release, +which will provide you your own copy of the source code, in which you can get a feel +for how it works (this can also be accomplished by forking the main branch). The second +is by importing the Ptera Software package using PyPI, which will allow you to call +Ptera Software's functions in your own scripts. If you are new to this tool, I +recommend first downloading a release, as this will give you access to the "examples" +directory. + +Next, make sure you have an IDE in which you can run Ptera Software. I recommend using +the Community Edition of PyCharm, which is free, powerful, and well documented. If +you've never set up a Python project before, follow +[this guide](https://www.jetbrains.com/help/pycharm/quick-start-guide.html) to set up a +new project in PyCharm. If you'll be downloading a release, follow that tutorial's +"Open an existing project guide." Otherwise, follow the "Create a new project guide." + +### Downloading A Release + +To download a release, navigate to +[the releases page](https://github.com/camUrban/PteraSoftware/releases) and download +the latest zipped directory. Extract the contents, and set up a python project as +described in the PyCharm tutorial. + +Then, open a command prompt window in your project's directory and enter: + +```pip install -r requirements.txt``` + +via the command prompt in your fork's directory. You may also want to run: + +```pip install -r requirements_dev.txt``` + +if you plan on making significant changes to the software. + +Finally, open the "examples" folder, which contains several heavily commented scripts +that demonstrate different features and simulations. Read through each example, and +then run them to admire their pretty output! + +### Importing As A Package + +If you wish to use this package as a dependency in your own project, simply run: + +```pip install pterasoftware``` + +via the command prompt in your project's directory. Then, in a script that you'd like +to use features from Ptera Software, add: + +```import pterasoftware as ps``` + +If you haven't previously downloaded Ptera Software's source code, you can also learn +about the available functions by reading their docstrings, which should be fetched +automatically by many IDEs. Otherwise, you can return to the GitHub and read through +the docstrings there. + +I am hoping to implement a web-based documentation guide soon! If you'd like to +contribute to this, feel free to open a feature request issue and start a conversation! + +### What If I'm Having Trouble Getting Set Up? + +Not to worry! I am working on a video that walks through getting Ptera Software up and +running. It will include every step, from downloading Python for the first time to +setting up your IDE to running the software. In the meantime, feel free to open an +issue for guidance. + +## Example Code + +The following code snippet is all that is needed (after running pip install +pterasoftware) to run the steady horseshoe solver on a custom airplane object. + +``` +import pterasoftware as ps + +example_airplane = ps.geometry.Airplane( + wings=[ + ps.geometry.Wing( + symmetric=True, + wing_cross_sections=[ + ps.geometry.WingCrossSection( + airfoil=ps.geometry.Airfoil(name="naca2412",), + ), + ps.geometry.WingCrossSection( + y_le=5.0, airfoil=ps.geometry.Airfoil(name="naca2412",), + ), + ], + ), + ], +) + +example_operating_point = ps.operating_point.OperatingPoint() + +example_problem = ps.problems.SteadyProblem( + airplane=example_airplane, + operating_point=example_operating_point +) + +example_solver = ps.steady_horseshoe_vortex_lattice_method.SteadyHorseshoeVortexLatticeMethodSolver( + steady_problem=example_problem +) + +example_solver.run() + +ps.output.draw(solver=example_solver, show_delta_pressures=True, show_streamlines=True) +``` + +## Example Output + +This package currently supports three different solvers, a steady horseshoe vortex +lattice method (VLM), a steady ring VLM, and an unsteady ring VLM (UVLM). Here are +examples of the output you can expect to receive from each of them. + +### Steady Horseshoe VLM + +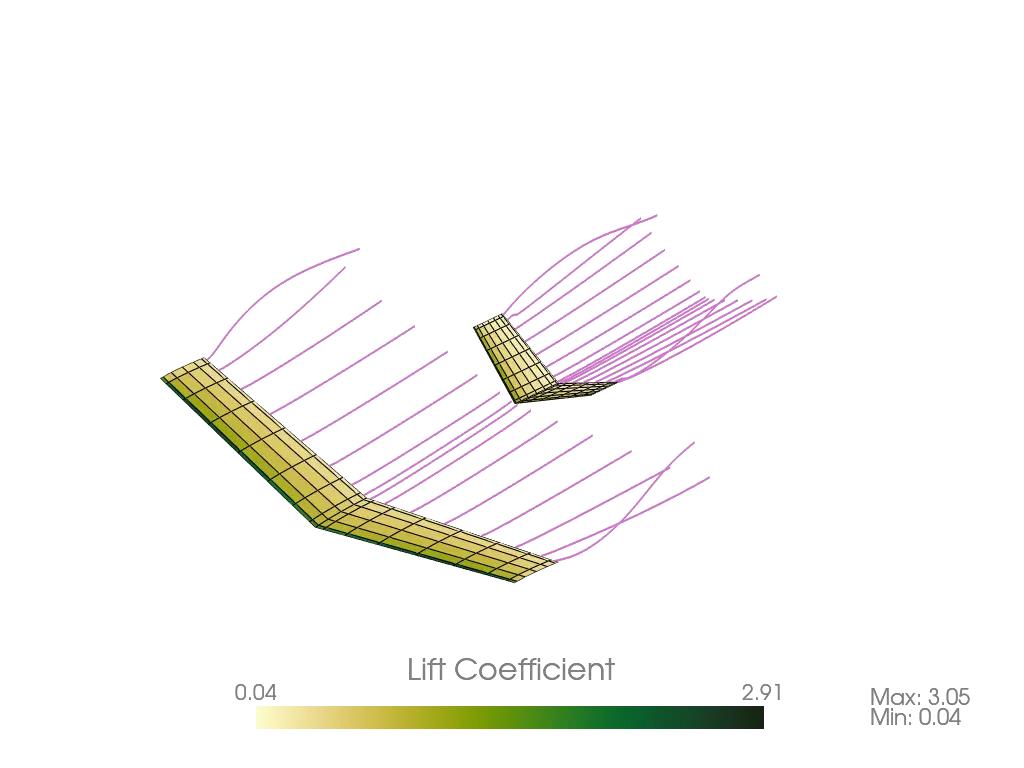 + +### Steady Ring VLM + +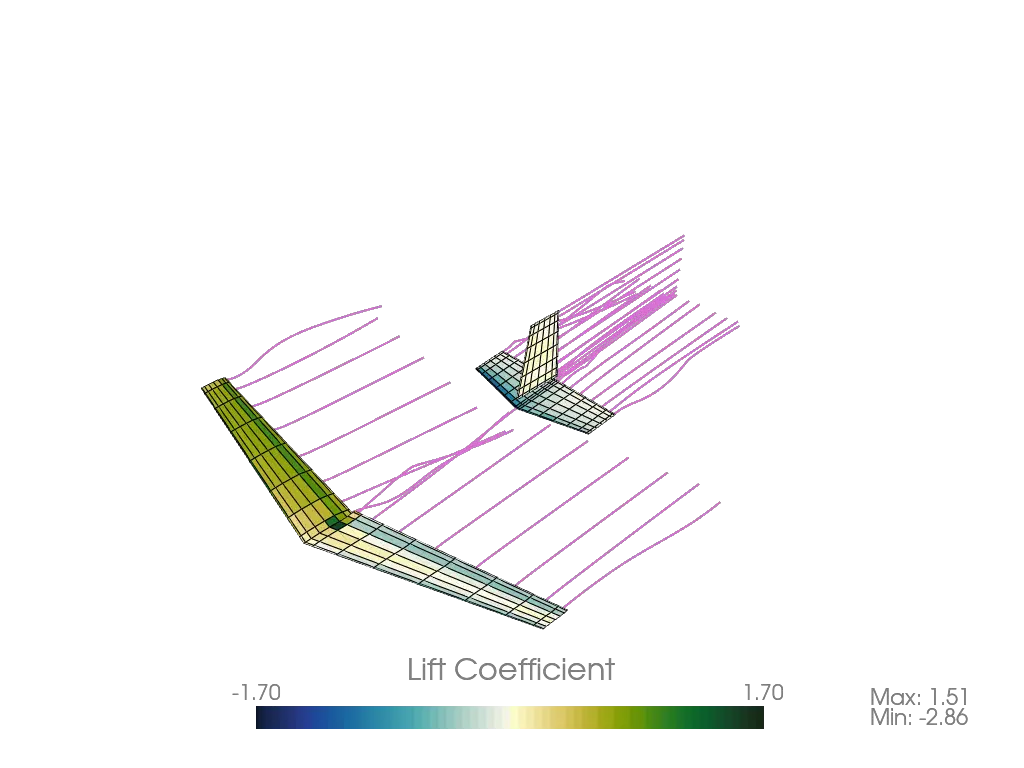 + +### Unsteady Ring VLM + +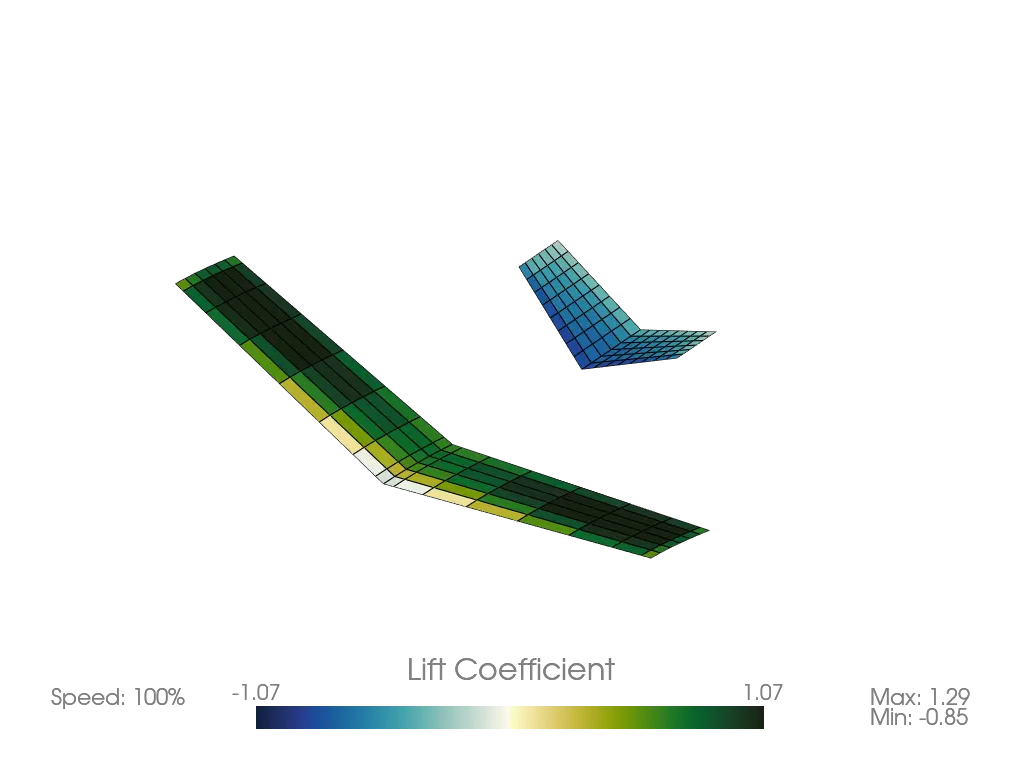 + +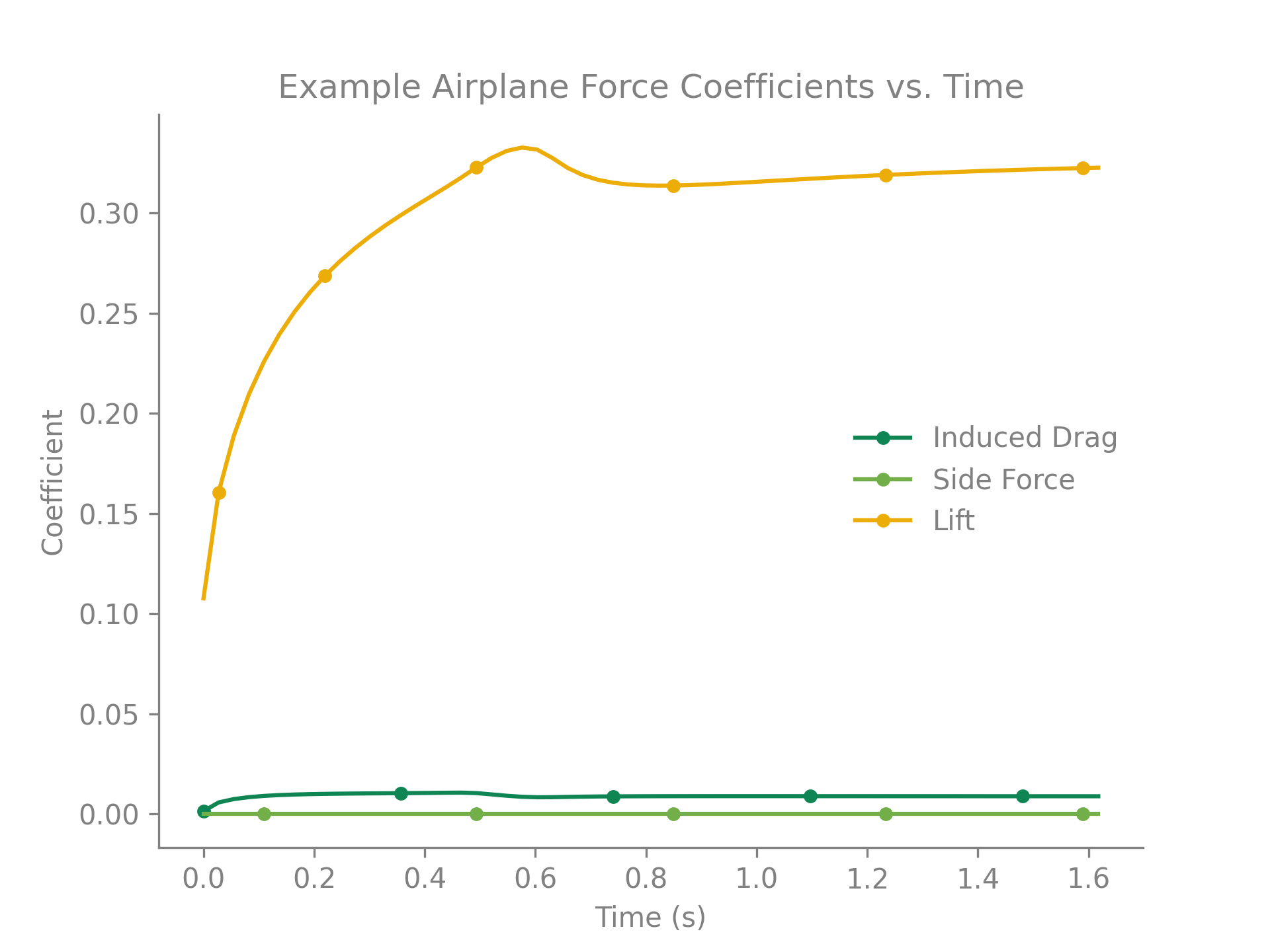 + + + +## Requirements + +Here are the requirements necessary to run Ptera Software: + +* matplotlib >= 3.5.2, < 4.0.0 +* numpy >= 1.22.4, < 1.24.0 +* pyvista >= 0.34.1, < 1.0.0 +* scipy >= 1.8.1, < 2.0.0 +* numba >= 0.55.2, < 1.0.0 +* cmocean >= 2.0.0, < 3.0.0 +* tqdm >= 4.64.0, < 5.0.0 +* webp >= 0.1.4, < 1.0.0 + +Additionally, these packages are useful for continued development of the software: + +* codecov >= 2.1.12, < 3.0.0 +* black >= 22.6.0, < 23.0.0 +* pre-commit >= 2.19.0, < 3.0.0 +* build >= 0.8.0, < 1.0.0 +* twine >= 4.0.1, < 5.0.0 +* setuptools >= 62.6.0, < 63.0.0 +* wheel >= 0.37.1, < 0.38.0 + +## Validation + +Since the release of version 1.0.0, Ptera Software is now validated against +experimental flapping-wing data! See the "validation" directory to run the test case +and read a report on the software's accuracy. + +## How to Contribute + +As I said before, the primary goal of this project is to increase the open-source +community's understanding and appreciation for unsteady aerodynamics in general and +flapping-wing flight in particular. This will only happen through your participation. +Feel free to request features, report bugs or security issues, and provide suggestions. +No comment is too big or small! + +Here is a list of changes I would like to make in the coming releases. If you want to +contribute and don't know where to start, this is for you! + +### Testing + +* We should make sure that all the integration tests compare output against expected +results. This means getting rid of all the "test_method_does_not_throw" tests. +* We should maintain the repository's testing coverage to be at least 80%. + +### Style and Documentation + +* Maintain the repository's A CodeFactor Rating. +* We should fill in any of the "Properly document this..." TODO statements. +* We should ensure that all files be at least 30% comment lines. +* We should continue to ensure that all source code is formatted using Black. + +### Features + +* We should create a setup tutorial video and add it to the documentation. This should +be geared toward a user who doesn't have Python, an IDE, or Ptera Software installed on +their computer yet. +* We should implement a leading-edge model to account for flow separation. See +"Modified Unsteady Vortex-Lattice Method to Study Flapping Wings in Hover Flight." by +Bruno Roccia, Sergio Preidikman, Julio Massa, and Dean Mook for details. +* We should create a command-line interface or GUI. +* We should try to implement aeroelastic effects in Ptera Software's solvers. +* Flapping wing controls is both fascinating and complicated. We should try to create a +workflow in Ptera Software for controls systems identification for flapping-wing +vehicles. + +## Credits + +Here is a list of all the people and packages that helped me created Ptera Software in +no particular order. Specific citations can be found in the source code's docstrings +where applicable. + +* Suhas Kodali +* Peter Sharpe +* Ramesh Agarwal +* Joseph Katz +* Allen Plotkin +* Austin Stover +* AeroSandbox +* Black +* Codecov +* Travis CI +* NumPy +* SciPy +* PyVista +* MatPlotLib +* Numba +* Pre-Commit +* SetupTools +* GitIgnore +* Shields.io +* PyPI +* Wheel +* Twine +* SemVer +* GitFlow +* Cmocean +* Tqdm +* WebP +* Build + +## Notes + +To the best of my ability, I am following SemVer conventions in naming my releases. I +am also using the GitFlow method of branching for this project's development. This +means that nightly builds will be available on the develop branch. The latest stable +releases can be found on the master branch. + + +%package -n python3-PteraSoftware +Summary: This is an open-source, unsteady aerodynamics solver for analyzing flapping-wing flight. +Provides: python-PteraSoftware +BuildRequires: python3-devel +BuildRequires: python3-setuptools +BuildRequires: python3-pip +%description -n python3-PteraSoftware + + +*** + + + + + + + + +*** + + + +This is Ptera Software: a fast, easy-to-use, and open-source package for analyzing +flapping-wing flight. + +## Motivation + +In late 2018, I became curious about biological flight. To sate this curiosity, I +wanted to computationally simulate some flapping-wing fliers. I quickly realized I had +two options: + +1. Spend thousands of dollars on a closed-source CFD program, which would take hours to +solve a simple case. +2. Try to learn someone else's open-source, unsteady solver written in a language I +didn't know, or using a framework that is overly complicated for my use case. + +Neither of these seemed like the right choice. + +Thankfully, my friend, Peter Sharpe, had just released his own open-source aerodynamics +solver: AeroSandbox. With his support, I have used AeroSandbox as a jumping-off point +to develop a solver package capable of unsteady simulations. + +Through the combined efforts of Peter Sharpe, Suhas Kodali, and me, Ptera Software was +born. It is an easy-to-use, open-source, and actively-maintained UVLM package capable +of analyzing flapping-wing flight. Moreover, it's written in Python, is well +documented, tested, and validated. + +With your help, I hope we will increase the open-source community's interest and +understanding of biological flight. + +## Features + +1. Various Aerodynamic Simulation Methods + * Steady simulations can be run with a standard horseshoe vortex-lattice method + (VLM) or a ring VLM. + * Unsteady simulations use a ring unsteady VLM (UVLM) solver. + * Unsteady simulations support both fixed and free wakes. + * Unsteady simulations implement vortex aging to reduce numerical instabilities. +2. Customizable Aircraft Geometry + * Aircraft can be defined as a collection of one or more wings of any dimensions and + positions. + * Wings can be defined as a collection of two or more wing cross sections of any + dimensions and positions. + * Wing cross sections can be specified to match the mean camber line of an airfoil. + * The package comes with a massive database of airfoil to chose from. + * Wings are automatically discretized into panels with customizable sizes and + spacings. +3. Customizable Aircraft Motion + * The relative motion of wings and wing cross sections can be defined using any + time-dependent functions of sweep, pitch, and heave angles. +4. Customizable Operating Points + * Parameters such as the free-stream velocity, density, angle of attack, angle of + sideslip, etc. can be changed by the user. +5. High-Speed Simulations + * Using Just-In-Time compilation, Ptera Software can solve many unsteady + flapping-wing simulations in less than a minute! + * Steady simulations take only seconds! +6. Simulations of Formation Flight + * Since v2.0.0, Ptera Software has supported simulations with more than one + airplane. + * This feature can be used to analyze the aerodynamics of flapping-wing formation + flight! +7. Features for Flapping-Wing Vehicle Design + * Ptera Software is focused on developing features to facilitate designing + flapping-wing vehicles. + * For example, use the functions in the trim module to automatically search for a + trim operating point for steady and unsteady simulations of aircraft. + +## Installation and Use + +First things first, you will need a copy of Python 3.8. Python 3.9 is not yet supported +due to a dependency issue in VTK. Download Python 3.8 from the official Python website. +At this time, I do not recommend using a version from the Anaconda distribution as it +could introduce compatibility issues with PyPI. + +There are two ways to use Ptera Software. The first is by downloading GitHub release, +which will provide you your own copy of the source code, in which you can get a feel +for how it works (this can also be accomplished by forking the main branch). The second +is by importing the Ptera Software package using PyPI, which will allow you to call +Ptera Software's functions in your own scripts. If you are new to this tool, I +recommend first downloading a release, as this will give you access to the "examples" +directory. + +Next, make sure you have an IDE in which you can run Ptera Software. I recommend using +the Community Edition of PyCharm, which is free, powerful, and well documented. If +you've never set up a Python project before, follow +[this guide](https://www.jetbrains.com/help/pycharm/quick-start-guide.html) to set up a +new project in PyCharm. If you'll be downloading a release, follow that tutorial's +"Open an existing project guide." Otherwise, follow the "Create a new project guide." + +### Downloading A Release + +To download a release, navigate to +[the releases page](https://github.com/camUrban/PteraSoftware/releases) and download +the latest zipped directory. Extract the contents, and set up a python project as +described in the PyCharm tutorial. + +Then, open a command prompt window in your project's directory and enter: + +```pip install -r requirements.txt``` + +via the command prompt in your fork's directory. You may also want to run: + +```pip install -r requirements_dev.txt``` + +if you plan on making significant changes to the software. + +Finally, open the "examples" folder, which contains several heavily commented scripts +that demonstrate different features and simulations. Read through each example, and +then run them to admire their pretty output! + +### Importing As A Package + +If you wish to use this package as a dependency in your own project, simply run: + +```pip install pterasoftware``` + +via the command prompt in your project's directory. Then, in a script that you'd like +to use features from Ptera Software, add: + +```import pterasoftware as ps``` + +If you haven't previously downloaded Ptera Software's source code, you can also learn +about the available functions by reading their docstrings, which should be fetched +automatically by many IDEs. Otherwise, you can return to the GitHub and read through +the docstrings there. + +I am hoping to implement a web-based documentation guide soon! If you'd like to +contribute to this, feel free to open a feature request issue and start a conversation! + +### What If I'm Having Trouble Getting Set Up? + +Not to worry! I am working on a video that walks through getting Ptera Software up and +running. It will include every step, from downloading Python for the first time to +setting up your IDE to running the software. In the meantime, feel free to open an +issue for guidance. + +## Example Code + +The following code snippet is all that is needed (after running pip install +pterasoftware) to run the steady horseshoe solver on a custom airplane object. + +``` +import pterasoftware as ps + +example_airplane = ps.geometry.Airplane( + wings=[ + ps.geometry.Wing( + symmetric=True, + wing_cross_sections=[ + ps.geometry.WingCrossSection( + airfoil=ps.geometry.Airfoil(name="naca2412",), + ), + ps.geometry.WingCrossSection( + y_le=5.0, airfoil=ps.geometry.Airfoil(name="naca2412",), + ), + ], + ), + ], +) + +example_operating_point = ps.operating_point.OperatingPoint() + +example_problem = ps.problems.SteadyProblem( + airplane=example_airplane, + operating_point=example_operating_point +) + +example_solver = ps.steady_horseshoe_vortex_lattice_method.SteadyHorseshoeVortexLatticeMethodSolver( + steady_problem=example_problem +) + +example_solver.run() + +ps.output.draw(solver=example_solver, show_delta_pressures=True, show_streamlines=True) +``` + +## Example Output + +This package currently supports three different solvers, a steady horseshoe vortex +lattice method (VLM), a steady ring VLM, and an unsteady ring VLM (UVLM). Here are +examples of the output you can expect to receive from each of them. + +### Steady Horseshoe VLM + + + +### Steady Ring VLM + + + +### Unsteady Ring VLM + + + + + + + +## Requirements + +Here are the requirements necessary to run Ptera Software: + +* matplotlib >= 3.5.2, < 4.0.0 +* numpy >= 1.22.4, < 1.24.0 +* pyvista >= 0.34.1, < 1.0.0 +* scipy >= 1.8.1, < 2.0.0 +* numba >= 0.55.2, < 1.0.0 +* cmocean >= 2.0.0, < 3.0.0 +* tqdm >= 4.64.0, < 5.0.0 +* webp >= 0.1.4, < 1.0.0 + +Additionally, these packages are useful for continued development of the software: + +* codecov >= 2.1.12, < 3.0.0 +* black >= 22.6.0, < 23.0.0 +* pre-commit >= 2.19.0, < 3.0.0 +* build >= 0.8.0, < 1.0.0 +* twine >= 4.0.1, < 5.0.0 +* setuptools >= 62.6.0, < 63.0.0 +* wheel >= 0.37.1, < 0.38.0 + +## Validation + +Since the release of version 1.0.0, Ptera Software is now validated against +experimental flapping-wing data! See the "validation" directory to run the test case +and read a report on the software's accuracy. + +## How to Contribute + +As I said before, the primary goal of this project is to increase the open-source +community's understanding and appreciation for unsteady aerodynamics in general and +flapping-wing flight in particular. This will only happen through your participation. +Feel free to request features, report bugs or security issues, and provide suggestions. +No comment is too big or small! + +Here is a list of changes I would like to make in the coming releases. If you want to +contribute and don't know where to start, this is for you! + +### Testing + +* We should make sure that all the integration tests compare output against expected +results. This means getting rid of all the "test_method_does_not_throw" tests. +* We should maintain the repository's testing coverage to be at least 80%. + +### Style and Documentation + +* Maintain the repository's A CodeFactor Rating. +* We should fill in any of the "Properly document this..." TODO statements. +* We should ensure that all files be at least 30% comment lines. +* We should continue to ensure that all source code is formatted using Black. + +### Features + +* We should create a setup tutorial video and add it to the documentation. This should +be geared toward a user who doesn't have Python, an IDE, or Ptera Software installed on +their computer yet. +* We should implement a leading-edge model to account for flow separation. See +"Modified Unsteady Vortex-Lattice Method to Study Flapping Wings in Hover Flight." by +Bruno Roccia, Sergio Preidikman, Julio Massa, and Dean Mook for details. +* We should create a command-line interface or GUI. +* We should try to implement aeroelastic effects in Ptera Software's solvers. +* Flapping wing controls is both fascinating and complicated. We should try to create a +workflow in Ptera Software for controls systems identification for flapping-wing +vehicles. + +## Credits + +Here is a list of all the people and packages that helped me created Ptera Software in +no particular order. Specific citations can be found in the source code's docstrings +where applicable. + +* Suhas Kodali +* Peter Sharpe +* Ramesh Agarwal +* Joseph Katz +* Allen Plotkin +* Austin Stover +* AeroSandbox +* Black +* Codecov +* Travis CI +* NumPy +* SciPy +* PyVista +* MatPlotLib +* Numba +* Pre-Commit +* SetupTools +* GitIgnore +* Shields.io +* PyPI +* Wheel +* Twine +* SemVer +* GitFlow +* Cmocean +* Tqdm +* WebP +* Build + +## Notes + +To the best of my ability, I am following SemVer conventions in naming my releases. I +am also using the GitFlow method of branching for this project's development. This +means that nightly builds will be available on the develop branch. The latest stable +releases can be found on the master branch. + + +%package help +Summary: Development documents and examples for PteraSoftware +Provides: python3-PteraSoftware-doc +%description help + + +*** + + + + + + + + +*** + + + +This is Ptera Software: a fast, easy-to-use, and open-source package for analyzing +flapping-wing flight. + +## Motivation + +In late 2018, I became curious about biological flight. To sate this curiosity, I +wanted to computationally simulate some flapping-wing fliers. I quickly realized I had +two options: + +1. Spend thousands of dollars on a closed-source CFD program, which would take hours to +solve a simple case. +2. Try to learn someone else's open-source, unsteady solver written in a language I +didn't know, or using a framework that is overly complicated for my use case. + +Neither of these seemed like the right choice. + +Thankfully, my friend, Peter Sharpe, had just released his own open-source aerodynamics +solver: AeroSandbox. With his support, I have used AeroSandbox as a jumping-off point +to develop a solver package capable of unsteady simulations. + +Through the combined efforts of Peter Sharpe, Suhas Kodali, and me, Ptera Software was +born. It is an easy-to-use, open-source, and actively-maintained UVLM package capable +of analyzing flapping-wing flight. Moreover, it's written in Python, is well +documented, tested, and validated. + +With your help, I hope we will increase the open-source community's interest and +understanding of biological flight. + +## Features + +1. Various Aerodynamic Simulation Methods + * Steady simulations can be run with a standard horseshoe vortex-lattice method + (VLM) or a ring VLM. + * Unsteady simulations use a ring unsteady VLM (UVLM) solver. + * Unsteady simulations support both fixed and free wakes. + * Unsteady simulations implement vortex aging to reduce numerical instabilities. +2. Customizable Aircraft Geometry + * Aircraft can be defined as a collection of one or more wings of any dimensions and + positions. + * Wings can be defined as a collection of two or more wing cross sections of any + dimensions and positions. + * Wing cross sections can be specified to match the mean camber line of an airfoil. + * The package comes with a massive database of airfoil to chose from. + * Wings are automatically discretized into panels with customizable sizes and + spacings. +3. Customizable Aircraft Motion + * The relative motion of wings and wing cross sections can be defined using any + time-dependent functions of sweep, pitch, and heave angles. +4. Customizable Operating Points + * Parameters such as the free-stream velocity, density, angle of attack, angle of + sideslip, etc. can be changed by the user. +5. High-Speed Simulations + * Using Just-In-Time compilation, Ptera Software can solve many unsteady + flapping-wing simulations in less than a minute! + * Steady simulations take only seconds! +6. Simulations of Formation Flight + * Since v2.0.0, Ptera Software has supported simulations with more than one + airplane. + * This feature can be used to analyze the aerodynamics of flapping-wing formation + flight! +7. Features for Flapping-Wing Vehicle Design + * Ptera Software is focused on developing features to facilitate designing + flapping-wing vehicles. + * For example, use the functions in the trim module to automatically search for a + trim operating point for steady and unsteady simulations of aircraft. + +## Installation and Use + +First things first, you will need a copy of Python 3.8. Python 3.9 is not yet supported +due to a dependency issue in VTK. Download Python 3.8 from the official Python website. +At this time, I do not recommend using a version from the Anaconda distribution as it +could introduce compatibility issues with PyPI. + +There are two ways to use Ptera Software. The first is by downloading GitHub release, +which will provide you your own copy of the source code, in which you can get a feel +for how it works (this can also be accomplished by forking the main branch). The second +is by importing the Ptera Software package using PyPI, which will allow you to call +Ptera Software's functions in your own scripts. If you are new to this tool, I +recommend first downloading a release, as this will give you access to the "examples" +directory. + +Next, make sure you have an IDE in which you can run Ptera Software. I recommend using +the Community Edition of PyCharm, which is free, powerful, and well documented. If +you've never set up a Python project before, follow +[this guide](https://www.jetbrains.com/help/pycharm/quick-start-guide.html) to set up a +new project in PyCharm. If you'll be downloading a release, follow that tutorial's +"Open an existing project guide." Otherwise, follow the "Create a new project guide." + +### Downloading A Release + +To download a release, navigate to +[the releases page](https://github.com/camUrban/PteraSoftware/releases) and download +the latest zipped directory. Extract the contents, and set up a python project as +described in the PyCharm tutorial. + +Then, open a command prompt window in your project's directory and enter: + +```pip install -r requirements.txt``` + +via the command prompt in your fork's directory. You may also want to run: + +```pip install -r requirements_dev.txt``` + +if you plan on making significant changes to the software. + +Finally, open the "examples" folder, which contains several heavily commented scripts +that demonstrate different features and simulations. Read through each example, and +then run them to admire their pretty output! + +### Importing As A Package + +If you wish to use this package as a dependency in your own project, simply run: + +```pip install pterasoftware``` + +via the command prompt in your project's directory. Then, in a script that you'd like +to use features from Ptera Software, add: + +```import pterasoftware as ps``` + +If you haven't previously downloaded Ptera Software's source code, you can also learn +about the available functions by reading their docstrings, which should be fetched +automatically by many IDEs. Otherwise, you can return to the GitHub and read through +the docstrings there. + +I am hoping to implement a web-based documentation guide soon! If you'd like to +contribute to this, feel free to open a feature request issue and start a conversation! + +### What If I'm Having Trouble Getting Set Up? + +Not to worry! I am working on a video that walks through getting Ptera Software up and +running. It will include every step, from downloading Python for the first time to +setting up your IDE to running the software. In the meantime, feel free to open an +issue for guidance. + +## Example Code + +The following code snippet is all that is needed (after running pip install +pterasoftware) to run the steady horseshoe solver on a custom airplane object. + +``` +import pterasoftware as ps + +example_airplane = ps.geometry.Airplane( + wings=[ + ps.geometry.Wing( + symmetric=True, + wing_cross_sections=[ + ps.geometry.WingCrossSection( + airfoil=ps.geometry.Airfoil(name="naca2412",), + ), + ps.geometry.WingCrossSection( + y_le=5.0, airfoil=ps.geometry.Airfoil(name="naca2412",), + ), + ], + ), + ], +) + +example_operating_point = ps.operating_point.OperatingPoint() + +example_problem = ps.problems.SteadyProblem( + airplane=example_airplane, + operating_point=example_operating_point +) + +example_solver = ps.steady_horseshoe_vortex_lattice_method.SteadyHorseshoeVortexLatticeMethodSolver( + steady_problem=example_problem +) + +example_solver.run() + +ps.output.draw(solver=example_solver, show_delta_pressures=True, show_streamlines=True) +``` + +## Example Output + +This package currently supports three different solvers, a steady horseshoe vortex +lattice method (VLM), a steady ring VLM, and an unsteady ring VLM (UVLM). Here are +examples of the output you can expect to receive from each of them. + +### Steady Horseshoe VLM + + + +### Steady Ring VLM + + + +### Unsteady Ring VLM + + + + + + + +## Requirements + +Here are the requirements necessary to run Ptera Software: + +* matplotlib >= 3.5.2, < 4.0.0 +* numpy >= 1.22.4, < 1.24.0 +* pyvista >= 0.34.1, < 1.0.0 +* scipy >= 1.8.1, < 2.0.0 +* numba >= 0.55.2, < 1.0.0 +* cmocean >= 2.0.0, < 3.0.0 +* tqdm >= 4.64.0, < 5.0.0 +* webp >= 0.1.4, < 1.0.0 + +Additionally, these packages are useful for continued development of the software: + +* codecov >= 2.1.12, < 3.0.0 +* black >= 22.6.0, < 23.0.0 +* pre-commit >= 2.19.0, < 3.0.0 +* build >= 0.8.0, < 1.0.0 +* twine >= 4.0.1, < 5.0.0 +* setuptools >= 62.6.0, < 63.0.0 +* wheel >= 0.37.1, < 0.38.0 + +## Validation + +Since the release of version 1.0.0, Ptera Software is now validated against +experimental flapping-wing data! See the "validation" directory to run the test case +and read a report on the software's accuracy. + +## How to Contribute + +As I said before, the primary goal of this project is to increase the open-source +community's understanding and appreciation for unsteady aerodynamics in general and +flapping-wing flight in particular. This will only happen through your participation. +Feel free to request features, report bugs or security issues, and provide suggestions. +No comment is too big or small! + +Here is a list of changes I would like to make in the coming releases. If you want to +contribute and don't know where to start, this is for you! + +### Testing + +* We should make sure that all the integration tests compare output against expected +results. This means getting rid of all the "test_method_does_not_throw" tests. +* We should maintain the repository's testing coverage to be at least 80%. + +### Style and Documentation + +* Maintain the repository's A CodeFactor Rating. +* We should fill in any of the "Properly document this..." TODO statements. +* We should ensure that all files be at least 30% comment lines. +* We should continue to ensure that all source code is formatted using Black. + +### Features + +* We should create a setup tutorial video and add it to the documentation. This should +be geared toward a user who doesn't have Python, an IDE, or Ptera Software installed on +their computer yet. +* We should implement a leading-edge model to account for flow separation. See +"Modified Unsteady Vortex-Lattice Method to Study Flapping Wings in Hover Flight." by +Bruno Roccia, Sergio Preidikman, Julio Massa, and Dean Mook for details. +* We should create a command-line interface or GUI. +* We should try to implement aeroelastic effects in Ptera Software's solvers. +* Flapping wing controls is both fascinating and complicated. We should try to create a +workflow in Ptera Software for controls systems identification for flapping-wing +vehicles. + +## Credits + +Here is a list of all the people and packages that helped me created Ptera Software in +no particular order. Specific citations can be found in the source code's docstrings +where applicable. + +* Suhas Kodali +* Peter Sharpe +* Ramesh Agarwal +* Joseph Katz +* Allen Plotkin +* Austin Stover +* AeroSandbox +* Black +* Codecov +* Travis CI +* NumPy +* SciPy +* PyVista +* MatPlotLib +* Numba +* Pre-Commit +* SetupTools +* GitIgnore +* Shields.io +* PyPI +* Wheel +* Twine +* SemVer +* GitFlow +* Cmocean +* Tqdm +* WebP +* Build + +## Notes + +To the best of my ability, I am following SemVer conventions in naming my releases. I +am also using the GitFlow method of branching for this project's development. This +means that nightly builds will be available on the develop branch. The latest stable +releases can be found on the master branch. + + +%prep +%autosetup -n PteraSoftware-2.2.1 + +%build +%py3_build + +%install +%py3_install +install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir} +if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +pushd %{buildroot} +if [ -d usr/lib ]; then + find usr/lib -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then + find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +if [ -d usr/bin ]; then + find usr/bin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then + find usr/sbin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +touch doclist.lst +if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then + find usr/share/man -type f -printf "/%h/%f.gz\n" >> doclist.lst +fi +popd +mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst . +mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst . + +%files -n python3-PteraSoftware -f filelist.lst +%dir %{python3_sitelib}/* + +%files help -f doclist.lst +%{_docdir}/* + +%changelog +* Thu May 18 2023 Python_Bot <Python_Bot@openeuler.org> - 2.2.1-1 +- Package Spec generated |
