%global _empty_manifest_terminate_build 0
Name: python-perfplot
Version: 0.10.2
Release: 1
Summary: Performance plots for Python code snippets
License: GNU General Public License v3 or later (GPLv3+)
URL: https://pypi.org/project/perfplot/
Source0: https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/web/packages/97/41/51d8b9caa150a050de16a229f627e4b37515dbff0075259e4e75aff7218b/perfplot-0.10.2.tar.gz
BuildArch: noarch
Requires: python3-matplotlib
Requires: python3-matplotx
Requires: python3-numpy
Requires: python3-rich
Requires: python3-typing_extensions
%description

[](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot)
[](https://pypi.org/pypi/perfplot/)
[](https://github.com/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://pepy.tech/project/perfplot)
[](https://discord.gg/hnTJ5MRX2Y)
[](https://github.com/nschloe/perfplot/actions?query=workflow%3Aci)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://lgtm.com/projects/g/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)
perfplot extends Python's [timeit](https://docs.python.org/3/library/timeit.html) by
testing snippets with input parameters (e.g., the size of an array) and plotting the
results.
For example, to compare different NumPy array concatenation methods, the script
```python
import numpy as np
import perfplot
perfplot.show(
setup=lambda n: np.random.rand(n), # or setup=np.random.rand
kernels=[
lambda a: np.c_[a, a],
lambda a: np.stack([a, a]).T,
lambda a: np.vstack([a, a]).T,
lambda a: np.column_stack([a, a]),
lambda a: np.concatenate([a[:, None], a[:, None]], axis=1),
],
labels=["c_", "stack", "vstack", "column_stack", "concat"],
n_range=[2**k for k in range(25)],
xlabel="len(a)",
# More optional arguments with their default values:
# logx="auto", # set to True or False to force scaling
# logy="auto",
# equality_check=np.allclose, # set to None to disable "correctness" assertion
# show_progress=True,
# target_time_per_measurement=1.0,
# max_time=None, # maximum time per measurement
# time_unit="s", # set to one of ("auto", "s", "ms", "us", or "ns") to force plot units
# relative_to=1, # plot the timings relative to one of the measurements
# flops=lambda n: 3*n, # FLOPS plots
)
```
produces
|  |  |
| -------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------- |
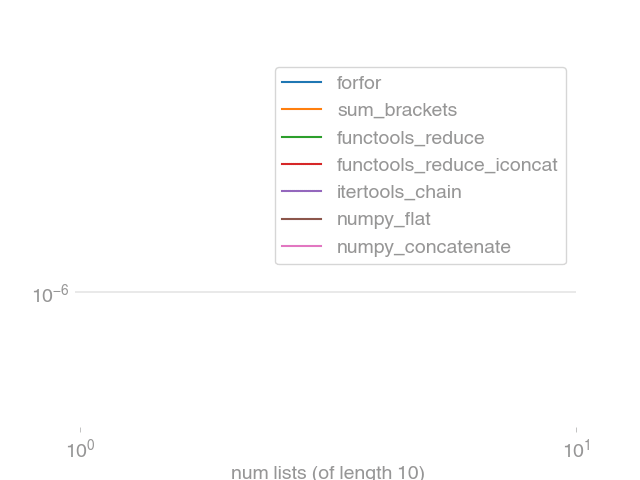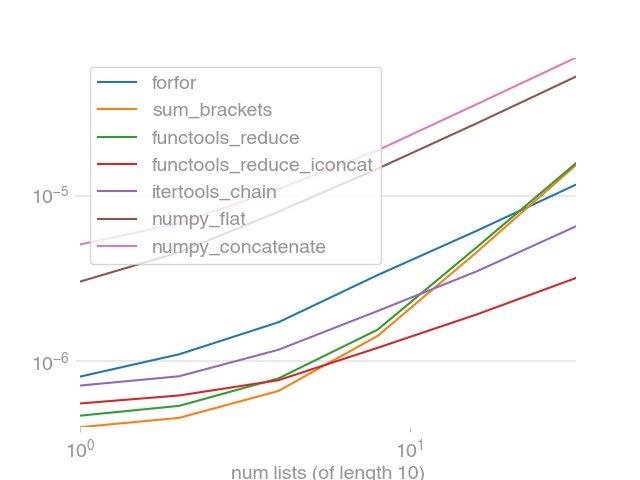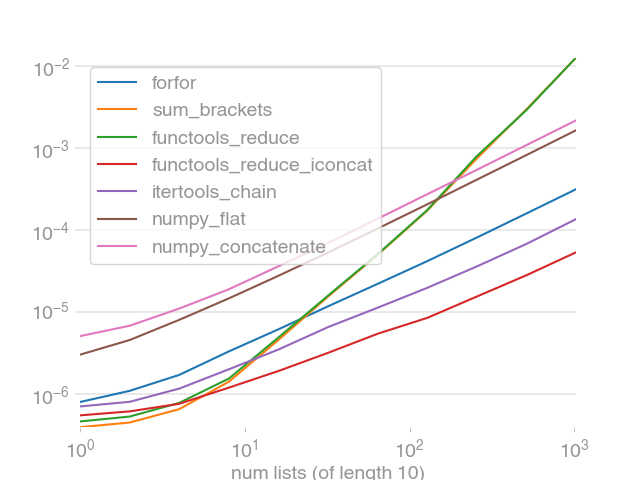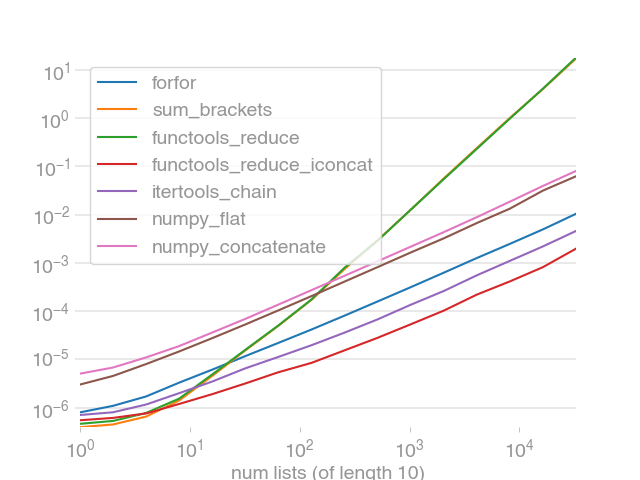
Clearly, `stack` and `vstack` are the best options for large arrays.
(By default, perfplot asserts the equality of the output of all snippets, too.)
If your plot takes a while to generate, you can also use
```python
perfplot.live(
# ...
)
```
 with the same arguments as above. It will plot the updates live.
Benchmarking and plotting can be separated. This allows multiple plots of the same data,
for example:
```python
out = perfplot.bench(
# same arguments as above (except the plot-related ones, like time_unit or log*)
)
out.show()
out.save("perf.png", transparent=True, bbox_inches="tight")
```
Other examples:
- [Making a flat list out of list of lists in Python](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45323085/353337)
- [Most efficient way to map function over numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/46470401/353337)
- [numpy: most efficient frequency counts for unique values in an array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/43096495/353337)
- [Most efficient way to reverse a numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/44921013/353337)
- [How to add an extra column to an numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/40218298/353337)
- [Initializing numpy matrix to something other than zero or one](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45006691/353337)
### Installation
perfplot is [available from the Python Package
Index](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot/), so simply do
```
pip install perfplot
```
to install.
### Testing
To run the perfplot unit tests, check out this repository and type
```
tox
```
### License
This software is published under the [GPLv3 license](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.en.html).
%package -n python3-perfplot
Summary: Performance plots for Python code snippets
Provides: python-perfplot
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3-setuptools
BuildRequires: python3-pip
%description -n python3-perfplot
with the same arguments as above. It will plot the updates live.
Benchmarking and plotting can be separated. This allows multiple plots of the same data,
for example:
```python
out = perfplot.bench(
# same arguments as above (except the plot-related ones, like time_unit or log*)
)
out.show()
out.save("perf.png", transparent=True, bbox_inches="tight")
```
Other examples:
- [Making a flat list out of list of lists in Python](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45323085/353337)
- [Most efficient way to map function over numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/46470401/353337)
- [numpy: most efficient frequency counts for unique values in an array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/43096495/353337)
- [Most efficient way to reverse a numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/44921013/353337)
- [How to add an extra column to an numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/40218298/353337)
- [Initializing numpy matrix to something other than zero or one](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45006691/353337)
### Installation
perfplot is [available from the Python Package
Index](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot/), so simply do
```
pip install perfplot
```
to install.
### Testing
To run the perfplot unit tests, check out this repository and type
```
tox
```
### License
This software is published under the [GPLv3 license](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.en.html).
%package -n python3-perfplot
Summary: Performance plots for Python code snippets
Provides: python-perfplot
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3-setuptools
BuildRequires: python3-pip
%description -n python3-perfplot

[](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot)
[](https://pypi.org/pypi/perfplot/)
[](https://github.com/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://pepy.tech/project/perfplot)
[](https://discord.gg/hnTJ5MRX2Y)
[](https://github.com/nschloe/perfplot/actions?query=workflow%3Aci)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://lgtm.com/projects/g/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)
perfplot extends Python's [timeit](https://docs.python.org/3/library/timeit.html) by
testing snippets with input parameters (e.g., the size of an array) and plotting the
results.
For example, to compare different NumPy array concatenation methods, the script
```python
import numpy as np
import perfplot
perfplot.show(
setup=lambda n: np.random.rand(n), # or setup=np.random.rand
kernels=[
lambda a: np.c_[a, a],
lambda a: np.stack([a, a]).T,
lambda a: np.vstack([a, a]).T,
lambda a: np.column_stack([a, a]),
lambda a: np.concatenate([a[:, None], a[:, None]], axis=1),
],
labels=["c_", "stack", "vstack", "column_stack", "concat"],
n_range=[2**k for k in range(25)],
xlabel="len(a)",
# More optional arguments with their default values:
# logx="auto", # set to True or False to force scaling
# logy="auto",
# equality_check=np.allclose, # set to None to disable "correctness" assertion
# show_progress=True,
# target_time_per_measurement=1.0,
# max_time=None, # maximum time per measurement
# time_unit="s", # set to one of ("auto", "s", "ms", "us", or "ns") to force plot units
# relative_to=1, # plot the timings relative to one of the measurements
# flops=lambda n: 3*n, # FLOPS plots
)
```
produces
|  |  |
| -------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------- |
Clearly, `stack` and `vstack` are the best options for large arrays.
(By default, perfplot asserts the equality of the output of all snippets, too.)
If your plot takes a while to generate, you can also use
```python
perfplot.live(
# ...
)
```
 with the same arguments as above. It will plot the updates live.
Benchmarking and plotting can be separated. This allows multiple plots of the same data,
for example:
```python
out = perfplot.bench(
# same arguments as above (except the plot-related ones, like time_unit or log*)
)
out.show()
out.save("perf.png", transparent=True, bbox_inches="tight")
```
Other examples:
- [Making a flat list out of list of lists in Python](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45323085/353337)
- [Most efficient way to map function over numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/46470401/353337)
- [numpy: most efficient frequency counts for unique values in an array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/43096495/353337)
- [Most efficient way to reverse a numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/44921013/353337)
- [How to add an extra column to an numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/40218298/353337)
- [Initializing numpy matrix to something other than zero or one](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45006691/353337)
### Installation
perfplot is [available from the Python Package
Index](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot/), so simply do
```
pip install perfplot
```
to install.
### Testing
To run the perfplot unit tests, check out this repository and type
```
tox
```
### License
This software is published under the [GPLv3 license](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.en.html).
%package help
Summary: Development documents and examples for perfplot
Provides: python3-perfplot-doc
%description help
with the same arguments as above. It will plot the updates live.
Benchmarking and plotting can be separated. This allows multiple plots of the same data,
for example:
```python
out = perfplot.bench(
# same arguments as above (except the plot-related ones, like time_unit or log*)
)
out.show()
out.save("perf.png", transparent=True, bbox_inches="tight")
```
Other examples:
- [Making a flat list out of list of lists in Python](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45323085/353337)
- [Most efficient way to map function over numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/46470401/353337)
- [numpy: most efficient frequency counts for unique values in an array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/43096495/353337)
- [Most efficient way to reverse a numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/44921013/353337)
- [How to add an extra column to an numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/40218298/353337)
- [Initializing numpy matrix to something other than zero or one](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45006691/353337)
### Installation
perfplot is [available from the Python Package
Index](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot/), so simply do
```
pip install perfplot
```
to install.
### Testing
To run the perfplot unit tests, check out this repository and type
```
tox
```
### License
This software is published under the [GPLv3 license](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.en.html).
%package help
Summary: Development documents and examples for perfplot
Provides: python3-perfplot-doc
%description help

[](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot)
[](https://pypi.org/pypi/perfplot/)
[](https://github.com/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://pepy.tech/project/perfplot)
[](https://discord.gg/hnTJ5MRX2Y)
[](https://github.com/nschloe/perfplot/actions?query=workflow%3Aci)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://lgtm.com/projects/g/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)
perfplot extends Python's [timeit](https://docs.python.org/3/library/timeit.html) by
testing snippets with input parameters (e.g., the size of an array) and plotting the
results.
For example, to compare different NumPy array concatenation methods, the script
```python
import numpy as np
import perfplot
perfplot.show(
setup=lambda n: np.random.rand(n), # or setup=np.random.rand
kernels=[
lambda a: np.c_[a, a],
lambda a: np.stack([a, a]).T,
lambda a: np.vstack([a, a]).T,
lambda a: np.column_stack([a, a]),
lambda a: np.concatenate([a[:, None], a[:, None]], axis=1),
],
labels=["c_", "stack", "vstack", "column_stack", "concat"],
n_range=[2**k for k in range(25)],
xlabel="len(a)",
# More optional arguments with their default values:
# logx="auto", # set to True or False to force scaling
# logy="auto",
# equality_check=np.allclose, # set to None to disable "correctness" assertion
# show_progress=True,
# target_time_per_measurement=1.0,
# max_time=None, # maximum time per measurement
# time_unit="s", # set to one of ("auto", "s", "ms", "us", or "ns") to force plot units
# relative_to=1, # plot the timings relative to one of the measurements
# flops=lambda n: 3*n, # FLOPS plots
)
```
produces
|  |  |
| -------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------- |
Clearly, `stack` and `vstack` are the best options for large arrays.
(By default, perfplot asserts the equality of the output of all snippets, too.)
If your plot takes a while to generate, you can also use
```python
perfplot.live(
# ...
)
```
 with the same arguments as above. It will plot the updates live.
Benchmarking and plotting can be separated. This allows multiple plots of the same data,
for example:
```python
out = perfplot.bench(
# same arguments as above (except the plot-related ones, like time_unit or log*)
)
out.show()
out.save("perf.png", transparent=True, bbox_inches="tight")
```
Other examples:
- [Making a flat list out of list of lists in Python](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45323085/353337)
- [Most efficient way to map function over numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/46470401/353337)
- [numpy: most efficient frequency counts for unique values in an array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/43096495/353337)
- [Most efficient way to reverse a numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/44921013/353337)
- [How to add an extra column to an numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/40218298/353337)
- [Initializing numpy matrix to something other than zero or one](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45006691/353337)
### Installation
perfplot is [available from the Python Package
Index](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot/), so simply do
```
pip install perfplot
```
to install.
### Testing
To run the perfplot unit tests, check out this repository and type
```
tox
```
### License
This software is published under the [GPLv3 license](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.en.html).
%prep
%autosetup -n perfplot-0.10.2
%build
%py3_build
%install
%py3_install
install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}
if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
pushd %{buildroot}
if [ -d usr/lib ]; then
find usr/lib -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then
find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/bin ]; then
find usr/bin -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then
find usr/sbin -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
touch doclist.lst
if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then
find usr/share/man -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f.gz\"\n" >> doclist.lst
fi
popd
mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst .
mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst .
%files -n python3-perfplot -f filelist.lst
%dir %{python3_sitelib}/*
%files help -f doclist.lst
%{_docdir}/*
%changelog
* Thu Jun 08 2023 Python_Bot - 0.10.2-1
- Package Spec generated
with the same arguments as above. It will plot the updates live.
Benchmarking and plotting can be separated. This allows multiple plots of the same data,
for example:
```python
out = perfplot.bench(
# same arguments as above (except the plot-related ones, like time_unit or log*)
)
out.show()
out.save("perf.png", transparent=True, bbox_inches="tight")
```
Other examples:
- [Making a flat list out of list of lists in Python](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45323085/353337)
- [Most efficient way to map function over numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/46470401/353337)
- [numpy: most efficient frequency counts for unique values in an array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/43096495/353337)
- [Most efficient way to reverse a numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/44921013/353337)
- [How to add an extra column to an numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/40218298/353337)
- [Initializing numpy matrix to something other than zero or one](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45006691/353337)
### Installation
perfplot is [available from the Python Package
Index](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot/), so simply do
```
pip install perfplot
```
to install.
### Testing
To run the perfplot unit tests, check out this repository and type
```
tox
```
### License
This software is published under the [GPLv3 license](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.en.html).
%prep
%autosetup -n perfplot-0.10.2
%build
%py3_build
%install
%py3_install
install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}
if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
pushd %{buildroot}
if [ -d usr/lib ]; then
find usr/lib -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then
find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/bin ]; then
find usr/bin -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then
find usr/sbin -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
touch doclist.lst
if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then
find usr/share/man -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f.gz\"\n" >> doclist.lst
fi
popd
mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst .
mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst .
%files -n python3-perfplot -f filelist.lst
%dir %{python3_sitelib}/*
%files help -f doclist.lst
%{_docdir}/*
%changelog
* Thu Jun 08 2023 Python_Bot - 0.10.2-1
- Package Spec generated
 with the same arguments as above. It will plot the updates live.
Benchmarking and plotting can be separated. This allows multiple plots of the same data,
for example:
```python
out = perfplot.bench(
# same arguments as above (except the plot-related ones, like time_unit or log*)
)
out.show()
out.save("perf.png", transparent=True, bbox_inches="tight")
```
Other examples:
- [Making a flat list out of list of lists in Python](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45323085/353337)
- [Most efficient way to map function over numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/46470401/353337)
- [numpy: most efficient frequency counts for unique values in an array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/43096495/353337)
- [Most efficient way to reverse a numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/44921013/353337)
- [How to add an extra column to an numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/40218298/353337)
- [Initializing numpy matrix to something other than zero or one](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45006691/353337)
### Installation
perfplot is [available from the Python Package
Index](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot/), so simply do
```
pip install perfplot
```
to install.
### Testing
To run the perfplot unit tests, check out this repository and type
```
tox
```
### License
This software is published under the [GPLv3 license](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.en.html).
%package -n python3-perfplot
Summary: Performance plots for Python code snippets
Provides: python-perfplot
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3-setuptools
BuildRequires: python3-pip
%description -n python3-perfplot
[](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot)
[](https://pypi.org/pypi/perfplot/)
[](https://github.com/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://pepy.tech/project/perfplot)
[](https://discord.gg/hnTJ5MRX2Y)
[](https://github.com/nschloe/perfplot/actions?query=workflow%3Aci)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://lgtm.com/projects/g/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)
perfplot extends Python's [timeit](https://docs.python.org/3/library/timeit.html) by
testing snippets with input parameters (e.g., the size of an array) and plotting the
results.
For example, to compare different NumPy array concatenation methods, the script
```python
import numpy as np
import perfplot
perfplot.show(
setup=lambda n: np.random.rand(n), # or setup=np.random.rand
kernels=[
lambda a: np.c_[a, a],
lambda a: np.stack([a, a]).T,
lambda a: np.vstack([a, a]).T,
lambda a: np.column_stack([a, a]),
lambda a: np.concatenate([a[:, None], a[:, None]], axis=1),
],
labels=["c_", "stack", "vstack", "column_stack", "concat"],
n_range=[2**k for k in range(25)],
xlabel="len(a)",
# More optional arguments with their default values:
# logx="auto", # set to True or False to force scaling
# logy="auto",
# equality_check=np.allclose, # set to None to disable "correctness" assertion
# show_progress=True,
# target_time_per_measurement=1.0,
# max_time=None, # maximum time per measurement
# time_unit="s", # set to one of ("auto", "s", "ms", "us", or "ns") to force plot units
# relative_to=1, # plot the timings relative to one of the measurements
# flops=lambda n: 3*n, # FLOPS plots
)
```
produces
|  |  |
| -------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------- |
Clearly, `stack` and `vstack` are the best options for large arrays.
(By default, perfplot asserts the equality of the output of all snippets, too.)
If your plot takes a while to generate, you can also use
```python
perfplot.live(
# ...
)
```
with the same arguments as above. It will plot the updates live.
Benchmarking and plotting can be separated. This allows multiple plots of the same data,
for example:
```python
out = perfplot.bench(
# same arguments as above (except the plot-related ones, like time_unit or log*)
)
out.show()
out.save("perf.png", transparent=True, bbox_inches="tight")
```
Other examples:
- [Making a flat list out of list of lists in Python](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45323085/353337)
- [Most efficient way to map function over numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/46470401/353337)
- [numpy: most efficient frequency counts for unique values in an array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/43096495/353337)
- [Most efficient way to reverse a numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/44921013/353337)
- [How to add an extra column to an numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/40218298/353337)
- [Initializing numpy matrix to something other than zero or one](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45006691/353337)
### Installation
perfplot is [available from the Python Package
Index](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot/), so simply do
```
pip install perfplot
```
to install.
### Testing
To run the perfplot unit tests, check out this repository and type
```
tox
```
### License
This software is published under the [GPLv3 license](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.en.html).
%package -n python3-perfplot
Summary: Performance plots for Python code snippets
Provides: python-perfplot
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3-setuptools
BuildRequires: python3-pip
%description -n python3-perfplot
[](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot)
[](https://pypi.org/pypi/perfplot/)
[](https://github.com/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://pepy.tech/project/perfplot)
[](https://discord.gg/hnTJ5MRX2Y)
[](https://github.com/nschloe/perfplot/actions?query=workflow%3Aci)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://lgtm.com/projects/g/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)
perfplot extends Python's [timeit](https://docs.python.org/3/library/timeit.html) by
testing snippets with input parameters (e.g., the size of an array) and plotting the
results.
For example, to compare different NumPy array concatenation methods, the script
```python
import numpy as np
import perfplot
perfplot.show(
setup=lambda n: np.random.rand(n), # or setup=np.random.rand
kernels=[
lambda a: np.c_[a, a],
lambda a: np.stack([a, a]).T,
lambda a: np.vstack([a, a]).T,
lambda a: np.column_stack([a, a]),
lambda a: np.concatenate([a[:, None], a[:, None]], axis=1),
],
labels=["c_", "stack", "vstack", "column_stack", "concat"],
n_range=[2**k for k in range(25)],
xlabel="len(a)",
# More optional arguments with their default values:
# logx="auto", # set to True or False to force scaling
# logy="auto",
# equality_check=np.allclose, # set to None to disable "correctness" assertion
# show_progress=True,
# target_time_per_measurement=1.0,
# max_time=None, # maximum time per measurement
# time_unit="s", # set to one of ("auto", "s", "ms", "us", or "ns") to force plot units
# relative_to=1, # plot the timings relative to one of the measurements
# flops=lambda n: 3*n, # FLOPS plots
)
```
produces
|  |  |
| -------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------- |
Clearly, `stack` and `vstack` are the best options for large arrays.
(By default, perfplot asserts the equality of the output of all snippets, too.)
If your plot takes a while to generate, you can also use
```python
perfplot.live(
# ...
)
```
 with the same arguments as above. It will plot the updates live.
Benchmarking and plotting can be separated. This allows multiple plots of the same data,
for example:
```python
out = perfplot.bench(
# same arguments as above (except the plot-related ones, like time_unit or log*)
)
out.show()
out.save("perf.png", transparent=True, bbox_inches="tight")
```
Other examples:
- [Making a flat list out of list of lists in Python](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45323085/353337)
- [Most efficient way to map function over numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/46470401/353337)
- [numpy: most efficient frequency counts for unique values in an array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/43096495/353337)
- [Most efficient way to reverse a numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/44921013/353337)
- [How to add an extra column to an numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/40218298/353337)
- [Initializing numpy matrix to something other than zero or one](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45006691/353337)
### Installation
perfplot is [available from the Python Package
Index](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot/), so simply do
```
pip install perfplot
```
to install.
### Testing
To run the perfplot unit tests, check out this repository and type
```
tox
```
### License
This software is published under the [GPLv3 license](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.en.html).
%package help
Summary: Development documents and examples for perfplot
Provides: python3-perfplot-doc
%description help
[](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot)
[](https://pypi.org/pypi/perfplot/)
[](https://github.com/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://pepy.tech/project/perfplot)
[](https://discord.gg/hnTJ5MRX2Y)
[](https://github.com/nschloe/perfplot/actions?query=workflow%3Aci)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://lgtm.com/projects/g/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)
perfplot extends Python's [timeit](https://docs.python.org/3/library/timeit.html) by
testing snippets with input parameters (e.g., the size of an array) and plotting the
results.
For example, to compare different NumPy array concatenation methods, the script
```python
import numpy as np
import perfplot
perfplot.show(
setup=lambda n: np.random.rand(n), # or setup=np.random.rand
kernels=[
lambda a: np.c_[a, a],
lambda a: np.stack([a, a]).T,
lambda a: np.vstack([a, a]).T,
lambda a: np.column_stack([a, a]),
lambda a: np.concatenate([a[:, None], a[:, None]], axis=1),
],
labels=["c_", "stack", "vstack", "column_stack", "concat"],
n_range=[2**k for k in range(25)],
xlabel="len(a)",
# More optional arguments with their default values:
# logx="auto", # set to True or False to force scaling
# logy="auto",
# equality_check=np.allclose, # set to None to disable "correctness" assertion
# show_progress=True,
# target_time_per_measurement=1.0,
# max_time=None, # maximum time per measurement
# time_unit="s", # set to one of ("auto", "s", "ms", "us", or "ns") to force plot units
# relative_to=1, # plot the timings relative to one of the measurements
# flops=lambda n: 3*n, # FLOPS plots
)
```
produces
|  |  |
| -------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------- |
Clearly, `stack` and `vstack` are the best options for large arrays.
(By default, perfplot asserts the equality of the output of all snippets, too.)
If your plot takes a while to generate, you can also use
```python
perfplot.live(
# ...
)
```
with the same arguments as above. It will plot the updates live.
Benchmarking and plotting can be separated. This allows multiple plots of the same data,
for example:
```python
out = perfplot.bench(
# same arguments as above (except the plot-related ones, like time_unit or log*)
)
out.show()
out.save("perf.png", transparent=True, bbox_inches="tight")
```
Other examples:
- [Making a flat list out of list of lists in Python](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45323085/353337)
- [Most efficient way to map function over numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/46470401/353337)
- [numpy: most efficient frequency counts for unique values in an array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/43096495/353337)
- [Most efficient way to reverse a numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/44921013/353337)
- [How to add an extra column to an numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/40218298/353337)
- [Initializing numpy matrix to something other than zero or one](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45006691/353337)
### Installation
perfplot is [available from the Python Package
Index](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot/), so simply do
```
pip install perfplot
```
to install.
### Testing
To run the perfplot unit tests, check out this repository and type
```
tox
```
### License
This software is published under the [GPLv3 license](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.en.html).
%package help
Summary: Development documents and examples for perfplot
Provides: python3-perfplot-doc
%description help
[](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot)
[](https://pypi.org/pypi/perfplot/)
[](https://github.com/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://pepy.tech/project/perfplot)
[](https://discord.gg/hnTJ5MRX2Y)
[](https://github.com/nschloe/perfplot/actions?query=workflow%3Aci)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://lgtm.com/projects/g/nschloe/perfplot)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)
perfplot extends Python's [timeit](https://docs.python.org/3/library/timeit.html) by
testing snippets with input parameters (e.g., the size of an array) and plotting the
results.
For example, to compare different NumPy array concatenation methods, the script
```python
import numpy as np
import perfplot
perfplot.show(
setup=lambda n: np.random.rand(n), # or setup=np.random.rand
kernels=[
lambda a: np.c_[a, a],
lambda a: np.stack([a, a]).T,
lambda a: np.vstack([a, a]).T,
lambda a: np.column_stack([a, a]),
lambda a: np.concatenate([a[:, None], a[:, None]], axis=1),
],
labels=["c_", "stack", "vstack", "column_stack", "concat"],
n_range=[2**k for k in range(25)],
xlabel="len(a)",
# More optional arguments with their default values:
# logx="auto", # set to True or False to force scaling
# logy="auto",
# equality_check=np.allclose, # set to None to disable "correctness" assertion
# show_progress=True,
# target_time_per_measurement=1.0,
# max_time=None, # maximum time per measurement
# time_unit="s", # set to one of ("auto", "s", "ms", "us", or "ns") to force plot units
# relative_to=1, # plot the timings relative to one of the measurements
# flops=lambda n: 3*n, # FLOPS plots
)
```
produces
|  |  |
| -------------------------------------------------- | ---------------------------------------------------- |
Clearly, `stack` and `vstack` are the best options for large arrays.
(By default, perfplot asserts the equality of the output of all snippets, too.)
If your plot takes a while to generate, you can also use
```python
perfplot.live(
# ...
)
```
 with the same arguments as above. It will plot the updates live.
Benchmarking and plotting can be separated. This allows multiple plots of the same data,
for example:
```python
out = perfplot.bench(
# same arguments as above (except the plot-related ones, like time_unit or log*)
)
out.show()
out.save("perf.png", transparent=True, bbox_inches="tight")
```
Other examples:
- [Making a flat list out of list of lists in Python](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45323085/353337)
- [Most efficient way to map function over numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/46470401/353337)
- [numpy: most efficient frequency counts for unique values in an array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/43096495/353337)
- [Most efficient way to reverse a numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/44921013/353337)
- [How to add an extra column to an numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/40218298/353337)
- [Initializing numpy matrix to something other than zero or one](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45006691/353337)
### Installation
perfplot is [available from the Python Package
Index](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot/), so simply do
```
pip install perfplot
```
to install.
### Testing
To run the perfplot unit tests, check out this repository and type
```
tox
```
### License
This software is published under the [GPLv3 license](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.en.html).
%prep
%autosetup -n perfplot-0.10.2
%build
%py3_build
%install
%py3_install
install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}
if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
pushd %{buildroot}
if [ -d usr/lib ]; then
find usr/lib -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then
find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/bin ]; then
find usr/bin -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then
find usr/sbin -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
touch doclist.lst
if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then
find usr/share/man -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f.gz\"\n" >> doclist.lst
fi
popd
mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst .
mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst .
%files -n python3-perfplot -f filelist.lst
%dir %{python3_sitelib}/*
%files help -f doclist.lst
%{_docdir}/*
%changelog
* Thu Jun 08 2023 Python_Bot
with the same arguments as above. It will plot the updates live.
Benchmarking and plotting can be separated. This allows multiple plots of the same data,
for example:
```python
out = perfplot.bench(
# same arguments as above (except the plot-related ones, like time_unit or log*)
)
out.show()
out.save("perf.png", transparent=True, bbox_inches="tight")
```
Other examples:
- [Making a flat list out of list of lists in Python](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45323085/353337)
- [Most efficient way to map function over numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/46470401/353337)
- [numpy: most efficient frequency counts for unique values in an array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/43096495/353337)
- [Most efficient way to reverse a numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/44921013/353337)
- [How to add an extra column to an numpy array](https://stackoverflow.com/a/40218298/353337)
- [Initializing numpy matrix to something other than zero or one](https://stackoverflow.com/a/45006691/353337)
### Installation
perfplot is [available from the Python Package
Index](https://pypi.org/project/perfplot/), so simply do
```
pip install perfplot
```
to install.
### Testing
To run the perfplot unit tests, check out this repository and type
```
tox
```
### License
This software is published under the [GPLv3 license](https://www.gnu.org/licenses/gpl-3.0.en.html).
%prep
%autosetup -n perfplot-0.10.2
%build
%py3_build
%install
%py3_install
install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}
if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
pushd %{buildroot}
if [ -d usr/lib ]; then
find usr/lib -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then
find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/bin ]; then
find usr/bin -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then
find usr/sbin -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
touch doclist.lst
if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then
find usr/share/man -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f.gz\"\n" >> doclist.lst
fi
popd
mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst .
mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst .
%files -n python3-perfplot -f filelist.lst
%dir %{python3_sitelib}/*
%files help -f doclist.lst
%{_docdir}/*
%changelog
* Thu Jun 08 2023 Python_Bot