diff options
| author | CoprDistGit <infra@openeuler.org> | 2023-05-29 12:27:40 +0000 |
|---|---|---|
| committer | CoprDistGit <infra@openeuler.org> | 2023-05-29 12:27:40 +0000 |
| commit | 539c775507564800f6250a0982573b064f18bc01 (patch) | |
| tree | 04559f1d562c8ec0396aaf0490d477d931f28c16 /python-tokenexchangeauthenticator.spec | |
| parent | 4fd4329308f817db3ec77ddaa685cf7452af1b30 (diff) | |
automatic import of python-tokenexchangeauthenticator
Diffstat (limited to 'python-tokenexchangeauthenticator.spec')
| -rw-r--r-- | python-tokenexchangeauthenticator.spec | 351 |
1 files changed, 351 insertions, 0 deletions
diff --git a/python-tokenexchangeauthenticator.spec b/python-tokenexchangeauthenticator.spec new file mode 100644 index 0000000..bfa6bfe --- /dev/null +++ b/python-tokenexchangeauthenticator.spec @@ -0,0 +1,351 @@ +%global _empty_manifest_terminate_build 0 +Name: python-TokenExchangeAuthenticator +Version: 0.3.4 +Release: 1 +Summary: Jupyterhub oauth extension +License: MIT +URL: https://github.com/statisticsnorway/jupyterhub-extensions +Source0: https://mirrors.nju.edu.cn/pypi/web/packages/85/fe/3acc3fc2f60f75f8a7353170a898a25156bca8cd05f5fa1612b27ca39600/TokenExchangeAuthenticator-0.3.4.tar.gz +BuildArch: noarch + +Requires: python3-jupyterhub +Requires: python3-oauthenticator +Requires: python3-pyjwt[crypto] + +%description +# TokenExchangeAuthenticator for JupyterHub. + +This Authenticator can be plugged in and used with JupyterHub. It is built on top of [OAuthenticator](https://github.com/jupyterhub/oauthenticator), and authenticates users using OIDC and retrieves external Identity Provider (IDP) tokens using [token exchange](https://www.keycloak.org/docs/latest/securing_apps/#_token-exchange). This implementation is compatible with Keycloak as an [Identity Broker](https://www.keycloak.org/docs/latest/server_admin/#_identity_broker) and Google as an external IDP (see [Internal Token to External Token Exchange](https://www.keycloak.org/docs/latest/securing_apps/#internal-token-to-external-token-exchange)). + +It also implements a refresh mechanism, ensuring that both the internal access token as well as any external IDP +tokens are updated individually. If the update is not possible, it forces a re-authentication of the user. + +## Sequence diagram +The OIDC + token exchange flow may be illustrated like in the following sequence diagram: + +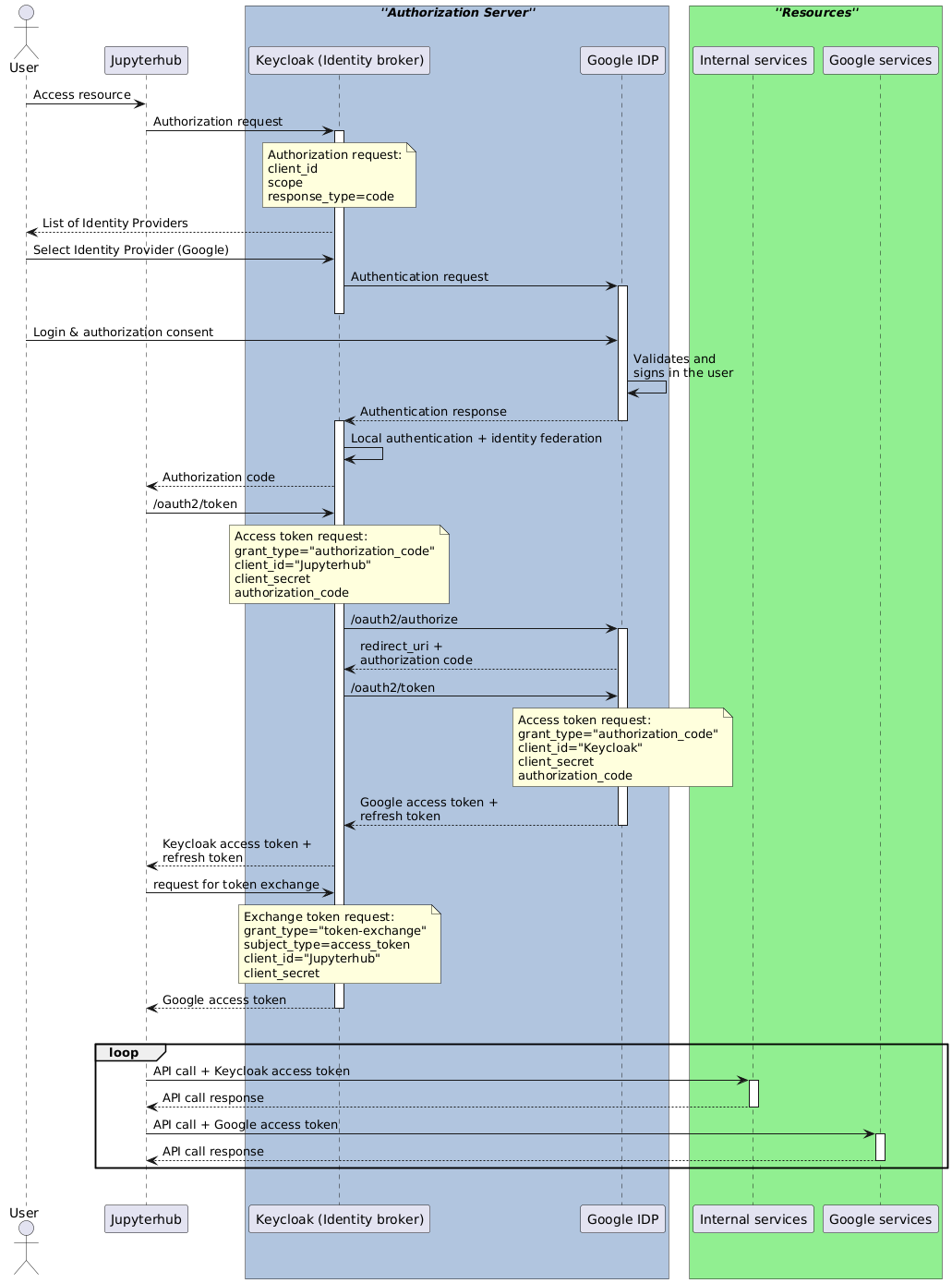 + +## Installation + +```bash +pip install tokenexchangeauthenticator +``` + +## Usage + +In your JupyterHub config file, set the authenticator and configure it: + +```python +# Enable the authenticator +c.JupyterHub.authenticator_class = 'tokenexchangeauthenticator.TokenExchangeAuthenticator' +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.username_key = 'preferred_username' +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.userdata_params = {'state': 'state', 'kc_idp_hint': 'google'} +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.logout_redirect_uri = 'https://my.domain.com/logout' +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.oauth_callback_url = 'https://my.domain.com/oauth_callback' + +# Specify the issuer url, to get all the endpoints automatically from .well-known/openid-configuration +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.oidc_issuer = 'https://my.keycloak.com/auth/realms/myrealm' + +# If you need to set a different scope, like adding the offline option for longer lived refresh token +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.scope = ['openid', 'email', 'offline_access'] +# Request access tokens for other services by passing their id's (this uses the token exchange mechanism) +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.exchange_tokens = ['google'] +``` + +#### Note on Google's authorization server +Google's authorization server only provideds the `refresh_token` in the response to the initial login request. +Hence, the Identity Broker (e.g. Keycloak) will only get the refresh token on the first login so that subsequent token +refresh may stop working (see [issue on stack overflow](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/62700314/keycloak-only-gets-google-refresh-token-on-first-login)). +This can be remedied by prompting for re-consent at every login like this: + +```python +# This will force the retrieval of a refresh_token on every login +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.extra_authorize_params = {'prompt': 'consent'} +``` + +It's also necessary to configure the client ID and secret. This may be set directly like this: +```python +# This will force the retrieval of a refresh_token on every login +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.client_id = 'client-id' +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.client_secret = 'secret' +``` + +Or by setting the following environment +variables: + +```bash +OAUTH_CLIENT_ID=client_id +OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET=client_secret +``` + +#### Expose the user's tokens + +The user's tokens are stored using Jupyterhub's [authentication state](https://jupyterhub.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/authenticators.html#authentication-state). +These can optionally be exposed at a custom path which will only be accessible inside the user's single-user notebook. +The path can be customised by setting: +```python +# If set, exposes the user's access token(s) at this relative path +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.local_user_exposed_path = '/my-custom-path/userinfo' +``` + +## Running tests +To run the tests locally: + +``` +$ pip install --upgrade --pre -r test-requirements.txt +``` + +``` +$ pytest -v ./tokenexchangeauthenticator/tests/ +``` +Or you run a specific test file with: + +``` +$ pytest -v ./tokenexchangeauthenticator/tests/<test-file-name> +``` + + + + +%package -n python3-TokenExchangeAuthenticator +Summary: Jupyterhub oauth extension +Provides: python-TokenExchangeAuthenticator +BuildRequires: python3-devel +BuildRequires: python3-setuptools +BuildRequires: python3-pip +%description -n python3-TokenExchangeAuthenticator +# TokenExchangeAuthenticator for JupyterHub. + +This Authenticator can be plugged in and used with JupyterHub. It is built on top of [OAuthenticator](https://github.com/jupyterhub/oauthenticator), and authenticates users using OIDC and retrieves external Identity Provider (IDP) tokens using [token exchange](https://www.keycloak.org/docs/latest/securing_apps/#_token-exchange). This implementation is compatible with Keycloak as an [Identity Broker](https://www.keycloak.org/docs/latest/server_admin/#_identity_broker) and Google as an external IDP (see [Internal Token to External Token Exchange](https://www.keycloak.org/docs/latest/securing_apps/#internal-token-to-external-token-exchange)). + +It also implements a refresh mechanism, ensuring that both the internal access token as well as any external IDP +tokens are updated individually. If the update is not possible, it forces a re-authentication of the user. + +## Sequence diagram +The OIDC + token exchange flow may be illustrated like in the following sequence diagram: + + + +## Installation + +```bash +pip install tokenexchangeauthenticator +``` + +## Usage + +In your JupyterHub config file, set the authenticator and configure it: + +```python +# Enable the authenticator +c.JupyterHub.authenticator_class = 'tokenexchangeauthenticator.TokenExchangeAuthenticator' +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.username_key = 'preferred_username' +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.userdata_params = {'state': 'state', 'kc_idp_hint': 'google'} +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.logout_redirect_uri = 'https://my.domain.com/logout' +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.oauth_callback_url = 'https://my.domain.com/oauth_callback' + +# Specify the issuer url, to get all the endpoints automatically from .well-known/openid-configuration +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.oidc_issuer = 'https://my.keycloak.com/auth/realms/myrealm' + +# If you need to set a different scope, like adding the offline option for longer lived refresh token +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.scope = ['openid', 'email', 'offline_access'] +# Request access tokens for other services by passing their id's (this uses the token exchange mechanism) +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.exchange_tokens = ['google'] +``` + +#### Note on Google's authorization server +Google's authorization server only provideds the `refresh_token` in the response to the initial login request. +Hence, the Identity Broker (e.g. Keycloak) will only get the refresh token on the first login so that subsequent token +refresh may stop working (see [issue on stack overflow](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/62700314/keycloak-only-gets-google-refresh-token-on-first-login)). +This can be remedied by prompting for re-consent at every login like this: + +```python +# This will force the retrieval of a refresh_token on every login +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.extra_authorize_params = {'prompt': 'consent'} +``` + +It's also necessary to configure the client ID and secret. This may be set directly like this: +```python +# This will force the retrieval of a refresh_token on every login +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.client_id = 'client-id' +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.client_secret = 'secret' +``` + +Or by setting the following environment +variables: + +```bash +OAUTH_CLIENT_ID=client_id +OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET=client_secret +``` + +#### Expose the user's tokens + +The user's tokens are stored using Jupyterhub's [authentication state](https://jupyterhub.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/authenticators.html#authentication-state). +These can optionally be exposed at a custom path which will only be accessible inside the user's single-user notebook. +The path can be customised by setting: +```python +# If set, exposes the user's access token(s) at this relative path +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.local_user_exposed_path = '/my-custom-path/userinfo' +``` + +## Running tests +To run the tests locally: + +``` +$ pip install --upgrade --pre -r test-requirements.txt +``` + +``` +$ pytest -v ./tokenexchangeauthenticator/tests/ +``` +Or you run a specific test file with: + +``` +$ pytest -v ./tokenexchangeauthenticator/tests/<test-file-name> +``` + + + + +%package help +Summary: Development documents and examples for TokenExchangeAuthenticator +Provides: python3-TokenExchangeAuthenticator-doc +%description help +# TokenExchangeAuthenticator for JupyterHub. + +This Authenticator can be plugged in and used with JupyterHub. It is built on top of [OAuthenticator](https://github.com/jupyterhub/oauthenticator), and authenticates users using OIDC and retrieves external Identity Provider (IDP) tokens using [token exchange](https://www.keycloak.org/docs/latest/securing_apps/#_token-exchange). This implementation is compatible with Keycloak as an [Identity Broker](https://www.keycloak.org/docs/latest/server_admin/#_identity_broker) and Google as an external IDP (see [Internal Token to External Token Exchange](https://www.keycloak.org/docs/latest/securing_apps/#internal-token-to-external-token-exchange)). + +It also implements a refresh mechanism, ensuring that both the internal access token as well as any external IDP +tokens are updated individually. If the update is not possible, it forces a re-authentication of the user. + +## Sequence diagram +The OIDC + token exchange flow may be illustrated like in the following sequence diagram: + + + +## Installation + +```bash +pip install tokenexchangeauthenticator +``` + +## Usage + +In your JupyterHub config file, set the authenticator and configure it: + +```python +# Enable the authenticator +c.JupyterHub.authenticator_class = 'tokenexchangeauthenticator.TokenExchangeAuthenticator' +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.username_key = 'preferred_username' +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.userdata_params = {'state': 'state', 'kc_idp_hint': 'google'} +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.logout_redirect_uri = 'https://my.domain.com/logout' +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.oauth_callback_url = 'https://my.domain.com/oauth_callback' + +# Specify the issuer url, to get all the endpoints automatically from .well-known/openid-configuration +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.oidc_issuer = 'https://my.keycloak.com/auth/realms/myrealm' + +# If you need to set a different scope, like adding the offline option for longer lived refresh token +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.scope = ['openid', 'email', 'offline_access'] +# Request access tokens for other services by passing their id's (this uses the token exchange mechanism) +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.exchange_tokens = ['google'] +``` + +#### Note on Google's authorization server +Google's authorization server only provideds the `refresh_token` in the response to the initial login request. +Hence, the Identity Broker (e.g. Keycloak) will only get the refresh token on the first login so that subsequent token +refresh may stop working (see [issue on stack overflow](https://stackoverflow.com/questions/62700314/keycloak-only-gets-google-refresh-token-on-first-login)). +This can be remedied by prompting for re-consent at every login like this: + +```python +# This will force the retrieval of a refresh_token on every login +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.extra_authorize_params = {'prompt': 'consent'} +``` + +It's also necessary to configure the client ID and secret. This may be set directly like this: +```python +# This will force the retrieval of a refresh_token on every login +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.client_id = 'client-id' +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.client_secret = 'secret' +``` + +Or by setting the following environment +variables: + +```bash +OAUTH_CLIENT_ID=client_id +OAUTH_CLIENT_SECRET=client_secret +``` + +#### Expose the user's tokens + +The user's tokens are stored using Jupyterhub's [authentication state](https://jupyterhub.readthedocs.io/en/stable/reference/authenticators.html#authentication-state). +These can optionally be exposed at a custom path which will only be accessible inside the user's single-user notebook. +The path can be customised by setting: +```python +# If set, exposes the user's access token(s) at this relative path +c.TokenExchangeAuthenticator.local_user_exposed_path = '/my-custom-path/userinfo' +``` + +## Running tests +To run the tests locally: + +``` +$ pip install --upgrade --pre -r test-requirements.txt +``` + +``` +$ pytest -v ./tokenexchangeauthenticator/tests/ +``` +Or you run a specific test file with: + +``` +$ pytest -v ./tokenexchangeauthenticator/tests/<test-file-name> +``` + + + + +%prep +%autosetup -n TokenExchangeAuthenticator-0.3.4 + +%build +%py3_build + +%install +%py3_install +install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir} +if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +pushd %{buildroot} +if [ -d usr/lib ]; then + find usr/lib -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then + find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +if [ -d usr/bin ]; then + find usr/bin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then + find usr/sbin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +touch doclist.lst +if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then + find usr/share/man -type f -printf "/%h/%f.gz\n" >> doclist.lst +fi +popd +mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst . +mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst . + +%files -n python3-TokenExchangeAuthenticator -f filelist.lst +%dir %{python3_sitelib}/* + +%files help -f doclist.lst +%{_docdir}/* + +%changelog +* Mon May 29 2023 Python_Bot <Python_Bot@openeuler.org> - 0.3.4-1 +- Package Spec generated |
