diff options
| -rw-r--r-- | .gitignore | 1 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | python-tsmoothie.spec | 576 | ||||
| -rw-r--r-- | sources | 1 |
3 files changed, 578 insertions, 0 deletions
@@ -0,0 +1 @@ +/tsmoothie-1.0.4.tar.gz diff --git a/python-tsmoothie.spec b/python-tsmoothie.spec new file mode 100644 index 0000000..6528bf8 --- /dev/null +++ b/python-tsmoothie.spec @@ -0,0 +1,576 @@ +%global _empty_manifest_terminate_build 0 +Name: python-tsmoothie +Version: 1.0.4 +Release: 1 +Summary: A python library for timeseries smoothing and outlier detection in a vectorized way. +License: MIT +URL: https://github.com/cerlymarco/tsmoothie +Source0: https://mirrors.nju.edu.cn/pypi/web/packages/c2/e9/1e7e4df17b1b6d79bfb6f53dfe69866b99179973f0a325348c43c8159fb2/tsmoothie-1.0.4.tar.gz +BuildArch: noarch + +Requires: python3-numpy +Requires: python3-scipy +Requires: python3-simdkalman + +%description +# tsmoothie + +A python library for time-series smoothing and outlier detection in a vectorized way. + +## Overview + +tsmoothie computes, in a fast and efficient way, the smoothing of single or multiple time-series. + +The smoothing techniques available are: + +- Exponential Smoothing +- Convolutional Smoothing with various window types (constant, hanning, hamming, bartlett, blackman) +- Spectral Smoothing with Fourier Transform +- Polynomial Smoothing +- Spline Smoothing of various kind (linear, cubic, natural cubic) +- Gaussian Smoothing +- Binner Smoothing +- LOWESS +- Seasonal Decompose Smoothing of various kind (convolution, lowess, natural cubic spline) +- Kalman Smoothing with customizable components (level, trend, seasonality, long seasonality) + +tsmoothie provides the calculation of intervals as result of the smoothing process. This can be useful to identify outliers and anomalies in time-series. + +In relation to the smoothing method used, the interval types available are: + +- sigma intervals +- confidence intervals +- predictions intervals +- kalman intervals + +tsmoothie can carry out a sliding smoothing approach to simulate an online usage. This is possible splitting the time-series into equal sized pieces and smoothing them independently. As always, this functionality is implemented in a vectorized way through the **WindowWrapper** class. + +tsmoothie can operate time-series bootstrap through the **BootstrappingWrapper** class. + +The supported bootstrap algorithms are: + +- none overlapping block bootstrap +- moving block bootstrap +- circular block bootstrap +- stationary bootstrap + +## Media + +Blog Posts: + +- [Time Series Smoothing for better Clustering](https://towardsdatascience.com/time-series-smoothing-for-better-clustering-121b98f308e8) +- [Time Series Smoothing for better Forecasting](https://towardsdatascience.com/time-series-smoothing-for-better-forecasting-7fbf10428b2) +- [Real-Time Time Series Anomaly Detection](https://towardsdatascience.com/real-time-time-series-anomaly-detection-981cf1e1ca13) +- [Extreme Event Time Series Preprocessing](https://towardsdatascience.com/extreme-event-time-series-preprocessing-90aa59d5630c) +- [Time Series Bootstrap in the age of Deep Learning](https://towardsdatascience.com/time-series-bootstrap-in-the-age-of-deep-learning-b98aa2aa32c4) + +## Installation + +```shell +pip install tsmoothie +``` + +The module depends only on NumPy, SciPy and simdkalman. Python 3.6 or above is supported. + +## Usage: _smoothing_ + +Below a couple of examples of how tsmoothie works. Full examples are available in the [notebooks folder](https://github.com/cerlymarco/tsmoothie/tree/master/notebooks). + +```python +# import libraries +import numpy as np +import matplotlib.pyplot as plt +from tsmoothie.utils_func import sim_randomwalk +from tsmoothie.smoother import LowessSmoother + +# generate 3 randomwalks of lenght 200 +np.random.seed(123) +data = sim_randomwalk(n_series=3, timesteps=200, + process_noise=10, measure_noise=30) + +# operate smoothing +smoother = LowessSmoother(smooth_fraction=0.1, iterations=1) +smoother.smooth(data) + +# generate intervals +low, up = smoother.get_intervals('prediction_interval') + +# plot the smoothed timeseries with intervals +plt.figure(figsize=(18,5)) + +for i in range(3): + + plt.subplot(1,3,i+1) + plt.plot(smoother.smooth_data[i], linewidth=3, color='blue') + plt.plot(smoother.data[i], '.k') + plt.title(f"timeseries {i+1}"); plt.xlabel('time') + + plt.fill_between(range(len(smoother.data[i])), low[i], up[i], alpha=0.3) +``` + +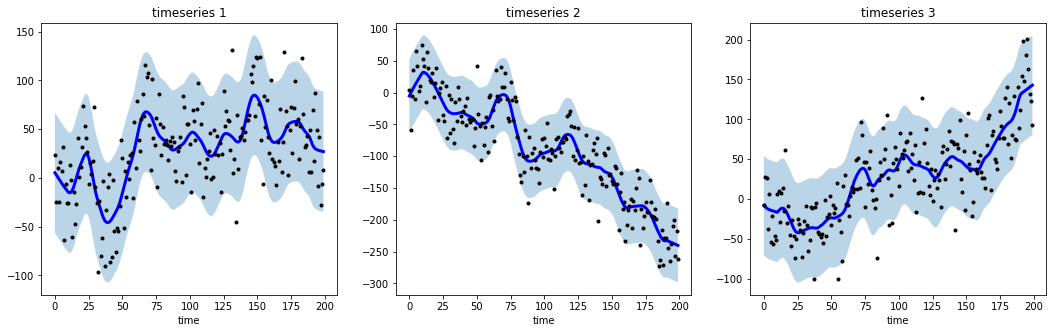 + +```python +# import libraries +import numpy as np +import matplotlib.pyplot as plt +from tsmoothie.utils_func import sim_seasonal_data +from tsmoothie.smoother import DecomposeSmoother + +# generate 3 periodic timeseries of lenght 300 +np.random.seed(123) +data = sim_seasonal_data(n_series=3, timesteps=300, + freq=24, measure_noise=30) + +# operate smoothing +smoother = DecomposeSmoother(smooth_type='lowess', periods=24, + smooth_fraction=0.3) +smoother.smooth(data) + +# generate intervals +low, up = smoother.get_intervals('sigma_interval') + +# plot the smoothed timeseries with intervals +plt.figure(figsize=(18,5)) + +for i in range(3): + + plt.subplot(1,3,i+1) + plt.plot(smoother.smooth_data[i], linewidth=3, color='blue') + plt.plot(smoother.data[i], '.k') + plt.title(f"timeseries {i+1}"); plt.xlabel('time') + + plt.fill_between(range(len(smoother.data[i])), low[i], up[i], alpha=0.3) +``` + +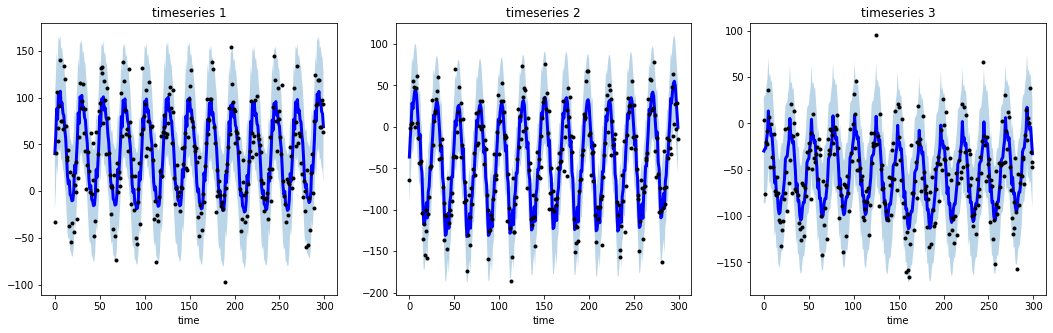 + +## Usage: _bootstrap_ + +```python +# import libraries +import numpy as np +import matplotlib.pyplot as plt +from tsmoothie.utils_func import sim_seasonal_data +from tsmoothie.smoother import ConvolutionSmoother +from tsmoothie.bootstrap import BootstrappingWrapper + +# generate a periodic timeseries of lenght 300 +np.random.seed(123) +data = sim_seasonal_data(n_series=1, timesteps=300, + freq=24, measure_noise=15) + +# operate bootstrap +bts = BootstrappingWrapper(ConvolutionSmoother(window_len=8, window_type='ones'), + bootstrap_type='mbb', block_length=24) +bts_samples = bts.sample(data, n_samples=100) + +# plot the bootstrapped timeseries +plt.figure(figsize=(13,5)) +plt.plot(bts_samples.T, alpha=0.3, c='orange') +plt.plot(data[0], c='blue', linewidth=2) +``` + +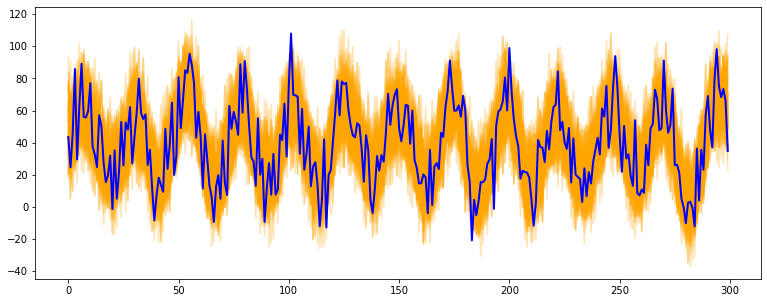 + +## References + +- Polynomial, Spline, Gaussian and Binner smoothing are carried out building a regression on custom basis expansions. These implementations are based on the amazing intuitions of Matthew Drury available [here](https://github.com/madrury/basis-expansions/blob/master/examples/comparison-of-smoothing-methods.ipynb) +- Time Series Modelling with Unobserved Components, Matteo M. Pelagatti +- Bootstrap Methods in Time Series Analysis, Fanny Bergström, Stockholms universitet + + + + +%package -n python3-tsmoothie +Summary: A python library for timeseries smoothing and outlier detection in a vectorized way. +Provides: python-tsmoothie +BuildRequires: python3-devel +BuildRequires: python3-setuptools +BuildRequires: python3-pip +%description -n python3-tsmoothie +# tsmoothie + +A python library for time-series smoothing and outlier detection in a vectorized way. + +## Overview + +tsmoothie computes, in a fast and efficient way, the smoothing of single or multiple time-series. + +The smoothing techniques available are: + +- Exponential Smoothing +- Convolutional Smoothing with various window types (constant, hanning, hamming, bartlett, blackman) +- Spectral Smoothing with Fourier Transform +- Polynomial Smoothing +- Spline Smoothing of various kind (linear, cubic, natural cubic) +- Gaussian Smoothing +- Binner Smoothing +- LOWESS +- Seasonal Decompose Smoothing of various kind (convolution, lowess, natural cubic spline) +- Kalman Smoothing with customizable components (level, trend, seasonality, long seasonality) + +tsmoothie provides the calculation of intervals as result of the smoothing process. This can be useful to identify outliers and anomalies in time-series. + +In relation to the smoothing method used, the interval types available are: + +- sigma intervals +- confidence intervals +- predictions intervals +- kalman intervals + +tsmoothie can carry out a sliding smoothing approach to simulate an online usage. This is possible splitting the time-series into equal sized pieces and smoothing them independently. As always, this functionality is implemented in a vectorized way through the **WindowWrapper** class. + +tsmoothie can operate time-series bootstrap through the **BootstrappingWrapper** class. + +The supported bootstrap algorithms are: + +- none overlapping block bootstrap +- moving block bootstrap +- circular block bootstrap +- stationary bootstrap + +## Media + +Blog Posts: + +- [Time Series Smoothing for better Clustering](https://towardsdatascience.com/time-series-smoothing-for-better-clustering-121b98f308e8) +- [Time Series Smoothing for better Forecasting](https://towardsdatascience.com/time-series-smoothing-for-better-forecasting-7fbf10428b2) +- [Real-Time Time Series Anomaly Detection](https://towardsdatascience.com/real-time-time-series-anomaly-detection-981cf1e1ca13) +- [Extreme Event Time Series Preprocessing](https://towardsdatascience.com/extreme-event-time-series-preprocessing-90aa59d5630c) +- [Time Series Bootstrap in the age of Deep Learning](https://towardsdatascience.com/time-series-bootstrap-in-the-age-of-deep-learning-b98aa2aa32c4) + +## Installation + +```shell +pip install tsmoothie +``` + +The module depends only on NumPy, SciPy and simdkalman. Python 3.6 or above is supported. + +## Usage: _smoothing_ + +Below a couple of examples of how tsmoothie works. Full examples are available in the [notebooks folder](https://github.com/cerlymarco/tsmoothie/tree/master/notebooks). + +```python +# import libraries +import numpy as np +import matplotlib.pyplot as plt +from tsmoothie.utils_func import sim_randomwalk +from tsmoothie.smoother import LowessSmoother + +# generate 3 randomwalks of lenght 200 +np.random.seed(123) +data = sim_randomwalk(n_series=3, timesteps=200, + process_noise=10, measure_noise=30) + +# operate smoothing +smoother = LowessSmoother(smooth_fraction=0.1, iterations=1) +smoother.smooth(data) + +# generate intervals +low, up = smoother.get_intervals('prediction_interval') + +# plot the smoothed timeseries with intervals +plt.figure(figsize=(18,5)) + +for i in range(3): + + plt.subplot(1,3,i+1) + plt.plot(smoother.smooth_data[i], linewidth=3, color='blue') + plt.plot(smoother.data[i], '.k') + plt.title(f"timeseries {i+1}"); plt.xlabel('time') + + plt.fill_between(range(len(smoother.data[i])), low[i], up[i], alpha=0.3) +``` + + + +```python +# import libraries +import numpy as np +import matplotlib.pyplot as plt +from tsmoothie.utils_func import sim_seasonal_data +from tsmoothie.smoother import DecomposeSmoother + +# generate 3 periodic timeseries of lenght 300 +np.random.seed(123) +data = sim_seasonal_data(n_series=3, timesteps=300, + freq=24, measure_noise=30) + +# operate smoothing +smoother = DecomposeSmoother(smooth_type='lowess', periods=24, + smooth_fraction=0.3) +smoother.smooth(data) + +# generate intervals +low, up = smoother.get_intervals('sigma_interval') + +# plot the smoothed timeseries with intervals +plt.figure(figsize=(18,5)) + +for i in range(3): + + plt.subplot(1,3,i+1) + plt.plot(smoother.smooth_data[i], linewidth=3, color='blue') + plt.plot(smoother.data[i], '.k') + plt.title(f"timeseries {i+1}"); plt.xlabel('time') + + plt.fill_between(range(len(smoother.data[i])), low[i], up[i], alpha=0.3) +``` + + + +## Usage: _bootstrap_ + +```python +# import libraries +import numpy as np +import matplotlib.pyplot as plt +from tsmoothie.utils_func import sim_seasonal_data +from tsmoothie.smoother import ConvolutionSmoother +from tsmoothie.bootstrap import BootstrappingWrapper + +# generate a periodic timeseries of lenght 300 +np.random.seed(123) +data = sim_seasonal_data(n_series=1, timesteps=300, + freq=24, measure_noise=15) + +# operate bootstrap +bts = BootstrappingWrapper(ConvolutionSmoother(window_len=8, window_type='ones'), + bootstrap_type='mbb', block_length=24) +bts_samples = bts.sample(data, n_samples=100) + +# plot the bootstrapped timeseries +plt.figure(figsize=(13,5)) +plt.plot(bts_samples.T, alpha=0.3, c='orange') +plt.plot(data[0], c='blue', linewidth=2) +``` + + + +## References + +- Polynomial, Spline, Gaussian and Binner smoothing are carried out building a regression on custom basis expansions. These implementations are based on the amazing intuitions of Matthew Drury available [here](https://github.com/madrury/basis-expansions/blob/master/examples/comparison-of-smoothing-methods.ipynb) +- Time Series Modelling with Unobserved Components, Matteo M. Pelagatti +- Bootstrap Methods in Time Series Analysis, Fanny Bergström, Stockholms universitet + + + + +%package help +Summary: Development documents and examples for tsmoothie +Provides: python3-tsmoothie-doc +%description help +# tsmoothie + +A python library for time-series smoothing and outlier detection in a vectorized way. + +## Overview + +tsmoothie computes, in a fast and efficient way, the smoothing of single or multiple time-series. + +The smoothing techniques available are: + +- Exponential Smoothing +- Convolutional Smoothing with various window types (constant, hanning, hamming, bartlett, blackman) +- Spectral Smoothing with Fourier Transform +- Polynomial Smoothing +- Spline Smoothing of various kind (linear, cubic, natural cubic) +- Gaussian Smoothing +- Binner Smoothing +- LOWESS +- Seasonal Decompose Smoothing of various kind (convolution, lowess, natural cubic spline) +- Kalman Smoothing with customizable components (level, trend, seasonality, long seasonality) + +tsmoothie provides the calculation of intervals as result of the smoothing process. This can be useful to identify outliers and anomalies in time-series. + +In relation to the smoothing method used, the interval types available are: + +- sigma intervals +- confidence intervals +- predictions intervals +- kalman intervals + +tsmoothie can carry out a sliding smoothing approach to simulate an online usage. This is possible splitting the time-series into equal sized pieces and smoothing them independently. As always, this functionality is implemented in a vectorized way through the **WindowWrapper** class. + +tsmoothie can operate time-series bootstrap through the **BootstrappingWrapper** class. + +The supported bootstrap algorithms are: + +- none overlapping block bootstrap +- moving block bootstrap +- circular block bootstrap +- stationary bootstrap + +## Media + +Blog Posts: + +- [Time Series Smoothing for better Clustering](https://towardsdatascience.com/time-series-smoothing-for-better-clustering-121b98f308e8) +- [Time Series Smoothing for better Forecasting](https://towardsdatascience.com/time-series-smoothing-for-better-forecasting-7fbf10428b2) +- [Real-Time Time Series Anomaly Detection](https://towardsdatascience.com/real-time-time-series-anomaly-detection-981cf1e1ca13) +- [Extreme Event Time Series Preprocessing](https://towardsdatascience.com/extreme-event-time-series-preprocessing-90aa59d5630c) +- [Time Series Bootstrap in the age of Deep Learning](https://towardsdatascience.com/time-series-bootstrap-in-the-age-of-deep-learning-b98aa2aa32c4) + +## Installation + +```shell +pip install tsmoothie +``` + +The module depends only on NumPy, SciPy and simdkalman. Python 3.6 or above is supported. + +## Usage: _smoothing_ + +Below a couple of examples of how tsmoothie works. Full examples are available in the [notebooks folder](https://github.com/cerlymarco/tsmoothie/tree/master/notebooks). + +```python +# import libraries +import numpy as np +import matplotlib.pyplot as plt +from tsmoothie.utils_func import sim_randomwalk +from tsmoothie.smoother import LowessSmoother + +# generate 3 randomwalks of lenght 200 +np.random.seed(123) +data = sim_randomwalk(n_series=3, timesteps=200, + process_noise=10, measure_noise=30) + +# operate smoothing +smoother = LowessSmoother(smooth_fraction=0.1, iterations=1) +smoother.smooth(data) + +# generate intervals +low, up = smoother.get_intervals('prediction_interval') + +# plot the smoothed timeseries with intervals +plt.figure(figsize=(18,5)) + +for i in range(3): + + plt.subplot(1,3,i+1) + plt.plot(smoother.smooth_data[i], linewidth=3, color='blue') + plt.plot(smoother.data[i], '.k') + plt.title(f"timeseries {i+1}"); plt.xlabel('time') + + plt.fill_between(range(len(smoother.data[i])), low[i], up[i], alpha=0.3) +``` + + + +```python +# import libraries +import numpy as np +import matplotlib.pyplot as plt +from tsmoothie.utils_func import sim_seasonal_data +from tsmoothie.smoother import DecomposeSmoother + +# generate 3 periodic timeseries of lenght 300 +np.random.seed(123) +data = sim_seasonal_data(n_series=3, timesteps=300, + freq=24, measure_noise=30) + +# operate smoothing +smoother = DecomposeSmoother(smooth_type='lowess', periods=24, + smooth_fraction=0.3) +smoother.smooth(data) + +# generate intervals +low, up = smoother.get_intervals('sigma_interval') + +# plot the smoothed timeseries with intervals +plt.figure(figsize=(18,5)) + +for i in range(3): + + plt.subplot(1,3,i+1) + plt.plot(smoother.smooth_data[i], linewidth=3, color='blue') + plt.plot(smoother.data[i], '.k') + plt.title(f"timeseries {i+1}"); plt.xlabel('time') + + plt.fill_between(range(len(smoother.data[i])), low[i], up[i], alpha=0.3) +``` + + + +## Usage: _bootstrap_ + +```python +# import libraries +import numpy as np +import matplotlib.pyplot as plt +from tsmoothie.utils_func import sim_seasonal_data +from tsmoothie.smoother import ConvolutionSmoother +from tsmoothie.bootstrap import BootstrappingWrapper + +# generate a periodic timeseries of lenght 300 +np.random.seed(123) +data = sim_seasonal_data(n_series=1, timesteps=300, + freq=24, measure_noise=15) + +# operate bootstrap +bts = BootstrappingWrapper(ConvolutionSmoother(window_len=8, window_type='ones'), + bootstrap_type='mbb', block_length=24) +bts_samples = bts.sample(data, n_samples=100) + +# plot the bootstrapped timeseries +plt.figure(figsize=(13,5)) +plt.plot(bts_samples.T, alpha=0.3, c='orange') +plt.plot(data[0], c='blue', linewidth=2) +``` + + + +## References + +- Polynomial, Spline, Gaussian and Binner smoothing are carried out building a regression on custom basis expansions. These implementations are based on the amazing intuitions of Matthew Drury available [here](https://github.com/madrury/basis-expansions/blob/master/examples/comparison-of-smoothing-methods.ipynb) +- Time Series Modelling with Unobserved Components, Matteo M. Pelagatti +- Bootstrap Methods in Time Series Analysis, Fanny Bergström, Stockholms universitet + + + + +%prep +%autosetup -n tsmoothie-1.0.4 + +%build +%py3_build + +%install +%py3_install +install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir} +if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi +pushd %{buildroot} +if [ -d usr/lib ]; then + find usr/lib -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then + find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +if [ -d usr/bin ]; then + find usr/bin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then + find usr/sbin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst +fi +touch doclist.lst +if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then + find usr/share/man -type f -printf "/%h/%f.gz\n" >> doclist.lst +fi +popd +mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst . +mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst . + +%files -n python3-tsmoothie -f filelist.lst +%dir %{python3_sitelib}/* + +%files help -f doclist.lst +%{_docdir}/* + +%changelog +* Tue Apr 11 2023 Python_Bot <Python_Bot@openeuler.org> - 1.0.4-1 +- Package Spec generated @@ -0,0 +1 @@ +b199562daadefaaba94412ad24a1b22b tsmoothie-1.0.4.tar.gz |
