translate_executor.py |
|---|
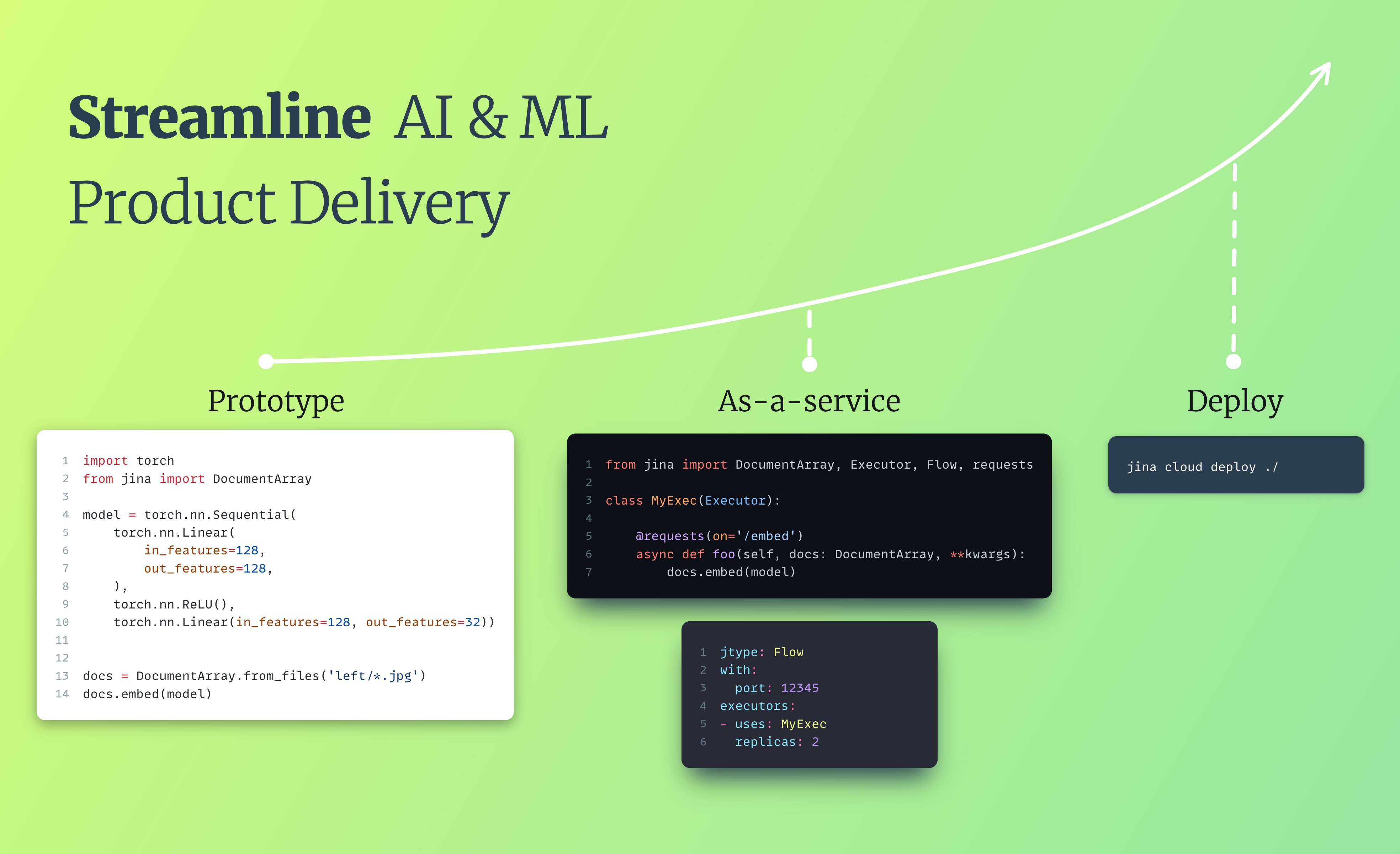
| ```python from docarray import DocumentArray from jina import Executor, requests from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM class Translator(Executor): def __init__(self, **kwargs): super().__init__(**kwargs) self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained( "facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-many-mmt", src_lang="fr_XX" ) self.model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained( "facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-many-mmt" ) @requests def translate(self, docs: DocumentArray, **kwargs): for doc in docs: doc.text = self._translate(doc.text) def _translate(self, text): encoded_en = self.tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt") generated_tokens = self.model.generate( **encoded_en, forced_bos_token_id=self.tokenizer.lang_code_to_id["en_XX"] ) return self.tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)[ 0 ] ``` |
Python API: deployment.py |
YAML: deployment.yml |
|---|---|
| ```python from jina import Deployment from translate_executor import Translator with Deployment(uses=Translator, timeout_ready=-1) as dep: dep.block() ``` | ```yaml jtype: Deployment with: uses: Translator py_modules: - translate_executor.py # name of the module containing Translator timeout_ready: -1 ``` And run the YAML Deployment with the CLI: `jina deployment --uses deployment.yml` |
Python API: flow.py |
YAML: flow.yml |
|---|---|
| ```python from jina import Flow flow = ( Flow() .add(uses=Translator, timeout_ready=-1) .add( uses='jinaai://jina-ai/TextToImage', timeout_ready=-1, install_requirements=True, ) ) # use the Executor from Executor hub with flow: flow.block() ``` | ```yaml jtype: Flow executors: - uses: Translator timeout_ready: -1 py_modules: - translate_executor.py - uses: jinaai://jina-ai/TextToImage timeout_ready: -1 install_requirements: true ``` Then run the YAML Flow with the CLI: `jina flow --uses flow.yml` |
translate_executor.py |
|---|
| ```python from docarray import DocumentArray from jina import Executor, requests from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM class Translator(Executor): def __init__(self, **kwargs): super().__init__(**kwargs) self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained( "facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-many-mmt", src_lang="fr_XX" ) self.model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained( "facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-many-mmt" ) @requests def translate(self, docs: DocumentArray, **kwargs): for doc in docs: doc.text = self._translate(doc.text) def _translate(self, text): encoded_en = self.tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt") generated_tokens = self.model.generate( **encoded_en, forced_bos_token_id=self.tokenizer.lang_code_to_id["en_XX"] ) return self.tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)[ 0 ] ``` |
Python API: deployment.py |
YAML: deployment.yml |
|---|---|
| ```python from jina import Deployment from translate_executor import Translator with Deployment(uses=Translator, timeout_ready=-1) as dep: dep.block() ``` | ```yaml jtype: Deployment with: uses: Translator py_modules: - translate_executor.py # name of the module containing Translator timeout_ready: -1 ``` And run the YAML Deployment with the CLI: `jina deployment --uses deployment.yml` |
Python API: flow.py |
YAML: flow.yml |
|---|---|
| ```python from jina import Flow flow = ( Flow() .add(uses=Translator, timeout_ready=-1) .add( uses='jinaai://jina-ai/TextToImage', timeout_ready=-1, install_requirements=True, ) ) # use the Executor from Executor hub with flow: flow.block() ``` | ```yaml jtype: Flow executors: - uses: Translator timeout_ready: -1 py_modules: - translate_executor.py - uses: jinaai://jina-ai/TextToImage timeout_ready: -1 install_requirements: true ``` Then run the YAML Flow with the CLI: `jina flow --uses flow.yml` |
translate_executor.py |
|---|
| ```python from docarray import DocumentArray from jina import Executor, requests from transformers import AutoTokenizer, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM class Translator(Executor): def __init__(self, **kwargs): super().__init__(**kwargs) self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained( "facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-many-mmt", src_lang="fr_XX" ) self.model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained( "facebook/mbart-large-50-many-to-many-mmt" ) @requests def translate(self, docs: DocumentArray, **kwargs): for doc in docs: doc.text = self._translate(doc.text) def _translate(self, text): encoded_en = self.tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt") generated_tokens = self.model.generate( **encoded_en, forced_bos_token_id=self.tokenizer.lang_code_to_id["en_XX"] ) return self.tokenizer.batch_decode(generated_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True)[ 0 ] ``` |
Python API: deployment.py |
YAML: deployment.yml |
|---|---|
| ```python from jina import Deployment from translate_executor import Translator with Deployment(uses=Translator, timeout_ready=-1) as dep: dep.block() ``` | ```yaml jtype: Deployment with: uses: Translator py_modules: - translate_executor.py # name of the module containing Translator timeout_ready: -1 ``` And run the YAML Deployment with the CLI: `jina deployment --uses deployment.yml` |
Python API: flow.py |
YAML: flow.yml |
|---|---|
| ```python from jina import Flow flow = ( Flow() .add(uses=Translator, timeout_ready=-1) .add( uses='jinaai://jina-ai/TextToImage', timeout_ready=-1, install_requirements=True, ) ) # use the Executor from Executor hub with flow: flow.block() ``` | ```yaml jtype: Flow executors: - uses: Translator timeout_ready: -1 py_modules: - translate_executor.py - uses: jinaai://jina-ai/TextToImage timeout_ready: -1 install_requirements: true ``` Then run the YAML Flow with the CLI: `jina flow --uses flow.yml` |