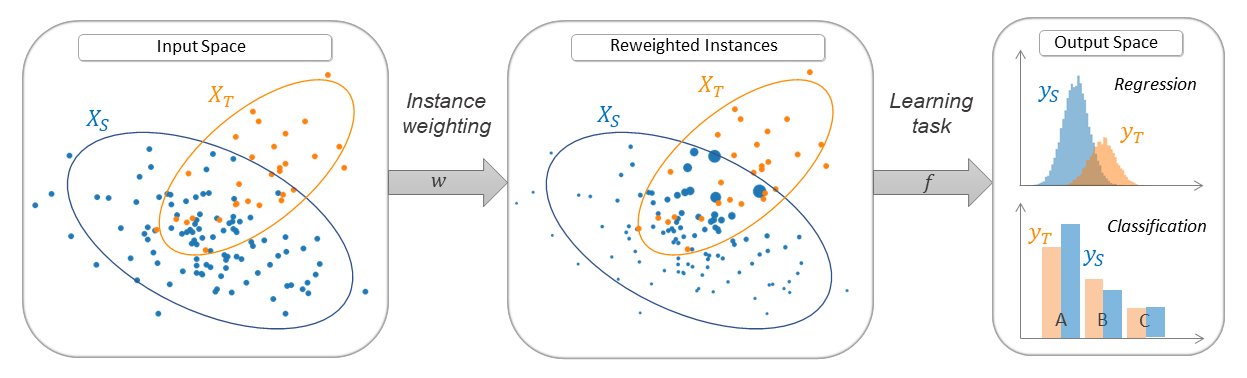
Sample bias correction

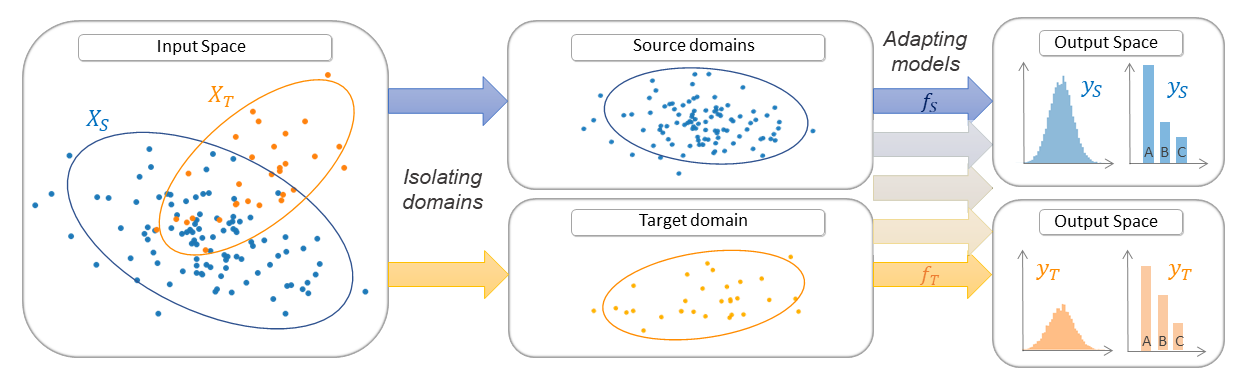
Model-based Transfer

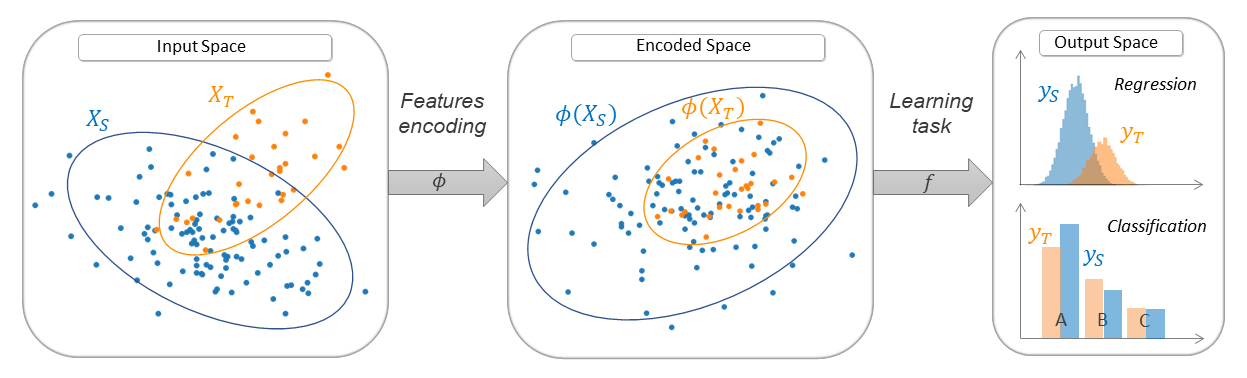
Deep Domain Adaptation

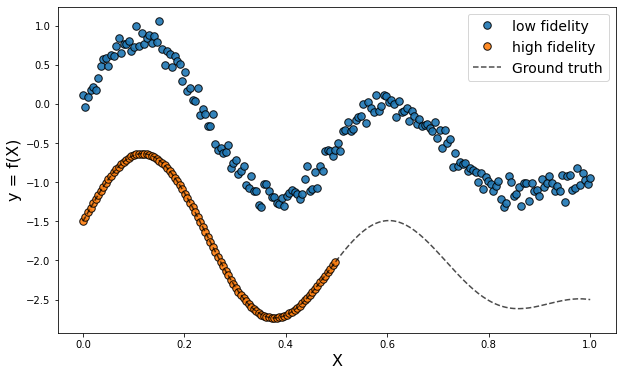
Multi-Fidelity Transfer
|
Sample bias correction 
|
Model-based Transfer 
|
|
Deep Domain Adaptation 
|
Multi-Fidelity Transfer 
|
|
Adapt Estimator ```python AdaptEstimator( estimator = """A scikit-learn estimator (like Ridge(alpha=1.) for example) or a Tensorflow Model""", Xt = "The target input features", yt = "The target output labels (if any)", **params = "Hyper-parameters of the AdaptEstimator" ) ``` |
Deep Adapt Estimator ```python DeepAdaptEstimator( encoder = "A Tensorflow Model (if required)", task = "A Tensorflow Model (if required)", discriminator = "A Tensorflow Model (if required)", Xt = "The target input features", yt = "The target output labels (if any)", **params = """Hyper-parameters of the DeepAdaptEstimator and the compile and fit params (optimizer, epochs...)""" ) ``` |
Scikit-learn Meta-Estimator ```python SklearnMetaEstimator( base_estimator = """A scikit-learn estimator (like Ridge(alpha=1.) for example)""", **params = "Hyper-parameters of the SklearnMetaEstimator" ) ``` |
 ](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/map.html)
## Quick Start
Here is a simple usage example of the ADAPT library. This is a simulation of a 1D sample bias problem with binary classfication task. The source input data are distributed according to a Gaussian distribution centered in -1 with standard deviation of 2. The target data are drawn from Gaussian distribution centered in 1 with standard deviation of 2. The output labels are equal to 1 in the interval [-1, 1] and 0 elsewhere. We apply the transfer method [KMM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KMM.html) which is an unsupervised instance-based algortihm.
```python
# Import standard librairies
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
# Import KMM method form adapt.instance_based module
from adapt.instance_based import KMM
np.random.seed(0)
# Create source dataset (Xs ~ N(-1, 2))
# ys = 1 for ys in [-1, 1] else, ys = 0
Xs = np.random.randn(1000, 1)*2-1
ys = (Xs[:, 0] > -1.) & (Xs[:, 0] < 1.)
# Create target dataset (Xt ~ N(1, 2)), yt ~ ys
Xt = np.random.randn(1000, 1)*2+1
yt = (Xt[:, 0] > -1.) & (Xt[:, 0] < 1.)
# Instantiate and fit a source only model for comparison
src_only = LogisticRegression(penalty="none")
src_only.fit(Xs, ys)
# Instantiate a KMM model : estimator and target input
# data Xt are given as parameters with the kernel parameters
adapt_model = KMM(
estimator=LogisticRegression(penalty="none"),
Xt=Xt,
kernel="rbf", # Gaussian kernel
gamma=1., # Bandwidth of the kernel
verbose=0,
random_state=0
)
# Fit the model.
adapt_model.fit(Xs, ys);
# Get the score on target data
adapt_model.score(Xt, yt)
```
```python
>>> 0.574
```
|
](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/map.html)
## Quick Start
Here is a simple usage example of the ADAPT library. This is a simulation of a 1D sample bias problem with binary classfication task. The source input data are distributed according to a Gaussian distribution centered in -1 with standard deviation of 2. The target data are drawn from Gaussian distribution centered in 1 with standard deviation of 2. The output labels are equal to 1 in the interval [-1, 1] and 0 elsewhere. We apply the transfer method [KMM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KMM.html) which is an unsupervised instance-based algortihm.
```python
# Import standard librairies
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
# Import KMM method form adapt.instance_based module
from adapt.instance_based import KMM
np.random.seed(0)
# Create source dataset (Xs ~ N(-1, 2))
# ys = 1 for ys in [-1, 1] else, ys = 0
Xs = np.random.randn(1000, 1)*2-1
ys = (Xs[:, 0] > -1.) & (Xs[:, 0] < 1.)
# Create target dataset (Xt ~ N(1, 2)), yt ~ ys
Xt = np.random.randn(1000, 1)*2+1
yt = (Xt[:, 0] > -1.) & (Xt[:, 0] < 1.)
# Instantiate and fit a source only model for comparison
src_only = LogisticRegression(penalty="none")
src_only.fit(Xs, ys)
# Instantiate a KMM model : estimator and target input
# data Xt are given as parameters with the kernel parameters
adapt_model = KMM(
estimator=LogisticRegression(penalty="none"),
Xt=Xt,
kernel="rbf", # Gaussian kernel
gamma=1., # Bandwidth of the kernel
verbose=0,
random_state=0
)
# Fit the model.
adapt_model.fit(Xs, ys);
# Get the score on target data
adapt_model.score(Xt, yt)
```
```python
>>> 0.574
```
|  |
|:--:|
| **Quick-Start Plotting Results**. *The dotted and dashed lines are respectively the class separation of the "source only" and KMM models. Note that the predicted positive class is on the right of the dotted line for the "source only" model but on the left of the dashed line for KMM. (The code for plotting the Figure is available [here](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/examples/Quick_start.html))* |
## Contents
ADAPT package is divided in three sub-modules containing the following domain adaptation methods:
### Feature-based methods
|
|:--:|
| **Quick-Start Plotting Results**. *The dotted and dashed lines are respectively the class separation of the "source only" and KMM models. Note that the predicted positive class is on the right of the dotted line for the "source only" model but on the left of the dashed line for KMM. (The code for plotting the Figure is available [here](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/examples/Quick_start.html))* |
## Contents
ADAPT package is divided in three sub-modules containing the following domain adaptation methods:
### Feature-based methods
 - [FA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.FA.html) (*Frustratingly Easy Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/0907.1815.pdf)
- [SA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.SA.html) (*Subspace Alignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.5241)
- [fMMD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.SA.html) (*feature Selection with MMD*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/Web/People/jgc/publication/Feature%20Selection%20for%20Transfer%20Learning.pdf)
- [DANN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.DANN.html) (*Discriminative Adversarial Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://jmlr.org/papers/volume17/15-239/15-239.pdf)
- [ADDA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.ADDA.html) (*Adversarial Discriminative Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1702.05464.pdf)
- [CORAL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CORAL.html) (*CORrelation ALignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.05547.pdf)
- [DeepCORAL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.DeepCORAL.html) (*Deep CORrelation ALignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1607.01719.pdf)
- [MCD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.MCD.html) (*Maximum Classifier Discrepancy*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1712.02560.pdf)
- [MDD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.MDD.html) (*Margin Disparity Discrepancy*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.05801.pdf)
- [WDGRL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.WDGRL.html) (*Wasserstein Distance Guided Representation Learning*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.01217.pdf)
- [CDAN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CDAN.html) (*Conditional Adversarial Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.10667.pdf)
- [CCSA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CCSA.html) (*Classification and Contrastive Semantic Alignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.10190)
### Instance-based methods
- [FA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.FA.html) (*Frustratingly Easy Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/0907.1815.pdf)
- [SA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.SA.html) (*Subspace Alignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.5241)
- [fMMD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.SA.html) (*feature Selection with MMD*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/Web/People/jgc/publication/Feature%20Selection%20for%20Transfer%20Learning.pdf)
- [DANN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.DANN.html) (*Discriminative Adversarial Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://jmlr.org/papers/volume17/15-239/15-239.pdf)
- [ADDA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.ADDA.html) (*Adversarial Discriminative Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1702.05464.pdf)
- [CORAL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CORAL.html) (*CORrelation ALignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.05547.pdf)
- [DeepCORAL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.DeepCORAL.html) (*Deep CORrelation ALignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1607.01719.pdf)
- [MCD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.MCD.html) (*Maximum Classifier Discrepancy*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1712.02560.pdf)
- [MDD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.MDD.html) (*Margin Disparity Discrepancy*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.05801.pdf)
- [WDGRL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.WDGRL.html) (*Wasserstein Distance Guided Representation Learning*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.01217.pdf)
- [CDAN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CDAN.html) (*Conditional Adversarial Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.10667.pdf)
- [CCSA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CCSA.html) (*Classification and Contrastive Semantic Alignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.10190)
### Instance-based methods
 - [LDM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.LDM.html) (*Linear Discrepancy Minimization*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/0902.3430.pdf)
- [KMM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KMM.html) (*Kernel Mean Matching*) [[paper]](https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2006/file/a2186aa7c086b46ad4e8bf81e2a3a19b-Paper.pdf)
- [KLIEP](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KLIEP.html) (*Kullback–Leibler Importance Estimation Procedure*) [[paper]](https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2007/file/be83ab3ecd0db773eb2dc1b0a17836a1-Paper.pdf)
- [TrAdaBoost](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TrAdaBoost.html) (*Transfer AdaBoost*) [[paper]](https://cse.hkust.edu.hk/~qyang/Docs/2007/tradaboost.pdf)
- [TrAdaBoostR2](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TrAdaBoostR2.html) (*Transfer AdaBoost for Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.utexas.edu/~dpardoe/papers/ICML10.pdf)
- [TwoStageTrAdaBoostR2](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TwoStageTrAdaBoostR2.html) (*Two Stage Transfer AdaBoost for Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.utexas.edu/~dpardoe/papers/ICML10.pdf)
- [NearestNeighborsWeighting](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.NearestNeighborsWeighting.html) (*Nearest Neighbors Weighting*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2102.02291.pdf)
- [WANN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.WANN.html) (*Weighting Adversarial Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2006.08251.pdf)
### Parameter-based methods
- [LDM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.LDM.html) (*Linear Discrepancy Minimization*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/0902.3430.pdf)
- [KMM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KMM.html) (*Kernel Mean Matching*) [[paper]](https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2006/file/a2186aa7c086b46ad4e8bf81e2a3a19b-Paper.pdf)
- [KLIEP](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KLIEP.html) (*Kullback–Leibler Importance Estimation Procedure*) [[paper]](https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2007/file/be83ab3ecd0db773eb2dc1b0a17836a1-Paper.pdf)
- [TrAdaBoost](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TrAdaBoost.html) (*Transfer AdaBoost*) [[paper]](https://cse.hkust.edu.hk/~qyang/Docs/2007/tradaboost.pdf)
- [TrAdaBoostR2](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TrAdaBoostR2.html) (*Transfer AdaBoost for Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.utexas.edu/~dpardoe/papers/ICML10.pdf)
- [TwoStageTrAdaBoostR2](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TwoStageTrAdaBoostR2.html) (*Two Stage Transfer AdaBoost for Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.utexas.edu/~dpardoe/papers/ICML10.pdf)
- [NearestNeighborsWeighting](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.NearestNeighborsWeighting.html) (*Nearest Neighbors Weighting*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2102.02291.pdf)
- [WANN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.WANN.html) (*Weighting Adversarial Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2006.08251.pdf)
### Parameter-based methods
 - [RegularTransferLR](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferLR.html) (*Regular Transfer with Linear Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/wp-content/uploads/2004/07/2004-chelba-emnlp.pdf)
- [RegularTransferLC](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferLC.html) (*Regular Transfer with Linear Classification*) [[paper]](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/wp-content/uploads/2004/07/2004-chelba-emnlp.pdf)
- [RegularTransferNN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferNN.html) (*Regular Transfer with Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://hal.inria.fr/hal-00911179v1/document)
- [FineTuning](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.FineTuning.html) (*Fine-Tuning*) [[paper]](https://hal.inria.fr/hal-00911179v1/document)
- [TransferTreeClassifier](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.TransferTreeClassifier.html) (*Transfer Tree Classifier*) [[paper]](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8995296)
- [TransferTreeForest](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.TransferTreeForest.html) (*Transfer Tree Forest*) [[paper]](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8995296)
## Reference
If you use this library in your research, please cite ADAPT using the following reference: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2107.03049.pdf
```
@article{de2021adapt,
title={ADAPT: Awesome Domain Adaptation Python Toolbox},
author={de Mathelin, Antoine and Deheeger, Fran{\c{c}}ois and Richard, Guillaume and Mougeot, Mathilde and Vayatis, Nicolas},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.03049},
year={2021}
}
```
## Acknowledgement
This work has been funded by Michelin and the Industrial Data Analytics and Machine Learning chair from ENS Paris-Saclay, Borelli center.
[
- [RegularTransferLR](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferLR.html) (*Regular Transfer with Linear Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/wp-content/uploads/2004/07/2004-chelba-emnlp.pdf)
- [RegularTransferLC](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferLC.html) (*Regular Transfer with Linear Classification*) [[paper]](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/wp-content/uploads/2004/07/2004-chelba-emnlp.pdf)
- [RegularTransferNN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferNN.html) (*Regular Transfer with Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://hal.inria.fr/hal-00911179v1/document)
- [FineTuning](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.FineTuning.html) (*Fine-Tuning*) [[paper]](https://hal.inria.fr/hal-00911179v1/document)
- [TransferTreeClassifier](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.TransferTreeClassifier.html) (*Transfer Tree Classifier*) [[paper]](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8995296)
- [TransferTreeForest](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.TransferTreeForest.html) (*Transfer Tree Forest*) [[paper]](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8995296)
## Reference
If you use this library in your research, please cite ADAPT using the following reference: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2107.03049.pdf
```
@article{de2021adapt,
title={ADAPT: Awesome Domain Adaptation Python Toolbox},
author={de Mathelin, Antoine and Deheeger, Fran{\c{c}}ois and Richard, Guillaume and Mougeot, Mathilde and Vayatis, Nicolas},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.03049},
year={2021}
}
```
## Acknowledgement
This work has been funded by Michelin and the Industrial Data Analytics and Machine Learning chair from ENS Paris-Saclay, Borelli center.
[ ](https://www.michelin.com/) [
](https://www.michelin.com/) [ ](https://centreborelli.ens-paris-saclay.fr/fr/chaire-idaml) [
](https://centreborelli.ens-paris-saclay.fr/fr/chaire-idaml) [ ](https://centreborelli.ens-paris-saclay.fr/fr)
%package -n python3-adapt
Summary: Awesome Domain Adaptation Python Toolbox for Tensorflow and Scikit-learn
Provides: python-adapt
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3-setuptools
BuildRequires: python3-pip
%description -n python3-adapt
ADAPT is an open source library providing numerous tools to perform Transfer Learning and Domain Adaptation.
The purpose of the ADAPT library is to facilitate the access to transfer learning algorithms for a large public, including industrial players. ADAPT is specifically designed for [Scikit-learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/) and [Tensorflow](https://www.tensorflow.org/) users with a "user-friendly" approach. All objects in ADAPT implement the ***fit***, ***predict*** and ***score*** methods like any scikit-learn object. A very detailed documentation with several examples is provided:
](https://centreborelli.ens-paris-saclay.fr/fr)
%package -n python3-adapt
Summary: Awesome Domain Adaptation Python Toolbox for Tensorflow and Scikit-learn
Provides: python-adapt
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3-setuptools
BuildRequires: python3-pip
%description -n python3-adapt
ADAPT is an open source library providing numerous tools to perform Transfer Learning and Domain Adaptation.
The purpose of the ADAPT library is to facilitate the access to transfer learning algorithms for a large public, including industrial players. ADAPT is specifically designed for [Scikit-learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/) and [Tensorflow](https://www.tensorflow.org/) users with a "user-friendly" approach. All objects in ADAPT implement the ***fit***, ***predict*** and ***score*** methods like any scikit-learn object. A very detailed documentation with several examples is provided:
|
Sample bias correction 
|
Model-based Transfer 
|
|
Deep Domain Adaptation 
|
Multi-Fidelity Transfer 
|
|
Adapt Estimator ```python AdaptEstimator( estimator = """A scikit-learn estimator (like Ridge(alpha=1.) for example) or a Tensorflow Model""", Xt = "The target input features", yt = "The target output labels (if any)", **params = "Hyper-parameters of the AdaptEstimator" ) ``` |
Deep Adapt Estimator ```python DeepAdaptEstimator( encoder = "A Tensorflow Model (if required)", task = "A Tensorflow Model (if required)", discriminator = "A Tensorflow Model (if required)", Xt = "The target input features", yt = "The target output labels (if any)", **params = """Hyper-parameters of the DeepAdaptEstimator and the compile and fit params (optimizer, epochs...)""" ) ``` |
Scikit-learn Meta-Estimator ```python SklearnMetaEstimator( base_estimator = """A scikit-learn estimator (like Ridge(alpha=1.) for example)""", **params = "Hyper-parameters of the SklearnMetaEstimator" ) ``` |
 ](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/map.html)
## Quick Start
Here is a simple usage example of the ADAPT library. This is a simulation of a 1D sample bias problem with binary classfication task. The source input data are distributed according to a Gaussian distribution centered in -1 with standard deviation of 2. The target data are drawn from Gaussian distribution centered in 1 with standard deviation of 2. The output labels are equal to 1 in the interval [-1, 1] and 0 elsewhere. We apply the transfer method [KMM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KMM.html) which is an unsupervised instance-based algortihm.
```python
# Import standard librairies
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
# Import KMM method form adapt.instance_based module
from adapt.instance_based import KMM
np.random.seed(0)
# Create source dataset (Xs ~ N(-1, 2))
# ys = 1 for ys in [-1, 1] else, ys = 0
Xs = np.random.randn(1000, 1)*2-1
ys = (Xs[:, 0] > -1.) & (Xs[:, 0] < 1.)
# Create target dataset (Xt ~ N(1, 2)), yt ~ ys
Xt = np.random.randn(1000, 1)*2+1
yt = (Xt[:, 0] > -1.) & (Xt[:, 0] < 1.)
# Instantiate and fit a source only model for comparison
src_only = LogisticRegression(penalty="none")
src_only.fit(Xs, ys)
# Instantiate a KMM model : estimator and target input
# data Xt are given as parameters with the kernel parameters
adapt_model = KMM(
estimator=LogisticRegression(penalty="none"),
Xt=Xt,
kernel="rbf", # Gaussian kernel
gamma=1., # Bandwidth of the kernel
verbose=0,
random_state=0
)
# Fit the model.
adapt_model.fit(Xs, ys);
# Get the score on target data
adapt_model.score(Xt, yt)
```
```python
>>> 0.574
```
|
](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/map.html)
## Quick Start
Here is a simple usage example of the ADAPT library. This is a simulation of a 1D sample bias problem with binary classfication task. The source input data are distributed according to a Gaussian distribution centered in -1 with standard deviation of 2. The target data are drawn from Gaussian distribution centered in 1 with standard deviation of 2. The output labels are equal to 1 in the interval [-1, 1] and 0 elsewhere. We apply the transfer method [KMM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KMM.html) which is an unsupervised instance-based algortihm.
```python
# Import standard librairies
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
# Import KMM method form adapt.instance_based module
from adapt.instance_based import KMM
np.random.seed(0)
# Create source dataset (Xs ~ N(-1, 2))
# ys = 1 for ys in [-1, 1] else, ys = 0
Xs = np.random.randn(1000, 1)*2-1
ys = (Xs[:, 0] > -1.) & (Xs[:, 0] < 1.)
# Create target dataset (Xt ~ N(1, 2)), yt ~ ys
Xt = np.random.randn(1000, 1)*2+1
yt = (Xt[:, 0] > -1.) & (Xt[:, 0] < 1.)
# Instantiate and fit a source only model for comparison
src_only = LogisticRegression(penalty="none")
src_only.fit(Xs, ys)
# Instantiate a KMM model : estimator and target input
# data Xt are given as parameters with the kernel parameters
adapt_model = KMM(
estimator=LogisticRegression(penalty="none"),
Xt=Xt,
kernel="rbf", # Gaussian kernel
gamma=1., # Bandwidth of the kernel
verbose=0,
random_state=0
)
# Fit the model.
adapt_model.fit(Xs, ys);
# Get the score on target data
adapt_model.score(Xt, yt)
```
```python
>>> 0.574
```
|  |
|:--:|
| **Quick-Start Plotting Results**. *The dotted and dashed lines are respectively the class separation of the "source only" and KMM models. Note that the predicted positive class is on the right of the dotted line for the "source only" model but on the left of the dashed line for KMM. (The code for plotting the Figure is available [here](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/examples/Quick_start.html))* |
## Contents
ADAPT package is divided in three sub-modules containing the following domain adaptation methods:
### Feature-based methods
|
|:--:|
| **Quick-Start Plotting Results**. *The dotted and dashed lines are respectively the class separation of the "source only" and KMM models. Note that the predicted positive class is on the right of the dotted line for the "source only" model but on the left of the dashed line for KMM. (The code for plotting the Figure is available [here](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/examples/Quick_start.html))* |
## Contents
ADAPT package is divided in three sub-modules containing the following domain adaptation methods:
### Feature-based methods
 - [FA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.FA.html) (*Frustratingly Easy Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/0907.1815.pdf)
- [SA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.SA.html) (*Subspace Alignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.5241)
- [fMMD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.SA.html) (*feature Selection with MMD*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/Web/People/jgc/publication/Feature%20Selection%20for%20Transfer%20Learning.pdf)
- [DANN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.DANN.html) (*Discriminative Adversarial Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://jmlr.org/papers/volume17/15-239/15-239.pdf)
- [ADDA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.ADDA.html) (*Adversarial Discriminative Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1702.05464.pdf)
- [CORAL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CORAL.html) (*CORrelation ALignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.05547.pdf)
- [DeepCORAL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.DeepCORAL.html) (*Deep CORrelation ALignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1607.01719.pdf)
- [MCD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.MCD.html) (*Maximum Classifier Discrepancy*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1712.02560.pdf)
- [MDD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.MDD.html) (*Margin Disparity Discrepancy*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.05801.pdf)
- [WDGRL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.WDGRL.html) (*Wasserstein Distance Guided Representation Learning*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.01217.pdf)
- [CDAN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CDAN.html) (*Conditional Adversarial Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.10667.pdf)
- [CCSA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CCSA.html) (*Classification and Contrastive Semantic Alignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.10190)
### Instance-based methods
- [FA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.FA.html) (*Frustratingly Easy Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/0907.1815.pdf)
- [SA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.SA.html) (*Subspace Alignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.5241)
- [fMMD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.SA.html) (*feature Selection with MMD*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/Web/People/jgc/publication/Feature%20Selection%20for%20Transfer%20Learning.pdf)
- [DANN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.DANN.html) (*Discriminative Adversarial Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://jmlr.org/papers/volume17/15-239/15-239.pdf)
- [ADDA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.ADDA.html) (*Adversarial Discriminative Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1702.05464.pdf)
- [CORAL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CORAL.html) (*CORrelation ALignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.05547.pdf)
- [DeepCORAL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.DeepCORAL.html) (*Deep CORrelation ALignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1607.01719.pdf)
- [MCD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.MCD.html) (*Maximum Classifier Discrepancy*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1712.02560.pdf)
- [MDD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.MDD.html) (*Margin Disparity Discrepancy*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.05801.pdf)
- [WDGRL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.WDGRL.html) (*Wasserstein Distance Guided Representation Learning*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.01217.pdf)
- [CDAN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CDAN.html) (*Conditional Adversarial Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.10667.pdf)
- [CCSA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CCSA.html) (*Classification and Contrastive Semantic Alignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.10190)
### Instance-based methods
 - [LDM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.LDM.html) (*Linear Discrepancy Minimization*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/0902.3430.pdf)
- [KMM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KMM.html) (*Kernel Mean Matching*) [[paper]](https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2006/file/a2186aa7c086b46ad4e8bf81e2a3a19b-Paper.pdf)
- [KLIEP](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KLIEP.html) (*Kullback–Leibler Importance Estimation Procedure*) [[paper]](https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2007/file/be83ab3ecd0db773eb2dc1b0a17836a1-Paper.pdf)
- [TrAdaBoost](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TrAdaBoost.html) (*Transfer AdaBoost*) [[paper]](https://cse.hkust.edu.hk/~qyang/Docs/2007/tradaboost.pdf)
- [TrAdaBoostR2](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TrAdaBoostR2.html) (*Transfer AdaBoost for Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.utexas.edu/~dpardoe/papers/ICML10.pdf)
- [TwoStageTrAdaBoostR2](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TwoStageTrAdaBoostR2.html) (*Two Stage Transfer AdaBoost for Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.utexas.edu/~dpardoe/papers/ICML10.pdf)
- [NearestNeighborsWeighting](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.NearestNeighborsWeighting.html) (*Nearest Neighbors Weighting*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2102.02291.pdf)
- [WANN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.WANN.html) (*Weighting Adversarial Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2006.08251.pdf)
### Parameter-based methods
- [LDM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.LDM.html) (*Linear Discrepancy Minimization*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/0902.3430.pdf)
- [KMM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KMM.html) (*Kernel Mean Matching*) [[paper]](https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2006/file/a2186aa7c086b46ad4e8bf81e2a3a19b-Paper.pdf)
- [KLIEP](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KLIEP.html) (*Kullback–Leibler Importance Estimation Procedure*) [[paper]](https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2007/file/be83ab3ecd0db773eb2dc1b0a17836a1-Paper.pdf)
- [TrAdaBoost](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TrAdaBoost.html) (*Transfer AdaBoost*) [[paper]](https://cse.hkust.edu.hk/~qyang/Docs/2007/tradaboost.pdf)
- [TrAdaBoostR2](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TrAdaBoostR2.html) (*Transfer AdaBoost for Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.utexas.edu/~dpardoe/papers/ICML10.pdf)
- [TwoStageTrAdaBoostR2](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TwoStageTrAdaBoostR2.html) (*Two Stage Transfer AdaBoost for Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.utexas.edu/~dpardoe/papers/ICML10.pdf)
- [NearestNeighborsWeighting](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.NearestNeighborsWeighting.html) (*Nearest Neighbors Weighting*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2102.02291.pdf)
- [WANN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.WANN.html) (*Weighting Adversarial Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2006.08251.pdf)
### Parameter-based methods
 - [RegularTransferLR](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferLR.html) (*Regular Transfer with Linear Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/wp-content/uploads/2004/07/2004-chelba-emnlp.pdf)
- [RegularTransferLC](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferLC.html) (*Regular Transfer with Linear Classification*) [[paper]](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/wp-content/uploads/2004/07/2004-chelba-emnlp.pdf)
- [RegularTransferNN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferNN.html) (*Regular Transfer with Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://hal.inria.fr/hal-00911179v1/document)
- [FineTuning](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.FineTuning.html) (*Fine-Tuning*) [[paper]](https://hal.inria.fr/hal-00911179v1/document)
- [TransferTreeClassifier](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.TransferTreeClassifier.html) (*Transfer Tree Classifier*) [[paper]](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8995296)
- [TransferTreeForest](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.TransferTreeForest.html) (*Transfer Tree Forest*) [[paper]](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8995296)
## Reference
If you use this library in your research, please cite ADAPT using the following reference: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2107.03049.pdf
```
@article{de2021adapt,
title={ADAPT: Awesome Domain Adaptation Python Toolbox},
author={de Mathelin, Antoine and Deheeger, Fran{\c{c}}ois and Richard, Guillaume and Mougeot, Mathilde and Vayatis, Nicolas},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.03049},
year={2021}
}
```
## Acknowledgement
This work has been funded by Michelin and the Industrial Data Analytics and Machine Learning chair from ENS Paris-Saclay, Borelli center.
[
- [RegularTransferLR](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferLR.html) (*Regular Transfer with Linear Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/wp-content/uploads/2004/07/2004-chelba-emnlp.pdf)
- [RegularTransferLC](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferLC.html) (*Regular Transfer with Linear Classification*) [[paper]](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/wp-content/uploads/2004/07/2004-chelba-emnlp.pdf)
- [RegularTransferNN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferNN.html) (*Regular Transfer with Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://hal.inria.fr/hal-00911179v1/document)
- [FineTuning](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.FineTuning.html) (*Fine-Tuning*) [[paper]](https://hal.inria.fr/hal-00911179v1/document)
- [TransferTreeClassifier](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.TransferTreeClassifier.html) (*Transfer Tree Classifier*) [[paper]](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8995296)
- [TransferTreeForest](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.TransferTreeForest.html) (*Transfer Tree Forest*) [[paper]](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8995296)
## Reference
If you use this library in your research, please cite ADAPT using the following reference: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2107.03049.pdf
```
@article{de2021adapt,
title={ADAPT: Awesome Domain Adaptation Python Toolbox},
author={de Mathelin, Antoine and Deheeger, Fran{\c{c}}ois and Richard, Guillaume and Mougeot, Mathilde and Vayatis, Nicolas},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.03049},
year={2021}
}
```
## Acknowledgement
This work has been funded by Michelin and the Industrial Data Analytics and Machine Learning chair from ENS Paris-Saclay, Borelli center.
[ ](https://www.michelin.com/) [
](https://www.michelin.com/) [ ](https://centreborelli.ens-paris-saclay.fr/fr/chaire-idaml) [
](https://centreborelli.ens-paris-saclay.fr/fr/chaire-idaml) [ ](https://centreborelli.ens-paris-saclay.fr/fr)
%package help
Summary: Development documents and examples for adapt
Provides: python3-adapt-doc
%description help
ADAPT is an open source library providing numerous tools to perform Transfer Learning and Domain Adaptation.
The purpose of the ADAPT library is to facilitate the access to transfer learning algorithms for a large public, including industrial players. ADAPT is specifically designed for [Scikit-learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/) and [Tensorflow](https://www.tensorflow.org/) users with a "user-friendly" approach. All objects in ADAPT implement the ***fit***, ***predict*** and ***score*** methods like any scikit-learn object. A very detailed documentation with several examples is provided:
](https://centreborelli.ens-paris-saclay.fr/fr)
%package help
Summary: Development documents and examples for adapt
Provides: python3-adapt-doc
%description help
ADAPT is an open source library providing numerous tools to perform Transfer Learning and Domain Adaptation.
The purpose of the ADAPT library is to facilitate the access to transfer learning algorithms for a large public, including industrial players. ADAPT is specifically designed for [Scikit-learn](https://scikit-learn.org/stable/) and [Tensorflow](https://www.tensorflow.org/) users with a "user-friendly" approach. All objects in ADAPT implement the ***fit***, ***predict*** and ***score*** methods like any scikit-learn object. A very detailed documentation with several examples is provided:
|
Sample bias correction 
|
Model-based Transfer 
|
|
Deep Domain Adaptation 
|
Multi-Fidelity Transfer 
|
|
Adapt Estimator ```python AdaptEstimator( estimator = """A scikit-learn estimator (like Ridge(alpha=1.) for example) or a Tensorflow Model""", Xt = "The target input features", yt = "The target output labels (if any)", **params = "Hyper-parameters of the AdaptEstimator" ) ``` |
Deep Adapt Estimator ```python DeepAdaptEstimator( encoder = "A Tensorflow Model (if required)", task = "A Tensorflow Model (if required)", discriminator = "A Tensorflow Model (if required)", Xt = "The target input features", yt = "The target output labels (if any)", **params = """Hyper-parameters of the DeepAdaptEstimator and the compile and fit params (optimizer, epochs...)""" ) ``` |
Scikit-learn Meta-Estimator ```python SklearnMetaEstimator( base_estimator = """A scikit-learn estimator (like Ridge(alpha=1.) for example)""", **params = "Hyper-parameters of the SklearnMetaEstimator" ) ``` |
 ](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/map.html)
## Quick Start
Here is a simple usage example of the ADAPT library. This is a simulation of a 1D sample bias problem with binary classfication task. The source input data are distributed according to a Gaussian distribution centered in -1 with standard deviation of 2. The target data are drawn from Gaussian distribution centered in 1 with standard deviation of 2. The output labels are equal to 1 in the interval [-1, 1] and 0 elsewhere. We apply the transfer method [KMM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KMM.html) which is an unsupervised instance-based algortihm.
```python
# Import standard librairies
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
# Import KMM method form adapt.instance_based module
from adapt.instance_based import KMM
np.random.seed(0)
# Create source dataset (Xs ~ N(-1, 2))
# ys = 1 for ys in [-1, 1] else, ys = 0
Xs = np.random.randn(1000, 1)*2-1
ys = (Xs[:, 0] > -1.) & (Xs[:, 0] < 1.)
# Create target dataset (Xt ~ N(1, 2)), yt ~ ys
Xt = np.random.randn(1000, 1)*2+1
yt = (Xt[:, 0] > -1.) & (Xt[:, 0] < 1.)
# Instantiate and fit a source only model for comparison
src_only = LogisticRegression(penalty="none")
src_only.fit(Xs, ys)
# Instantiate a KMM model : estimator and target input
# data Xt are given as parameters with the kernel parameters
adapt_model = KMM(
estimator=LogisticRegression(penalty="none"),
Xt=Xt,
kernel="rbf", # Gaussian kernel
gamma=1., # Bandwidth of the kernel
verbose=0,
random_state=0
)
# Fit the model.
adapt_model.fit(Xs, ys);
# Get the score on target data
adapt_model.score(Xt, yt)
```
```python
>>> 0.574
```
|
](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/map.html)
## Quick Start
Here is a simple usage example of the ADAPT library. This is a simulation of a 1D sample bias problem with binary classfication task. The source input data are distributed according to a Gaussian distribution centered in -1 with standard deviation of 2. The target data are drawn from Gaussian distribution centered in 1 with standard deviation of 2. The output labels are equal to 1 in the interval [-1, 1] and 0 elsewhere. We apply the transfer method [KMM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KMM.html) which is an unsupervised instance-based algortihm.
```python
# Import standard librairies
import numpy as np
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
# Import KMM method form adapt.instance_based module
from adapt.instance_based import KMM
np.random.seed(0)
# Create source dataset (Xs ~ N(-1, 2))
# ys = 1 for ys in [-1, 1] else, ys = 0
Xs = np.random.randn(1000, 1)*2-1
ys = (Xs[:, 0] > -1.) & (Xs[:, 0] < 1.)
# Create target dataset (Xt ~ N(1, 2)), yt ~ ys
Xt = np.random.randn(1000, 1)*2+1
yt = (Xt[:, 0] > -1.) & (Xt[:, 0] < 1.)
# Instantiate and fit a source only model for comparison
src_only = LogisticRegression(penalty="none")
src_only.fit(Xs, ys)
# Instantiate a KMM model : estimator and target input
# data Xt are given as parameters with the kernel parameters
adapt_model = KMM(
estimator=LogisticRegression(penalty="none"),
Xt=Xt,
kernel="rbf", # Gaussian kernel
gamma=1., # Bandwidth of the kernel
verbose=0,
random_state=0
)
# Fit the model.
adapt_model.fit(Xs, ys);
# Get the score on target data
adapt_model.score(Xt, yt)
```
```python
>>> 0.574
```
|  |
|:--:|
| **Quick-Start Plotting Results**. *The dotted and dashed lines are respectively the class separation of the "source only" and KMM models. Note that the predicted positive class is on the right of the dotted line for the "source only" model but on the left of the dashed line for KMM. (The code for plotting the Figure is available [here](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/examples/Quick_start.html))* |
## Contents
ADAPT package is divided in three sub-modules containing the following domain adaptation methods:
### Feature-based methods
|
|:--:|
| **Quick-Start Plotting Results**. *The dotted and dashed lines are respectively the class separation of the "source only" and KMM models. Note that the predicted positive class is on the right of the dotted line for the "source only" model but on the left of the dashed line for KMM. (The code for plotting the Figure is available [here](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/examples/Quick_start.html))* |
## Contents
ADAPT package is divided in three sub-modules containing the following domain adaptation methods:
### Feature-based methods
 - [FA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.FA.html) (*Frustratingly Easy Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/0907.1815.pdf)
- [SA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.SA.html) (*Subspace Alignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.5241)
- [fMMD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.SA.html) (*feature Selection with MMD*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/Web/People/jgc/publication/Feature%20Selection%20for%20Transfer%20Learning.pdf)
- [DANN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.DANN.html) (*Discriminative Adversarial Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://jmlr.org/papers/volume17/15-239/15-239.pdf)
- [ADDA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.ADDA.html) (*Adversarial Discriminative Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1702.05464.pdf)
- [CORAL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CORAL.html) (*CORrelation ALignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.05547.pdf)
- [DeepCORAL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.DeepCORAL.html) (*Deep CORrelation ALignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1607.01719.pdf)
- [MCD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.MCD.html) (*Maximum Classifier Discrepancy*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1712.02560.pdf)
- [MDD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.MDD.html) (*Margin Disparity Discrepancy*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.05801.pdf)
- [WDGRL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.WDGRL.html) (*Wasserstein Distance Guided Representation Learning*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.01217.pdf)
- [CDAN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CDAN.html) (*Conditional Adversarial Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.10667.pdf)
- [CCSA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CCSA.html) (*Classification and Contrastive Semantic Alignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.10190)
### Instance-based methods
- [FA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.FA.html) (*Frustratingly Easy Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/0907.1815.pdf)
- [SA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.SA.html) (*Subspace Alignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.5241)
- [fMMD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.SA.html) (*feature Selection with MMD*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.cmu.edu/afs/cs/Web/People/jgc/publication/Feature%20Selection%20for%20Transfer%20Learning.pdf)
- [DANN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.DANN.html) (*Discriminative Adversarial Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://jmlr.org/papers/volume17/15-239/15-239.pdf)
- [ADDA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.ADDA.html) (*Adversarial Discriminative Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1702.05464.pdf)
- [CORAL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CORAL.html) (*CORrelation ALignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1511.05547.pdf)
- [DeepCORAL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.DeepCORAL.html) (*Deep CORrelation ALignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1607.01719.pdf)
- [MCD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.MCD.html) (*Maximum Classifier Discrepancy*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1712.02560.pdf)
- [MDD](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.MDD.html) (*Margin Disparity Discrepancy*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1904.05801.pdf)
- [WDGRL](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.WDGRL.html) (*Wasserstein Distance Guided Representation Learning*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.01217.pdf)
- [CDAN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CDAN.html) (*Conditional Adversarial Domain Adaptation*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.10667.pdf)
- [CCSA](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.feature_based.CCSA.html) (*Classification and Contrastive Semantic Alignment*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/abs/1709.10190)
### Instance-based methods
 - [LDM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.LDM.html) (*Linear Discrepancy Minimization*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/0902.3430.pdf)
- [KMM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KMM.html) (*Kernel Mean Matching*) [[paper]](https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2006/file/a2186aa7c086b46ad4e8bf81e2a3a19b-Paper.pdf)
- [KLIEP](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KLIEP.html) (*Kullback–Leibler Importance Estimation Procedure*) [[paper]](https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2007/file/be83ab3ecd0db773eb2dc1b0a17836a1-Paper.pdf)
- [TrAdaBoost](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TrAdaBoost.html) (*Transfer AdaBoost*) [[paper]](https://cse.hkust.edu.hk/~qyang/Docs/2007/tradaboost.pdf)
- [TrAdaBoostR2](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TrAdaBoostR2.html) (*Transfer AdaBoost for Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.utexas.edu/~dpardoe/papers/ICML10.pdf)
- [TwoStageTrAdaBoostR2](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TwoStageTrAdaBoostR2.html) (*Two Stage Transfer AdaBoost for Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.utexas.edu/~dpardoe/papers/ICML10.pdf)
- [NearestNeighborsWeighting](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.NearestNeighborsWeighting.html) (*Nearest Neighbors Weighting*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2102.02291.pdf)
- [WANN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.WANN.html) (*Weighting Adversarial Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2006.08251.pdf)
### Parameter-based methods
- [LDM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.LDM.html) (*Linear Discrepancy Minimization*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/0902.3430.pdf)
- [KMM](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KMM.html) (*Kernel Mean Matching*) [[paper]](https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2006/file/a2186aa7c086b46ad4e8bf81e2a3a19b-Paper.pdf)
- [KLIEP](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.KLIEP.html) (*Kullback–Leibler Importance Estimation Procedure*) [[paper]](https://proceedings.neurips.cc/paper/2007/file/be83ab3ecd0db773eb2dc1b0a17836a1-Paper.pdf)
- [TrAdaBoost](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TrAdaBoost.html) (*Transfer AdaBoost*) [[paper]](https://cse.hkust.edu.hk/~qyang/Docs/2007/tradaboost.pdf)
- [TrAdaBoostR2](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TrAdaBoostR2.html) (*Transfer AdaBoost for Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.utexas.edu/~dpardoe/papers/ICML10.pdf)
- [TwoStageTrAdaBoostR2](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.TwoStageTrAdaBoostR2.html) (*Two Stage Transfer AdaBoost for Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.cs.utexas.edu/~dpardoe/papers/ICML10.pdf)
- [NearestNeighborsWeighting](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.NearestNeighborsWeighting.html) (*Nearest Neighbors Weighting*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2102.02291.pdf)
- [WANN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.instance_based.WANN.html) (*Weighting Adversarial Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://arxiv.org/pdf/2006.08251.pdf)
### Parameter-based methods
 - [RegularTransferLR](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferLR.html) (*Regular Transfer with Linear Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/wp-content/uploads/2004/07/2004-chelba-emnlp.pdf)
- [RegularTransferLC](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferLC.html) (*Regular Transfer with Linear Classification*) [[paper]](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/wp-content/uploads/2004/07/2004-chelba-emnlp.pdf)
- [RegularTransferNN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferNN.html) (*Regular Transfer with Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://hal.inria.fr/hal-00911179v1/document)
- [FineTuning](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.FineTuning.html) (*Fine-Tuning*) [[paper]](https://hal.inria.fr/hal-00911179v1/document)
- [TransferTreeClassifier](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.TransferTreeClassifier.html) (*Transfer Tree Classifier*) [[paper]](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8995296)
- [TransferTreeForest](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.TransferTreeForest.html) (*Transfer Tree Forest*) [[paper]](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8995296)
## Reference
If you use this library in your research, please cite ADAPT using the following reference: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2107.03049.pdf
```
@article{de2021adapt,
title={ADAPT: Awesome Domain Adaptation Python Toolbox},
author={de Mathelin, Antoine and Deheeger, Fran{\c{c}}ois and Richard, Guillaume and Mougeot, Mathilde and Vayatis, Nicolas},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.03049},
year={2021}
}
```
## Acknowledgement
This work has been funded by Michelin and the Industrial Data Analytics and Machine Learning chair from ENS Paris-Saclay, Borelli center.
[
- [RegularTransferLR](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferLR.html) (*Regular Transfer with Linear Regression*) [[paper]](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/wp-content/uploads/2004/07/2004-chelba-emnlp.pdf)
- [RegularTransferLC](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferLC.html) (*Regular Transfer with Linear Classification*) [[paper]](https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/wp-content/uploads/2004/07/2004-chelba-emnlp.pdf)
- [RegularTransferNN](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.RegularTransferNN.html) (*Regular Transfer with Neural Network*) [[paper]](https://hal.inria.fr/hal-00911179v1/document)
- [FineTuning](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.FineTuning.html) (*Fine-Tuning*) [[paper]](https://hal.inria.fr/hal-00911179v1/document)
- [TransferTreeClassifier](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.TransferTreeClassifier.html) (*Transfer Tree Classifier*) [[paper]](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8995296)
- [TransferTreeForest](https://adapt-python.github.io/adapt/generated/adapt.parameter_based.TransferTreeForest.html) (*Transfer Tree Forest*) [[paper]](https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8995296)
## Reference
If you use this library in your research, please cite ADAPT using the following reference: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2107.03049.pdf
```
@article{de2021adapt,
title={ADAPT: Awesome Domain Adaptation Python Toolbox},
author={de Mathelin, Antoine and Deheeger, Fran{\c{c}}ois and Richard, Guillaume and Mougeot, Mathilde and Vayatis, Nicolas},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2107.03049},
year={2021}
}
```
## Acknowledgement
This work has been funded by Michelin and the Industrial Data Analytics and Machine Learning chair from ENS Paris-Saclay, Borelli center.
[ ](https://www.michelin.com/) [
](https://www.michelin.com/) [ ](https://centreborelli.ens-paris-saclay.fr/fr/chaire-idaml) [
](https://centreborelli.ens-paris-saclay.fr/fr/chaire-idaml) [ ](https://centreborelli.ens-paris-saclay.fr/fr)
%prep
%autosetup -n adapt-0.4.2
%build
%py3_build
%install
%py3_install
install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}
if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
pushd %{buildroot}
if [ -d usr/lib ]; then
find usr/lib -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then
find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/bin ]; then
find usr/bin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then
find usr/sbin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
touch doclist.lst
if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then
find usr/share/man -type f -printf "/%h/%f.gz\n" >> doclist.lst
fi
popd
mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst .
mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst .
%files -n python3-adapt -f filelist.lst
%dir %{python3_sitelib}/*
%files help -f doclist.lst
%{_docdir}/*
%changelog
* Fri Apr 21 2023 Python_Bot
](https://centreborelli.ens-paris-saclay.fr/fr)
%prep
%autosetup -n adapt-0.4.2
%build
%py3_build
%install
%py3_install
install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}
if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
pushd %{buildroot}
if [ -d usr/lib ]; then
find usr/lib -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then
find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/bin ]; then
find usr/bin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then
find usr/sbin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
touch doclist.lst
if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then
find usr/share/man -type f -printf "/%h/%f.gz\n" >> doclist.lst
fi
popd
mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst .
mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst .
%files -n python3-adapt -f filelist.lst
%dir %{python3_sitelib}/*
%files help -f doclist.lst
%{_docdir}/*
%changelog
* Fri Apr 21 2023 Python_Bot