%global _empty_manifest_terminate_build 0
Name: python-overboard
Version: 1.0.1
Release: 1
Summary: Pure Python dashboard for monitoring deep learning experiments
License: GNU General Public License v3 (GPLv3)
URL: https://github.com/jotaf98/overboard
Source0: https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/web/packages/63/ff/c19cdc360225b537d4ea3f74685ad646b2f902f8146946b334f7d5245db2/overboard-1.0.1.tar.gz
BuildArch: noarch
Requires: python3-pyqt5
Requires: python3-pyqtgraph
Requires: python3-pyopengl
Requires: python3-fs
Requires: python3-overboard-logger
%description
# OverBoard
OverBoard is a lightweight yet powerful dashboard to monitor your experiments.
Load remote experiments in real-time through SSH/FTP and others.
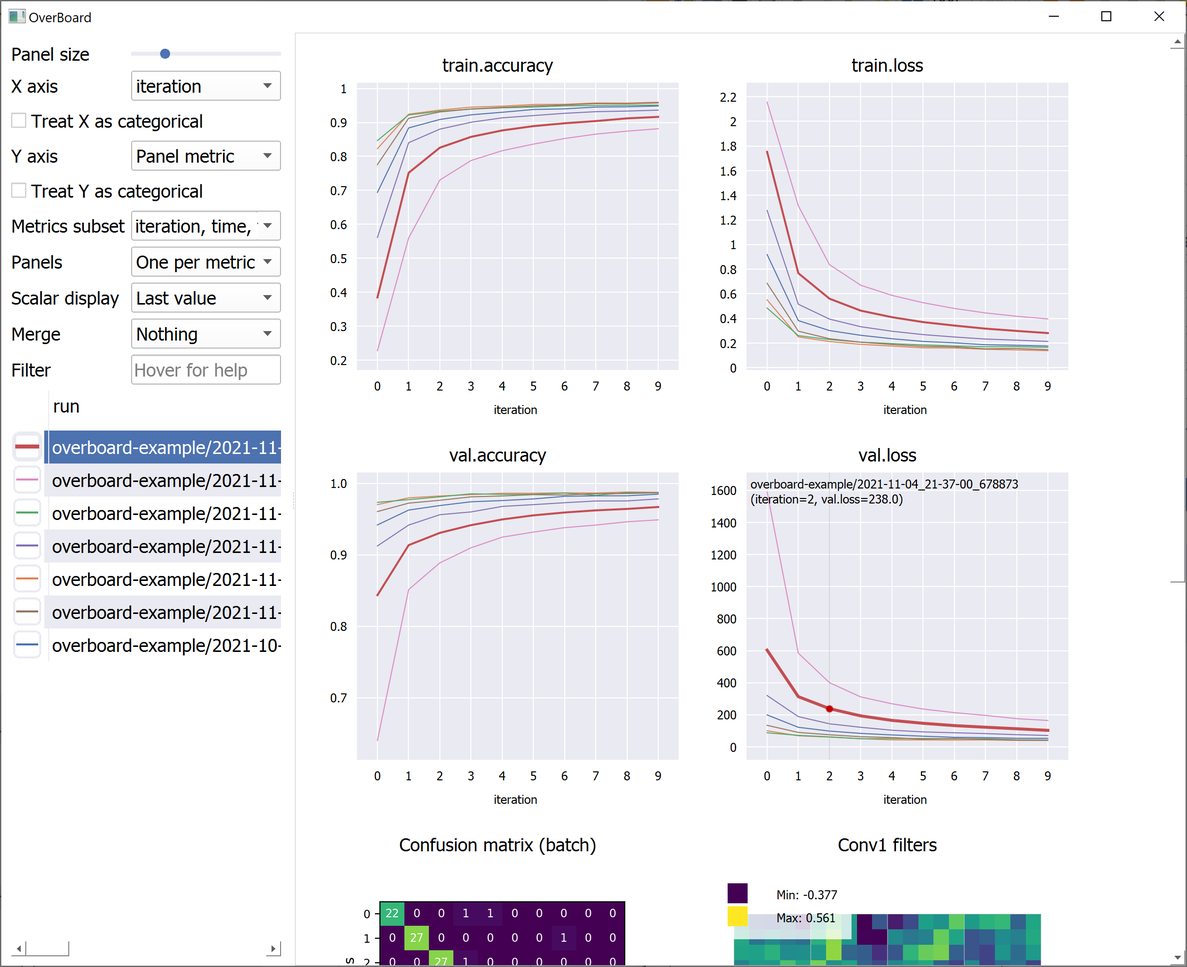
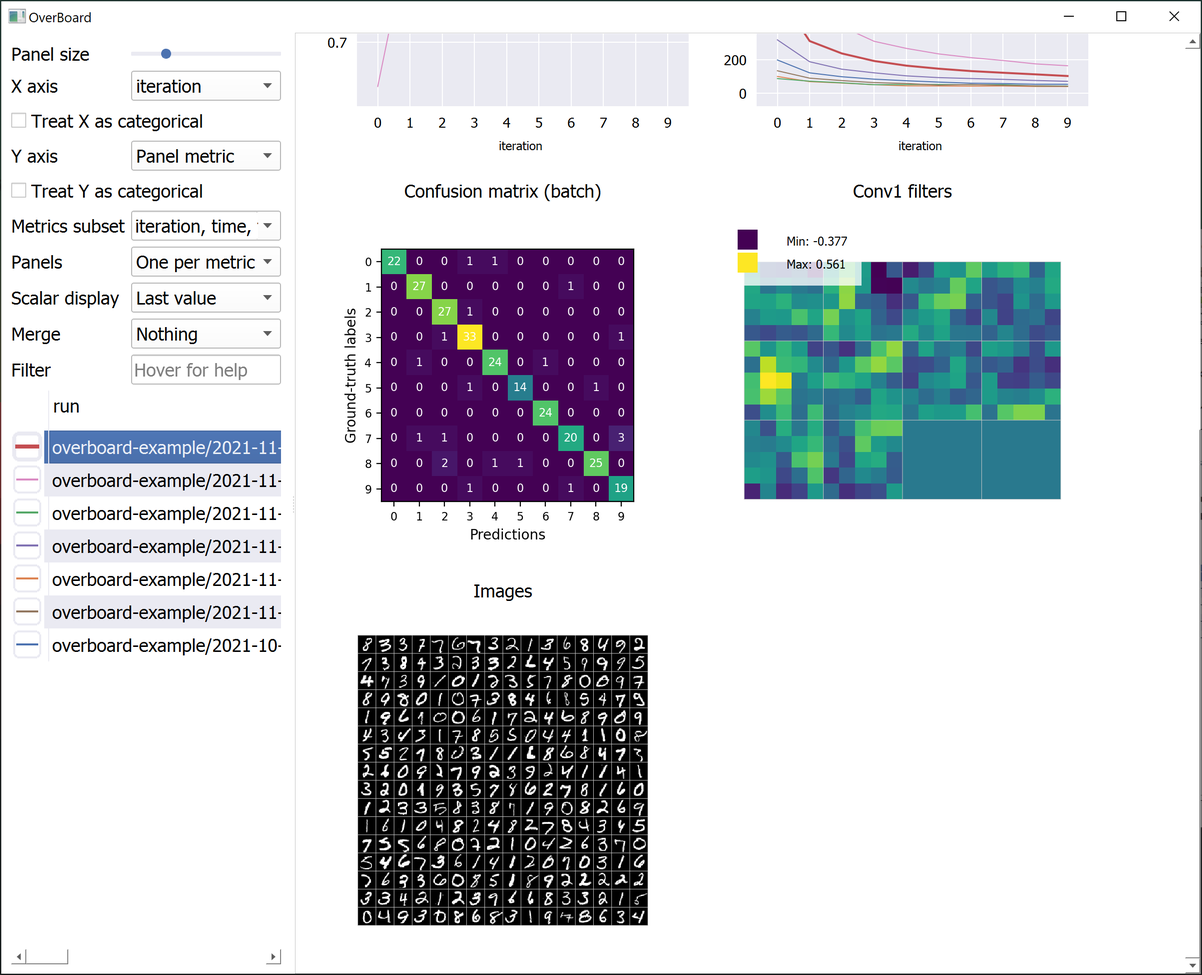
Custom visualisations (tensors and any custom plot with familiar MatPlotLib syntax).
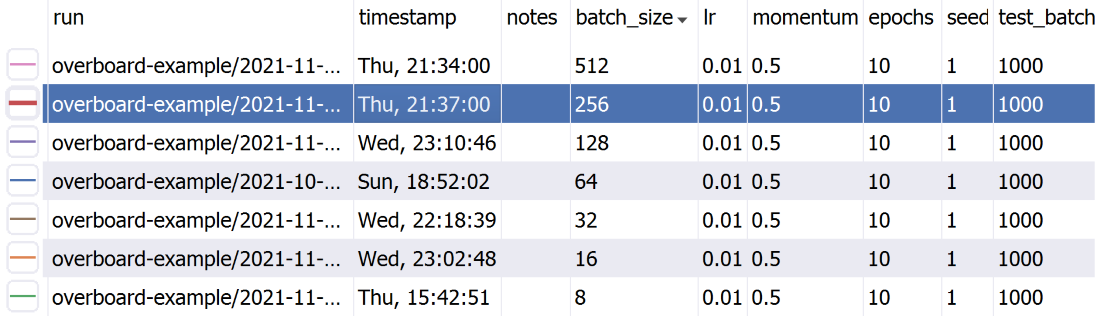
A sortable table of hyper-parameters with Python-syntax filtering.
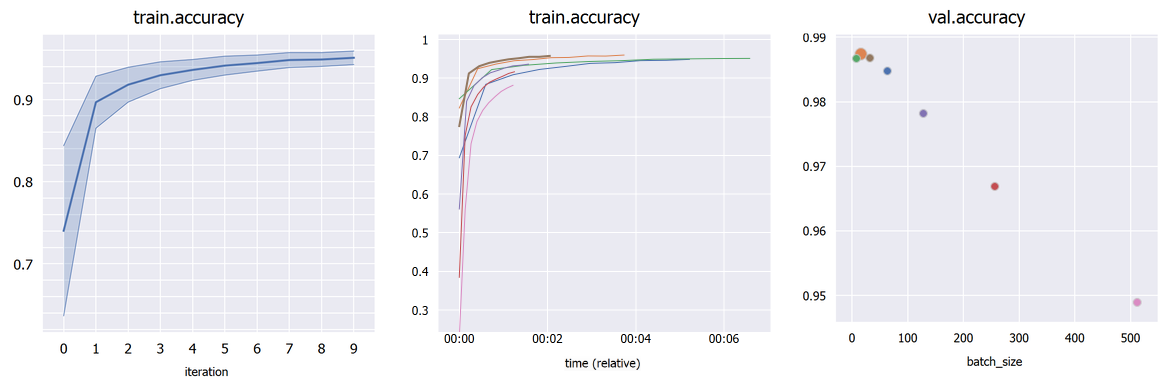
Plot percentile intervals (shaded plots), custom X/Y axes, and hyper-parameters (bubble plots).
# Installation
You can install the dependencies with:
- With Conda: `conda install pyqt=5.12 pyqtgraph=0.11 -c conda-forge`
- With pip: `pip install pyqt5==5.12 pyqtgraph==0.11`
Finally, OverBoard itself can be installed with: `pip install fs==2.4 overboard`
(Conda seems to be too strict when installing [PyFileSystem/fs](https://www.pyfilesystem.org), so pip should be preferred.)
Optional:
- `pip install fs.sshfs` to support remote files through SSH.
- PyOpenGL 3.1 (either through conda or pip) if you intend to use custom 3D plots with [PyQtGraph](https://pyqtgraph.readthedocs.io/en/latest/3dgraphics.html).
- MatPlotLib if you intend to use it for custom plots.
## Installation - logger only
Your scripts can log data without installing the full GUI and its dependencies (so your remote GPU cluster does not need PyQt at all).
Just use: `pip install overboard_logger`
And remember to import `overboard_logger` instead of `overboard` in your scripts.
# Usage
- Main interface: `python3 -m overboard `
- Logging experiments is simple:
```python
from overboard import Logger
with Logger('./logs') as logger:
for iteration in range(100):
logger.append({'loss': 0, 'error': 0})
```
You can also pass in a `meta` keyword argument, which can be a `dict` with hyper-parameters names and values (or other meta-data), to help organize your experiments. These will be displayed in a handy table, which supports sorting and filtering. The `meta` data can also be an `argparse.Namespace`, which is useful if your hyper-parameters are command-line arguments parsed with `argparse`.
By default a unique folder (using the current timestamp) is created for the logs. For full documentation on initialization arguments and other methods, type `pydoc overboard` on the command-line (Python built-in doc viewer).
You can also check the `examples` directory:
- [`examples/basic.py`](examples/basic.py): A minimal example. Generates some test logs.
- [`examples/mnist.py`](examples/mnist.py): The mandatory MNIST example. Also shows a custom MatPlotLib plot (a confusion matrix).
- [`examples/example_2d.py`](examples/example_2d.py): Example custom 2D plot, with PyQtGraph (faster than MatPlotLib).
- [`examples/example_3d.py`](examples/example_3d.py): Example custom 3D plot, with PyQtGraph. Requires PyOpenGL.
A note about importing: You can either import the `Logger` class from `overboard` or from `overboard_logger`. If you installed the "logger only" version as described above (no dependencies), then you can only import from `overboard_logger`.
## Remote experiments
It's as simple as:
```
python -m overboard ssh://username:password@hostname/path-to-experiments
```
...replacing your SSH user name, password, host name/server, and the directory where OverBoard should look for experiments. The default port is 22, which you can override with :23 or another port number after the host name.
There are a [number of other settings](https://github.com/althonos/fs.sshfs#constructor), which you can append after the path. For example, append `?keepalive=60&config_path=~/.ssh/config` to set the keepalive packets interval to 60 seconds, and specify an OpenSSH configuration file path.
[Other remote file systems](https://www.pyfilesystem.org/page/index-of-filesystems/) are available by using [appropriate prefixes](https://docs.pyfilesystem.org/en/latest/openers.html) (e.g. `ftp://`).
## Interface tips & tricks
- Click a plot title to hide it (moving it to the bottom) or to show it again.
- Click a plot line to select that experiment in the table, and vice-versa.
- Use the mouse wheel to zoom and drag to pan in a plot or custom visualization.
- Click the "A" button in the bottom-left of a plot to reset the zoom/pan.
- Choose an hyper-parameter as the "X axis" in the sidebar to compare different hyper-parameters graphically (*bubble plot*). Click a bubble to highlight that experiment. If the hyper-parameter is numerical but has wildly different orders of magnitude, check "Treat X as categorical". By default, each bubble's Y coordinate (e.g. accuracy) is taken from the last iteration; in "Scalar display" you can choose the maximum or minimum across iterations.
- If you have multiple runs with different random seeds (stored as hyper-parameter "seed" for example), select "Merge: seed" in the sidebar to merge them into *shaded plots* (you can then select whether to show the mean, median, range or standard deviations).
- You can *split* all experiments into different plots by selected "Panels: One per run" in the sidebar, and selecting a metric to plot in "Y axis". Similarly, they can be split by a hyper-parameter value (e.g. a different algorithm in each panel, but each has multiple plots/runs).
## Author
[João Henriques](http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~joao/), [Visual Geometry Group (VGG)](http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/), University of Oxford
%package -n python3-overboard
Summary: Pure Python dashboard for monitoring deep learning experiments
Provides: python-overboard
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3-setuptools
BuildRequires: python3-pip
%description -n python3-overboard
# OverBoard
OverBoard is a lightweight yet powerful dashboard to monitor your experiments.
Load remote experiments in real-time through SSH/FTP and others.

Custom visualisations (tensors and any custom plot with familiar MatPlotLib syntax).

A sortable table of hyper-parameters with Python-syntax filtering.

Plot percentile intervals (shaded plots), custom X/Y axes, and hyper-parameters (bubble plots).

# Installation
You can install the dependencies with:
- With Conda: `conda install pyqt=5.12 pyqtgraph=0.11 -c conda-forge`
- With pip: `pip install pyqt5==5.12 pyqtgraph==0.11`
Finally, OverBoard itself can be installed with: `pip install fs==2.4 overboard`
(Conda seems to be too strict when installing [PyFileSystem/fs](https://www.pyfilesystem.org), so pip should be preferred.)
Optional:
- `pip install fs.sshfs` to support remote files through SSH.
- PyOpenGL 3.1 (either through conda or pip) if you intend to use custom 3D plots with [PyQtGraph](https://pyqtgraph.readthedocs.io/en/latest/3dgraphics.html).
- MatPlotLib if you intend to use it for custom plots.
## Installation - logger only
Your scripts can log data without installing the full GUI and its dependencies (so your remote GPU cluster does not need PyQt at all).
Just use: `pip install overboard_logger`
And remember to import `overboard_logger` instead of `overboard` in your scripts.
# Usage
- Main interface: `python3 -m overboard `
- Logging experiments is simple:
```python
from overboard import Logger
with Logger('./logs') as logger:
for iteration in range(100):
logger.append({'loss': 0, 'error': 0})
```
You can also pass in a `meta` keyword argument, which can be a `dict` with hyper-parameters names and values (or other meta-data), to help organize your experiments. These will be displayed in a handy table, which supports sorting and filtering. The `meta` data can also be an `argparse.Namespace`, which is useful if your hyper-parameters are command-line arguments parsed with `argparse`.
By default a unique folder (using the current timestamp) is created for the logs. For full documentation on initialization arguments and other methods, type `pydoc overboard` on the command-line (Python built-in doc viewer).
You can also check the `examples` directory:
- [`examples/basic.py`](examples/basic.py): A minimal example. Generates some test logs.
- [`examples/mnist.py`](examples/mnist.py): The mandatory MNIST example. Also shows a custom MatPlotLib plot (a confusion matrix).
- [`examples/example_2d.py`](examples/example_2d.py): Example custom 2D plot, with PyQtGraph (faster than MatPlotLib).
- [`examples/example_3d.py`](examples/example_3d.py): Example custom 3D plot, with PyQtGraph. Requires PyOpenGL.
A note about importing: You can either import the `Logger` class from `overboard` or from `overboard_logger`. If you installed the "logger only" version as described above (no dependencies), then you can only import from `overboard_logger`.
## Remote experiments
It's as simple as:
```
python -m overboard ssh://username:password@hostname/path-to-experiments
```
...replacing your SSH user name, password, host name/server, and the directory where OverBoard should look for experiments. The default port is 22, which you can override with :23 or another port number after the host name.
There are a [number of other settings](https://github.com/althonos/fs.sshfs#constructor), which you can append after the path. For example, append `?keepalive=60&config_path=~/.ssh/config` to set the keepalive packets interval to 60 seconds, and specify an OpenSSH configuration file path.
[Other remote file systems](https://www.pyfilesystem.org/page/index-of-filesystems/) are available by using [appropriate prefixes](https://docs.pyfilesystem.org/en/latest/openers.html) (e.g. `ftp://`).
## Interface tips & tricks
- Click a plot title to hide it (moving it to the bottom) or to show it again.
- Click a plot line to select that experiment in the table, and vice-versa.
- Use the mouse wheel to zoom and drag to pan in a plot or custom visualization.
- Click the "A" button in the bottom-left of a plot to reset the zoom/pan.
- Choose an hyper-parameter as the "X axis" in the sidebar to compare different hyper-parameters graphically (*bubble plot*). Click a bubble to highlight that experiment. If the hyper-parameter is numerical but has wildly different orders of magnitude, check "Treat X as categorical". By default, each bubble's Y coordinate (e.g. accuracy) is taken from the last iteration; in "Scalar display" you can choose the maximum or minimum across iterations.
- If you have multiple runs with different random seeds (stored as hyper-parameter "seed" for example), select "Merge: seed" in the sidebar to merge them into *shaded plots* (you can then select whether to show the mean, median, range or standard deviations).
- You can *split* all experiments into different plots by selected "Panels: One per run" in the sidebar, and selecting a metric to plot in "Y axis". Similarly, they can be split by a hyper-parameter value (e.g. a different algorithm in each panel, but each has multiple plots/runs).
## Author
[João Henriques](http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~joao/), [Visual Geometry Group (VGG)](http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/), University of Oxford
%package help
Summary: Development documents and examples for overboard
Provides: python3-overboard-doc
%description help
# OverBoard
OverBoard is a lightweight yet powerful dashboard to monitor your experiments.
Load remote experiments in real-time through SSH/FTP and others.

Custom visualisations (tensors and any custom plot with familiar MatPlotLib syntax).

A sortable table of hyper-parameters with Python-syntax filtering.

Plot percentile intervals (shaded plots), custom X/Y axes, and hyper-parameters (bubble plots).

# Installation
You can install the dependencies with:
- With Conda: `conda install pyqt=5.12 pyqtgraph=0.11 -c conda-forge`
- With pip: `pip install pyqt5==5.12 pyqtgraph==0.11`
Finally, OverBoard itself can be installed with: `pip install fs==2.4 overboard`
(Conda seems to be too strict when installing [PyFileSystem/fs](https://www.pyfilesystem.org), so pip should be preferred.)
Optional:
- `pip install fs.sshfs` to support remote files through SSH.
- PyOpenGL 3.1 (either through conda or pip) if you intend to use custom 3D plots with [PyQtGraph](https://pyqtgraph.readthedocs.io/en/latest/3dgraphics.html).
- MatPlotLib if you intend to use it for custom plots.
## Installation - logger only
Your scripts can log data without installing the full GUI and its dependencies (so your remote GPU cluster does not need PyQt at all).
Just use: `pip install overboard_logger`
And remember to import `overboard_logger` instead of `overboard` in your scripts.
# Usage
- Main interface: `python3 -m overboard `
- Logging experiments is simple:
```python
from overboard import Logger
with Logger('./logs') as logger:
for iteration in range(100):
logger.append({'loss': 0, 'error': 0})
```
You can also pass in a `meta` keyword argument, which can be a `dict` with hyper-parameters names and values (or other meta-data), to help organize your experiments. These will be displayed in a handy table, which supports sorting and filtering. The `meta` data can also be an `argparse.Namespace`, which is useful if your hyper-parameters are command-line arguments parsed with `argparse`.
By default a unique folder (using the current timestamp) is created for the logs. For full documentation on initialization arguments and other methods, type `pydoc overboard` on the command-line (Python built-in doc viewer).
You can also check the `examples` directory:
- [`examples/basic.py`](examples/basic.py): A minimal example. Generates some test logs.
- [`examples/mnist.py`](examples/mnist.py): The mandatory MNIST example. Also shows a custom MatPlotLib plot (a confusion matrix).
- [`examples/example_2d.py`](examples/example_2d.py): Example custom 2D plot, with PyQtGraph (faster than MatPlotLib).
- [`examples/example_3d.py`](examples/example_3d.py): Example custom 3D plot, with PyQtGraph. Requires PyOpenGL.
A note about importing: You can either import the `Logger` class from `overboard` or from `overboard_logger`. If you installed the "logger only" version as described above (no dependencies), then you can only import from `overboard_logger`.
## Remote experiments
It's as simple as:
```
python -m overboard ssh://username:password@hostname/path-to-experiments
```
...replacing your SSH user name, password, host name/server, and the directory where OverBoard should look for experiments. The default port is 22, which you can override with :23 or another port number after the host name.
There are a [number of other settings](https://github.com/althonos/fs.sshfs#constructor), which you can append after the path. For example, append `?keepalive=60&config_path=~/.ssh/config` to set the keepalive packets interval to 60 seconds, and specify an OpenSSH configuration file path.
[Other remote file systems](https://www.pyfilesystem.org/page/index-of-filesystems/) are available by using [appropriate prefixes](https://docs.pyfilesystem.org/en/latest/openers.html) (e.g. `ftp://`).
## Interface tips & tricks
- Click a plot title to hide it (moving it to the bottom) or to show it again.
- Click a plot line to select that experiment in the table, and vice-versa.
- Use the mouse wheel to zoom and drag to pan in a plot or custom visualization.
- Click the "A" button in the bottom-left of a plot to reset the zoom/pan.
- Choose an hyper-parameter as the "X axis" in the sidebar to compare different hyper-parameters graphically (*bubble plot*). Click a bubble to highlight that experiment. If the hyper-parameter is numerical but has wildly different orders of magnitude, check "Treat X as categorical". By default, each bubble's Y coordinate (e.g. accuracy) is taken from the last iteration; in "Scalar display" you can choose the maximum or minimum across iterations.
- If you have multiple runs with different random seeds (stored as hyper-parameter "seed" for example), select "Merge: seed" in the sidebar to merge them into *shaded plots* (you can then select whether to show the mean, median, range or standard deviations).
- You can *split* all experiments into different plots by selected "Panels: One per run" in the sidebar, and selecting a metric to plot in "Y axis". Similarly, they can be split by a hyper-parameter value (e.g. a different algorithm in each panel, but each has multiple plots/runs).
## Author
[João Henriques](http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~joao/), [Visual Geometry Group (VGG)](http://www.robots.ox.ac.uk/~vgg/), University of Oxford
%prep
%autosetup -n overboard-1.0.1
%build
%py3_build
%install
%py3_install
install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}
if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
pushd %{buildroot}
if [ -d usr/lib ]; then
find usr/lib -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then
find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/bin ]; then
find usr/bin -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then
find usr/sbin -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
touch doclist.lst
if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then
find usr/share/man -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f.gz\"\n" >> doclist.lst
fi
popd
mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst .
mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst .
%files -n python3-overboard -f filelist.lst
%dir %{python3_sitelib}/*
%files help -f doclist.lst
%{_docdir}/*
%changelog
* Thu Jun 08 2023 Python_Bot - 1.0.1-1
- Package Spec generated







