%global _empty_manifest_terminate_build 0
Name: python-jupyterlab-lsp
Version: 4.0.1
Release: 1
Summary: Coding assistance for JupyterLab with Language Server Protocol
License: BSD-3-Clause
URL: https://pypi.org/project/jupyterlab-lsp/
Source0: https://mirrors.nju.edu.cn/pypi/web/packages/c1/e0/0995a3659e0770b69b2446e3bc40d736ab6eec0ff2def04853ba36aaef3e/jupyterlab-lsp-4.0.1.tar.gz
BuildArch: noarch
Requires: python3-jupyter-lsp
Requires: python3-jupyterlab
%description
# Language Server Protocol integration for Jupyter(Lab)
[](https://github.com/jupyter-lsp/jupyterlab-lsp/actions?query=workflow%3ACI+branch%3Amaster)
[](https://jupyterlab-lsp.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/jupyter-lsp/demo-python/main?urlpath=lab)
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/jupyter-lsp/demo-r/main?urlpath=lab)
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/jupyter-lsp/demo-julia/main?urlpath=lab)
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/jupyter-lsp/jupyterlab-lsp/master?urlpath=lab%2Ftree%2Fexamples%2FPython.ipynb)
**[Installation](#installation) | [Configuring](./docs/Configuring.ipynb) | [Changelog](./CHANGELOG.md) | [Roadmap](./docs/Roadmap.ipynb) | [Contributing](./CONTRIBUTING.md) | [Extending](./docs/Extending.ipynb)**
## Features
> Examples show Python code, but most features also work in R, bash, typescript, and [many other languages][language-servers].
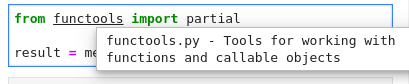
### Hover
Hover over any piece of code; if an underline appears, you can press Ctrl
to get a tooltip with function/class signature, module documentation or any other
piece of information that the language server provides
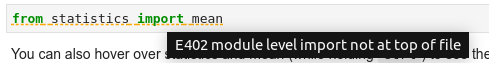
### Diagnostics
Critical errors have red underline, warnings are orange, etc. Hover
over the underlined code to see a more detailed message
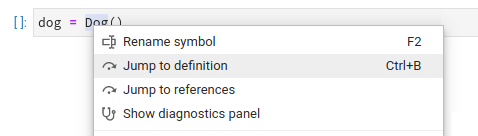
### Jump to Definition and References
Use the context menu entry, or Alt + :computer_mouse: to jump to definitions/references (you can change it to Ctrl/⌘ in settings); use Alt + o to jump back.
### Highlight References
Place your cursor on a variable, function, etc and all the usages will be highlighted
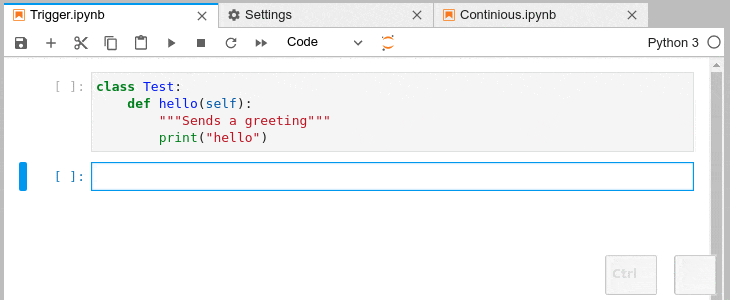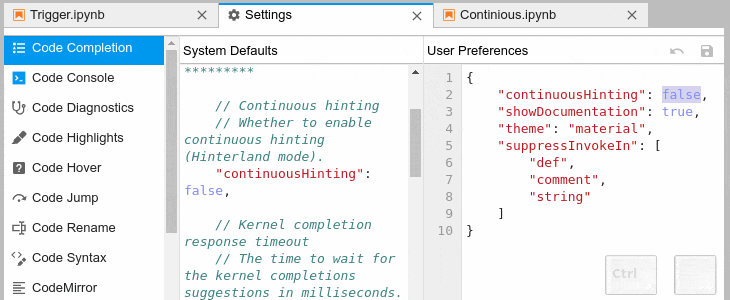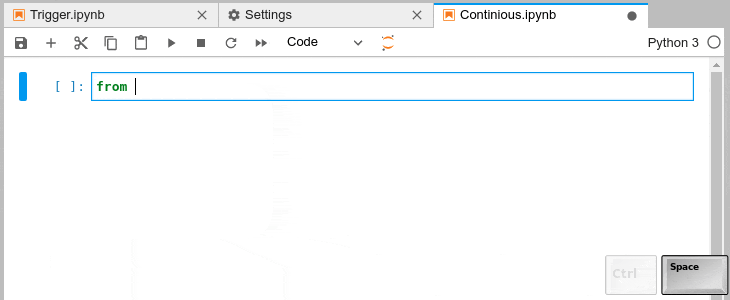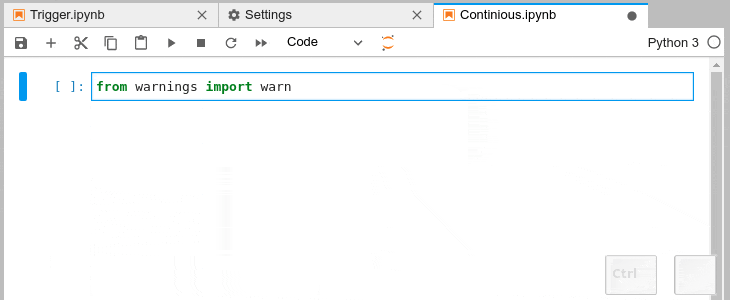
### Automatic Completion and Continuous Hinting
- Certain characters, for example '.' (dot) in Python, will automatically trigger
completion.
- You can choose to receive the completion suggestions as you type by enabling `continuousHinting` setting.
### Automatic Signature Suggestions
Function signatures will automatically be displayed
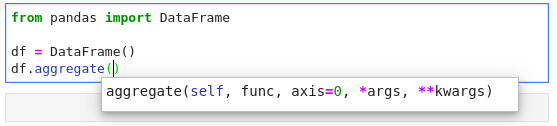
### Kernel-less Autocompletion
Advanced static-analysis autocompletion without a running kernel
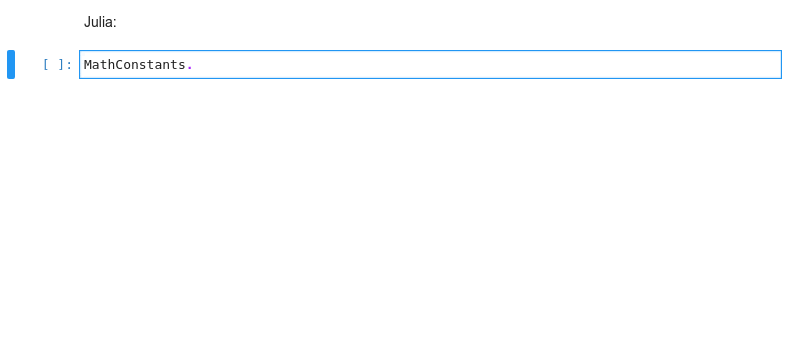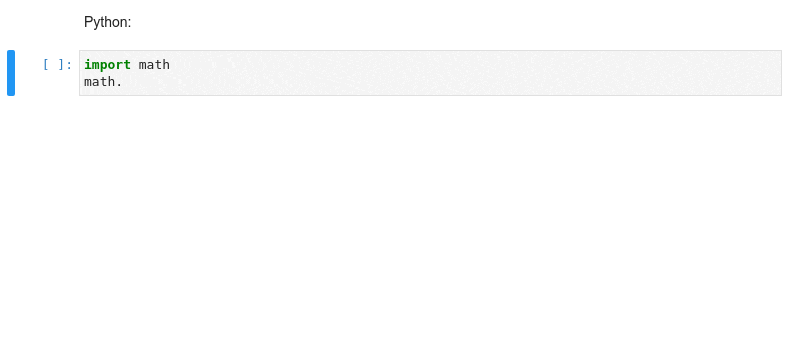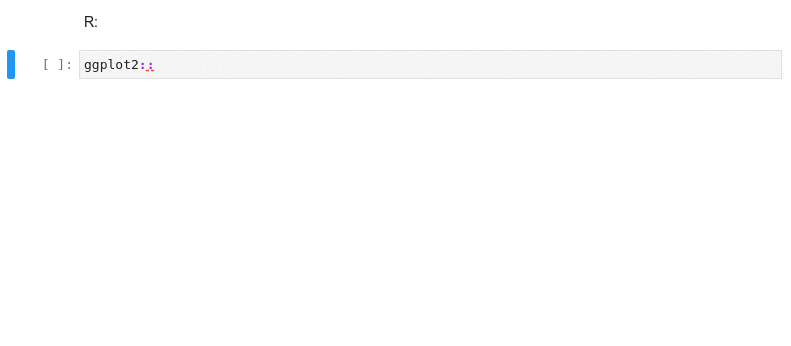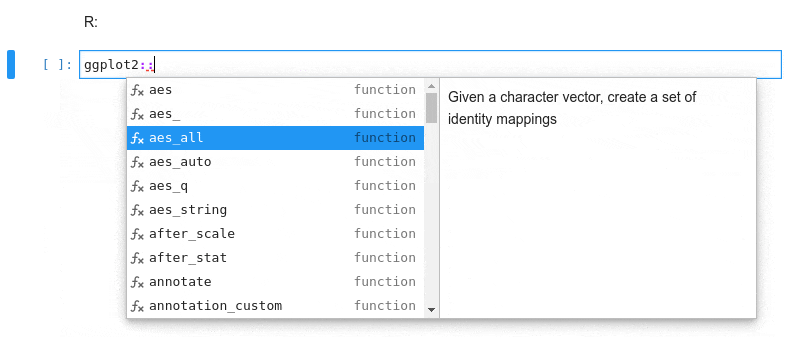
#### The runtime kernel suggestions are still there
When a kernel is available the suggestions from the kernel (such as keys of a
dict and columns of a DataFrame) are merged with the suggestions
from the Language Server (in notebook).
If the kernel is too slow to respond promptly only the Language Server suggestions will be shown (default threshold: 0.6s).
You can configure the completer to not attempt to fetch the kernel completions if the kernel is busy (skipping the 0.6s timeout).
You can deactivate the kernel suggestions by adding `"Kernel"` to the `disableCompletionsFrom` in the `completion` section
of _Advanced Settings_. Alternatively if you _only_ want kernel completions you can add `"LSP"` to the same
setting; Or add both if you like to code in hardcore mode and get no completions, or if another provider has been added.
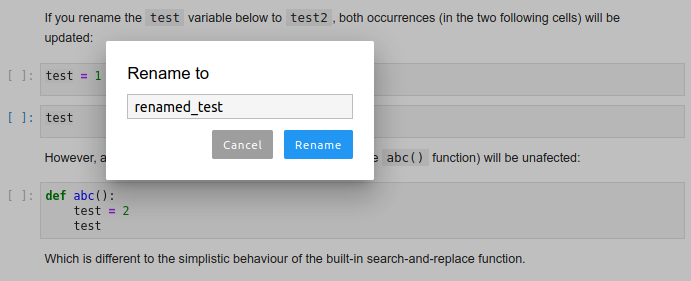
### Rename
Rename variables, functions and more, in both: notebooks and the file editor.
Use the context menu option or the F2 shortcut to invoke.
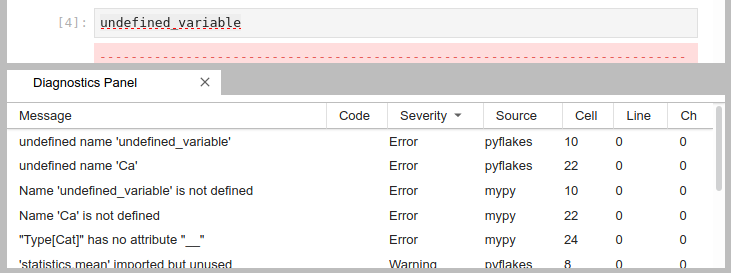
### Diagnostics panel
Sort and jump between the diagnostics using the diagnostics panel.
Open it searching for "Show diagnostics panel" in JupyterLab commands palette or from the context menu.
Use context menu on rows in the panel to filter out diagnostics or copy their message.
## Prerequisites
You will need to have both of the following installed:
- JupyterLab >=3.6.0,<4.0.0a0
- Python 3.8+
In addition, if you wish to use javascript, html, markdown or any other NodeJS-based language server you will need to have appropriate NodeJS version installed.
> Note: Installation for JupyterLab 2.x requires a different procedure, please consult the documentation for the extension [version 2.x][version 2.x docs].
## Installation
> For more extensive installation instructions, see the [documentation][installation-documentation].
For the current stable version, the following steps are recommended.
Use of a python `virtualenv` or a conda env is also recommended.
1. install python 3
```bash
conda install -c conda-forge python=3
```
1. install JupyterLab and the extensions
```bash
conda install -c conda-forge 'jupyterlab>=3.0.0,<4.0.0a0' jupyterlab-lsp
# or
pip install 'jupyterlab>=3.0.0,<4.0.0a0' jupyterlab-lsp
```
> Note: `jupyterlab-lsp` provides both the server extension and the lab extension.
> Note: With conda, you could take advantage of the bundles: `jupyter-lsp-python`
> or `jupyter-lsp-r` to install both the server extension and the language server.
1. install LSP servers for languages of your choice; for example, for Python
([pylsp](https://github.com/python-lsp/python-lsp-server)) and
R ([languageserver](https://github.com/REditorSupport/languageserver)) servers:
```bash
pip install 'python-lsp-server[all]'
R -e 'install.packages("languageserver")'
```
or from `conda-forge`
```bash
conda install -c conda-forge python-lsp-server r-languageserver
```
Please see our full list of
[supported language servers][language-servers]
which includes installation hints for the common package managers (npm/pip/conda).
In general, any LSP server from the
[Microsoft list](https://microsoft.github.io/language-server-protocol/implementors/servers/)
should work after [some additional configuration](./CONTRIBUTING.md#specs).
Note: it is worth visiting the repository of each server you install as
many provide additional configuration options.
1. Restart JupyterLab
If JupyterLab is running when you installed the extension, a restart is required
for the server extension and any language servers to be recognized by JupyterLab.
1. (Optional, IPython users only) to improve the performance of autocompletion,
disable Jedi in IPython (the LSP servers for Python use Jedi too).
You can do that temporarily with:
```ipython
%config Completer.use_jedi = False
```
or permanently by setting `c.Completer.use_jedi = False` in your
[`ipython_config.py` file](https://ipython.readthedocs.io/en/stable/config/intro.html?highlight=ipython_config.py#systemwide-configuration).
1. (Optional, Linux/OSX-only) As a security measure by default Jupyter server only allows
access to files under the Jupyter root directory (the place where you launch the Jupyter server).
Thus, in order to allow `jupyterlab-lsp` to navigate to external files such as packages
installed system-wide or to libraries inside a virtual environment (`conda`,
`pip`, ...) this access control mechanism needs to be circumvented: inside your Jupyter
root directory create a symlink named _.lsp_symlink_ pointing to your system root `/`.
```
ln -s / .lsp_symlink
```
As this symlink is a hidden file the Jupyter server must be instructed to
serve hidden files. Either use the appropriate command line flag:
```
jupyter lab --ContentsManager.allow_hidden=True
```
or, alternatively, set the corresponding setting inside your `jupyter_server_config.py`.
Help in implementing a custom [`ContentsManager`](https://github.com/jupyter-lsp/jupyterlab-lsp/issues/850)
which will enable navigating to external files without the symlink is welcome.
### Configuring the servers
Server configurations can be edited using the Advanced Settings editor in JupyterLab (_Settings > Advanced Settings Editor_). For settings specific to each server, please see the [table of language servers][language-servers]. Example settings might include:
> Note: for the new (currently recommended) python-lsp-server replace `pyls` occurrences with `pylsp`
```json
{
"language_servers": {
"pyls": {
"serverSettings": {
"pyls.plugins.pydocstyle.enabled": true,
"pyls.plugins.pyflakes.enabled": false,
"pyls.plugins.flake8.enabled": true
}
},
"r-languageserver": {
"serverSettings": {
"r.lsp.debug": false,
"r.lsp.diagnostics": false
}
}
}
}
```
The `serverSettings` key specifies the configurations sent to the language servers. These can be written using stringified dot accessors like above (in the VSCode style), or as nested JSON objects, e.g.:
```json
{
"language_servers": {
"pyls": {
"serverSettings": {
"pyls": {
"plugins": {
"pydocstyle": {
"enabled": true
},
"pyflakes": {
"enabled": false
},
"flake8": {
"enabled": true
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
```
#### Other configuration methods
Some language servers, such as `pyls`, provide other configuration methods _in addition_ to language-server configuration messages (accessed using the Advanced Settings Editor). For example, `pyls` allows users to configure the server using a local configuration file. You can change the inspection/diagnostics for server plugins like `pycodestyle` there.
The exact configuration details will vary between operating systems (please see the [configuration section of pycodestyle documentation](https://pycodestyle.readthedocs.io/en/latest/intro.html#configuration)), but as an example, on Linux you would simply need to create a file called `~/.config/pycodestyle`, which may look like that:
```cfg
[pycodestyle]
ignore = E402, E703
max-line-length = 120
```
In the example above:
- ignoring E402 allows imports which are not on the very top of the file,
- ignoring E703 allows terminating semicolon (useful for matplotlib plots),
- the maximal allowed line length is increased to 120.
After changing the configuration you may need to restart the JupyterLab, and please be advised that the errors in configuration may prevent the servers from functioning properly.
Again, please do check the pycodestyle documentation for specific error codes, and check the configuration of other feature providers and language servers as needed.
## Acknowledgements
This would not be possible without the fantastic initial work at
[wylieconlon/lsp-editor-adapter](https://github.com/wylieconlon/lsp-editor-adapter).
[language-servers]: https://jupyterlab-lsp.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Language%20Servers.html
[installation-documentation]: https://jupyterlab-lsp.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Installation.html
[version 2.x docs]: https://jupyterlab-lsp.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/Installation.html
%package -n python3-jupyterlab-lsp
Summary: Coding assistance for JupyterLab with Language Server Protocol
Provides: python-jupyterlab-lsp
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3-setuptools
BuildRequires: python3-pip
%description -n python3-jupyterlab-lsp
# Language Server Protocol integration for Jupyter(Lab)
[](https://github.com/jupyter-lsp/jupyterlab-lsp/actions?query=workflow%3ACI+branch%3Amaster)
[](https://jupyterlab-lsp.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/jupyter-lsp/demo-python/main?urlpath=lab)
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/jupyter-lsp/demo-r/main?urlpath=lab)
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/jupyter-lsp/demo-julia/main?urlpath=lab)
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/jupyter-lsp/jupyterlab-lsp/master?urlpath=lab%2Ftree%2Fexamples%2FPython.ipynb)
**[Installation](#installation) | [Configuring](./docs/Configuring.ipynb) | [Changelog](./CHANGELOG.md) | [Roadmap](./docs/Roadmap.ipynb) | [Contributing](./CONTRIBUTING.md) | [Extending](./docs/Extending.ipynb)**
## Features
> Examples show Python code, but most features also work in R, bash, typescript, and [many other languages][language-servers].
### Hover
Hover over any piece of code; if an underline appears, you can press Ctrl
to get a tooltip with function/class signature, module documentation or any other
piece of information that the language server provides

### Diagnostics
Critical errors have red underline, warnings are orange, etc. Hover
over the underlined code to see a more detailed message

### Jump to Definition and References
Use the context menu entry, or Alt + :computer_mouse: to jump to definitions/references (you can change it to Ctrl/⌘ in settings); use Alt + o to jump back.

### Highlight References
Place your cursor on a variable, function, etc and all the usages will be highlighted
### Automatic Completion and Continuous Hinting
- Certain characters, for example '.' (dot) in Python, will automatically trigger
completion.
- You can choose to receive the completion suggestions as you type by enabling `continuousHinting` setting.

### Automatic Signature Suggestions
Function signatures will automatically be displayed

### Kernel-less Autocompletion
Advanced static-analysis autocompletion without a running kernel

#### The runtime kernel suggestions are still there
When a kernel is available the suggestions from the kernel (such as keys of a
dict and columns of a DataFrame) are merged with the suggestions
from the Language Server (in notebook).
If the kernel is too slow to respond promptly only the Language Server suggestions will be shown (default threshold: 0.6s).
You can configure the completer to not attempt to fetch the kernel completions if the kernel is busy (skipping the 0.6s timeout).
You can deactivate the kernel suggestions by adding `"Kernel"` to the `disableCompletionsFrom` in the `completion` section
of _Advanced Settings_. Alternatively if you _only_ want kernel completions you can add `"LSP"` to the same
setting; Or add both if you like to code in hardcore mode and get no completions, or if another provider has been added.
### Rename
Rename variables, functions and more, in both: notebooks and the file editor.
Use the context menu option or the F2 shortcut to invoke.

### Diagnostics panel
Sort and jump between the diagnostics using the diagnostics panel.
Open it searching for "Show diagnostics panel" in JupyterLab commands palette or from the context menu.
Use context menu on rows in the panel to filter out diagnostics or copy their message.

## Prerequisites
You will need to have both of the following installed:
- JupyterLab >=3.6.0,<4.0.0a0
- Python 3.8+
In addition, if you wish to use javascript, html, markdown or any other NodeJS-based language server you will need to have appropriate NodeJS version installed.
> Note: Installation for JupyterLab 2.x requires a different procedure, please consult the documentation for the extension [version 2.x][version 2.x docs].
## Installation
> For more extensive installation instructions, see the [documentation][installation-documentation].
For the current stable version, the following steps are recommended.
Use of a python `virtualenv` or a conda env is also recommended.
1. install python 3
```bash
conda install -c conda-forge python=3
```
1. install JupyterLab and the extensions
```bash
conda install -c conda-forge 'jupyterlab>=3.0.0,<4.0.0a0' jupyterlab-lsp
# or
pip install 'jupyterlab>=3.0.0,<4.0.0a0' jupyterlab-lsp
```
> Note: `jupyterlab-lsp` provides both the server extension and the lab extension.
> Note: With conda, you could take advantage of the bundles: `jupyter-lsp-python`
> or `jupyter-lsp-r` to install both the server extension and the language server.
1. install LSP servers for languages of your choice; for example, for Python
([pylsp](https://github.com/python-lsp/python-lsp-server)) and
R ([languageserver](https://github.com/REditorSupport/languageserver)) servers:
```bash
pip install 'python-lsp-server[all]'
R -e 'install.packages("languageserver")'
```
or from `conda-forge`
```bash
conda install -c conda-forge python-lsp-server r-languageserver
```
Please see our full list of
[supported language servers][language-servers]
which includes installation hints for the common package managers (npm/pip/conda).
In general, any LSP server from the
[Microsoft list](https://microsoft.github.io/language-server-protocol/implementors/servers/)
should work after [some additional configuration](./CONTRIBUTING.md#specs).
Note: it is worth visiting the repository of each server you install as
many provide additional configuration options.
1. Restart JupyterLab
If JupyterLab is running when you installed the extension, a restart is required
for the server extension and any language servers to be recognized by JupyterLab.
1. (Optional, IPython users only) to improve the performance of autocompletion,
disable Jedi in IPython (the LSP servers for Python use Jedi too).
You can do that temporarily with:
```ipython
%config Completer.use_jedi = False
```
or permanently by setting `c.Completer.use_jedi = False` in your
[`ipython_config.py` file](https://ipython.readthedocs.io/en/stable/config/intro.html?highlight=ipython_config.py#systemwide-configuration).
1. (Optional, Linux/OSX-only) As a security measure by default Jupyter server only allows
access to files under the Jupyter root directory (the place where you launch the Jupyter server).
Thus, in order to allow `jupyterlab-lsp` to navigate to external files such as packages
installed system-wide or to libraries inside a virtual environment (`conda`,
`pip`, ...) this access control mechanism needs to be circumvented: inside your Jupyter
root directory create a symlink named _.lsp_symlink_ pointing to your system root `/`.
```
ln -s / .lsp_symlink
```
As this symlink is a hidden file the Jupyter server must be instructed to
serve hidden files. Either use the appropriate command line flag:
```
jupyter lab --ContentsManager.allow_hidden=True
```
or, alternatively, set the corresponding setting inside your `jupyter_server_config.py`.
Help in implementing a custom [`ContentsManager`](https://github.com/jupyter-lsp/jupyterlab-lsp/issues/850)
which will enable navigating to external files without the symlink is welcome.
### Configuring the servers
Server configurations can be edited using the Advanced Settings editor in JupyterLab (_Settings > Advanced Settings Editor_). For settings specific to each server, please see the [table of language servers][language-servers]. Example settings might include:
> Note: for the new (currently recommended) python-lsp-server replace `pyls` occurrences with `pylsp`
```json
{
"language_servers": {
"pyls": {
"serverSettings": {
"pyls.plugins.pydocstyle.enabled": true,
"pyls.plugins.pyflakes.enabled": false,
"pyls.plugins.flake8.enabled": true
}
},
"r-languageserver": {
"serverSettings": {
"r.lsp.debug": false,
"r.lsp.diagnostics": false
}
}
}
}
```
The `serverSettings` key specifies the configurations sent to the language servers. These can be written using stringified dot accessors like above (in the VSCode style), or as nested JSON objects, e.g.:
```json
{
"language_servers": {
"pyls": {
"serverSettings": {
"pyls": {
"plugins": {
"pydocstyle": {
"enabled": true
},
"pyflakes": {
"enabled": false
},
"flake8": {
"enabled": true
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
```
#### Other configuration methods
Some language servers, such as `pyls`, provide other configuration methods _in addition_ to language-server configuration messages (accessed using the Advanced Settings Editor). For example, `pyls` allows users to configure the server using a local configuration file. You can change the inspection/diagnostics for server plugins like `pycodestyle` there.
The exact configuration details will vary between operating systems (please see the [configuration section of pycodestyle documentation](https://pycodestyle.readthedocs.io/en/latest/intro.html#configuration)), but as an example, on Linux you would simply need to create a file called `~/.config/pycodestyle`, which may look like that:
```cfg
[pycodestyle]
ignore = E402, E703
max-line-length = 120
```
In the example above:
- ignoring E402 allows imports which are not on the very top of the file,
- ignoring E703 allows terminating semicolon (useful for matplotlib plots),
- the maximal allowed line length is increased to 120.
After changing the configuration you may need to restart the JupyterLab, and please be advised that the errors in configuration may prevent the servers from functioning properly.
Again, please do check the pycodestyle documentation for specific error codes, and check the configuration of other feature providers and language servers as needed.
## Acknowledgements
This would not be possible without the fantastic initial work at
[wylieconlon/lsp-editor-adapter](https://github.com/wylieconlon/lsp-editor-adapter).
[language-servers]: https://jupyterlab-lsp.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Language%20Servers.html
[installation-documentation]: https://jupyterlab-lsp.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Installation.html
[version 2.x docs]: https://jupyterlab-lsp.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/Installation.html
%package help
Summary: Development documents and examples for jupyterlab-lsp
Provides: python3-jupyterlab-lsp-doc
%description help
# Language Server Protocol integration for Jupyter(Lab)
[](https://github.com/jupyter-lsp/jupyterlab-lsp/actions?query=workflow%3ACI+branch%3Amaster)
[](https://jupyterlab-lsp.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/jupyter-lsp/demo-python/main?urlpath=lab)
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/jupyter-lsp/demo-r/main?urlpath=lab)
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/jupyter-lsp/demo-julia/main?urlpath=lab)
[](https://mybinder.org/v2/gh/jupyter-lsp/jupyterlab-lsp/master?urlpath=lab%2Ftree%2Fexamples%2FPython.ipynb)
**[Installation](#installation) | [Configuring](./docs/Configuring.ipynb) | [Changelog](./CHANGELOG.md) | [Roadmap](./docs/Roadmap.ipynb) | [Contributing](./CONTRIBUTING.md) | [Extending](./docs/Extending.ipynb)**
## Features
> Examples show Python code, but most features also work in R, bash, typescript, and [many other languages][language-servers].
### Hover
Hover over any piece of code; if an underline appears, you can press Ctrl
to get a tooltip with function/class signature, module documentation or any other
piece of information that the language server provides

### Diagnostics
Critical errors have red underline, warnings are orange, etc. Hover
over the underlined code to see a more detailed message

### Jump to Definition and References
Use the context menu entry, or Alt + :computer_mouse: to jump to definitions/references (you can change it to Ctrl/⌘ in settings); use Alt + o to jump back.

### Highlight References
Place your cursor on a variable, function, etc and all the usages will be highlighted
### Automatic Completion and Continuous Hinting
- Certain characters, for example '.' (dot) in Python, will automatically trigger
completion.
- You can choose to receive the completion suggestions as you type by enabling `continuousHinting` setting.

### Automatic Signature Suggestions
Function signatures will automatically be displayed

### Kernel-less Autocompletion
Advanced static-analysis autocompletion without a running kernel

#### The runtime kernel suggestions are still there
When a kernel is available the suggestions from the kernel (such as keys of a
dict and columns of a DataFrame) are merged with the suggestions
from the Language Server (in notebook).
If the kernel is too slow to respond promptly only the Language Server suggestions will be shown (default threshold: 0.6s).
You can configure the completer to not attempt to fetch the kernel completions if the kernel is busy (skipping the 0.6s timeout).
You can deactivate the kernel suggestions by adding `"Kernel"` to the `disableCompletionsFrom` in the `completion` section
of _Advanced Settings_. Alternatively if you _only_ want kernel completions you can add `"LSP"` to the same
setting; Or add both if you like to code in hardcore mode and get no completions, or if another provider has been added.
### Rename
Rename variables, functions and more, in both: notebooks and the file editor.
Use the context menu option or the F2 shortcut to invoke.

### Diagnostics panel
Sort and jump between the diagnostics using the diagnostics panel.
Open it searching for "Show diagnostics panel" in JupyterLab commands palette or from the context menu.
Use context menu on rows in the panel to filter out diagnostics or copy their message.

## Prerequisites
You will need to have both of the following installed:
- JupyterLab >=3.6.0,<4.0.0a0
- Python 3.8+
In addition, if you wish to use javascript, html, markdown or any other NodeJS-based language server you will need to have appropriate NodeJS version installed.
> Note: Installation for JupyterLab 2.x requires a different procedure, please consult the documentation for the extension [version 2.x][version 2.x docs].
## Installation
> For more extensive installation instructions, see the [documentation][installation-documentation].
For the current stable version, the following steps are recommended.
Use of a python `virtualenv` or a conda env is also recommended.
1. install python 3
```bash
conda install -c conda-forge python=3
```
1. install JupyterLab and the extensions
```bash
conda install -c conda-forge 'jupyterlab>=3.0.0,<4.0.0a0' jupyterlab-lsp
# or
pip install 'jupyterlab>=3.0.0,<4.0.0a0' jupyterlab-lsp
```
> Note: `jupyterlab-lsp` provides both the server extension and the lab extension.
> Note: With conda, you could take advantage of the bundles: `jupyter-lsp-python`
> or `jupyter-lsp-r` to install both the server extension and the language server.
1. install LSP servers for languages of your choice; for example, for Python
([pylsp](https://github.com/python-lsp/python-lsp-server)) and
R ([languageserver](https://github.com/REditorSupport/languageserver)) servers:
```bash
pip install 'python-lsp-server[all]'
R -e 'install.packages("languageserver")'
```
or from `conda-forge`
```bash
conda install -c conda-forge python-lsp-server r-languageserver
```
Please see our full list of
[supported language servers][language-servers]
which includes installation hints for the common package managers (npm/pip/conda).
In general, any LSP server from the
[Microsoft list](https://microsoft.github.io/language-server-protocol/implementors/servers/)
should work after [some additional configuration](./CONTRIBUTING.md#specs).
Note: it is worth visiting the repository of each server you install as
many provide additional configuration options.
1. Restart JupyterLab
If JupyterLab is running when you installed the extension, a restart is required
for the server extension and any language servers to be recognized by JupyterLab.
1. (Optional, IPython users only) to improve the performance of autocompletion,
disable Jedi in IPython (the LSP servers for Python use Jedi too).
You can do that temporarily with:
```ipython
%config Completer.use_jedi = False
```
or permanently by setting `c.Completer.use_jedi = False` in your
[`ipython_config.py` file](https://ipython.readthedocs.io/en/stable/config/intro.html?highlight=ipython_config.py#systemwide-configuration).
1. (Optional, Linux/OSX-only) As a security measure by default Jupyter server only allows
access to files under the Jupyter root directory (the place where you launch the Jupyter server).
Thus, in order to allow `jupyterlab-lsp` to navigate to external files such as packages
installed system-wide or to libraries inside a virtual environment (`conda`,
`pip`, ...) this access control mechanism needs to be circumvented: inside your Jupyter
root directory create a symlink named _.lsp_symlink_ pointing to your system root `/`.
```
ln -s / .lsp_symlink
```
As this symlink is a hidden file the Jupyter server must be instructed to
serve hidden files. Either use the appropriate command line flag:
```
jupyter lab --ContentsManager.allow_hidden=True
```
or, alternatively, set the corresponding setting inside your `jupyter_server_config.py`.
Help in implementing a custom [`ContentsManager`](https://github.com/jupyter-lsp/jupyterlab-lsp/issues/850)
which will enable navigating to external files without the symlink is welcome.
### Configuring the servers
Server configurations can be edited using the Advanced Settings editor in JupyterLab (_Settings > Advanced Settings Editor_). For settings specific to each server, please see the [table of language servers][language-servers]. Example settings might include:
> Note: for the new (currently recommended) python-lsp-server replace `pyls` occurrences with `pylsp`
```json
{
"language_servers": {
"pyls": {
"serverSettings": {
"pyls.plugins.pydocstyle.enabled": true,
"pyls.plugins.pyflakes.enabled": false,
"pyls.plugins.flake8.enabled": true
}
},
"r-languageserver": {
"serverSettings": {
"r.lsp.debug": false,
"r.lsp.diagnostics": false
}
}
}
}
```
The `serverSettings` key specifies the configurations sent to the language servers. These can be written using stringified dot accessors like above (in the VSCode style), or as nested JSON objects, e.g.:
```json
{
"language_servers": {
"pyls": {
"serverSettings": {
"pyls": {
"plugins": {
"pydocstyle": {
"enabled": true
},
"pyflakes": {
"enabled": false
},
"flake8": {
"enabled": true
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
```
#### Other configuration methods
Some language servers, such as `pyls`, provide other configuration methods _in addition_ to language-server configuration messages (accessed using the Advanced Settings Editor). For example, `pyls` allows users to configure the server using a local configuration file. You can change the inspection/diagnostics for server plugins like `pycodestyle` there.
The exact configuration details will vary between operating systems (please see the [configuration section of pycodestyle documentation](https://pycodestyle.readthedocs.io/en/latest/intro.html#configuration)), but as an example, on Linux you would simply need to create a file called `~/.config/pycodestyle`, which may look like that:
```cfg
[pycodestyle]
ignore = E402, E703
max-line-length = 120
```
In the example above:
- ignoring E402 allows imports which are not on the very top of the file,
- ignoring E703 allows terminating semicolon (useful for matplotlib plots),
- the maximal allowed line length is increased to 120.
After changing the configuration you may need to restart the JupyterLab, and please be advised that the errors in configuration may prevent the servers from functioning properly.
Again, please do check the pycodestyle documentation for specific error codes, and check the configuration of other feature providers and language servers as needed.
## Acknowledgements
This would not be possible without the fantastic initial work at
[wylieconlon/lsp-editor-adapter](https://github.com/wylieconlon/lsp-editor-adapter).
[language-servers]: https://jupyterlab-lsp.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Language%20Servers.html
[installation-documentation]: https://jupyterlab-lsp.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Installation.html
[version 2.x docs]: https://jupyterlab-lsp.readthedocs.io/en/2.x/Installation.html
%prep
%autosetup -n jupyterlab-lsp-4.0.1
%build
%py3_build
%install
%py3_install
install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}
if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
pushd %{buildroot}
if [ -d usr/lib ]; then
find usr/lib -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then
find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/bin ]; then
find usr/bin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then
find usr/sbin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
touch doclist.lst
if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then
find usr/share/man -type f -printf "/%h/%f.gz\n" >> doclist.lst
fi
popd
mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst .
mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst .
%files -n python3-jupyterlab-lsp -f filelist.lst
%dir %{python3_sitelib}/*
%files help -f doclist.lst
%{_docdir}/*
%changelog
* Wed Apr 12 2023 Python_Bot - 4.0.1-1
- Package Spec generated