%global _empty_manifest_terminate_build 0
Name: python-GMM-Demux
Version: 0.2.1.3
Release: 1
Summary: A multiplet removal tool for processing cell hashing data
License: MIT License
URL: https://github.com/CHPGenetics/GMM-demux
Source0: https://mirrors.nju.edu.cn/pypi/web/packages/a4/e6/8cdb23eaf6e3c7b03a960acb11590ba6397deba9ac7258fc05ab2c7b855d/GMM_Demux-0.2.1.3.tar.gz
BuildArch: noarch
Requires: python3-pandas
Requires: python3-numpy
Requires: python3-scipy
Requires: python3-tabulate
Requires: python3-argparse
Requires: python3-statistics
Requires: python3-BitVector
Requires: python3-sklearn
%description
# GMM-Demux
GMM-Demux is a Gaussian-Mixture-Model-based software for processing sample barcoding data (cell hashing and MULTI-seq).
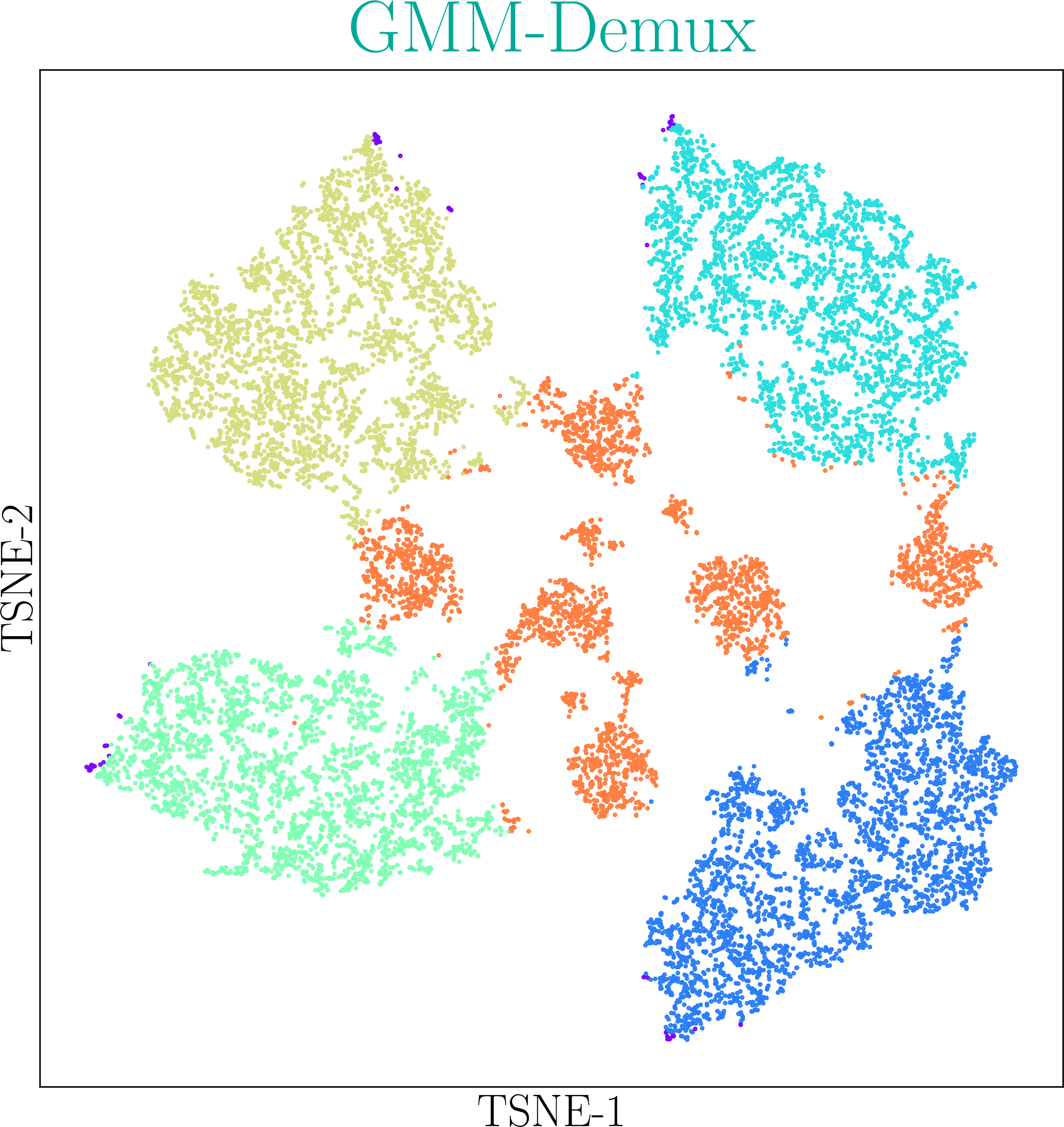
GMM-Demux identifies Multi-Sample Multiplets (MSMs) in a sample barcoding dataset. Below shows an example distribution of MSMs in a PBMC scRNA-seq dataset. Orange dots in the scatter plot are MSMs.
 ## Description
GMM-Demux removes Multi-Sample-Multiplets (MSMs) in a cell hashing dataset and estimates the percentages of Same-Sample-Multiplets (SSMs) and singlets in the remaining dataset.
GMM-Demux also verifies if a putative cell type exists, or is it merely an artifact induced by multiplets.
Multiplet-induced fake cell types are called "phony cell types".
Examples of phony cell types in a PBMC CITE-seq dataset is provided in the figure below:
## Description
GMM-Demux removes Multi-Sample-Multiplets (MSMs) in a cell hashing dataset and estimates the percentages of Same-Sample-Multiplets (SSMs) and singlets in the remaining dataset.
GMM-Demux also verifies if a putative cell type exists, or is it merely an artifact induced by multiplets.
Multiplet-induced fake cell types are called "phony cell types".
Examples of phony cell types in a PBMC CITE-seq dataset is provided in the figure below:
 In the above figure, both the CD3+CD19+ and the CD4+CD8+ cell types are multiplet-induced fake cell types.
Phony type clusters have large percentages of MSMs, as above figure shows. Both phony type clusters have large MSM percentages.
Percentages of MSMs are used as key features by GMM-Demux to classify GEM clusters.
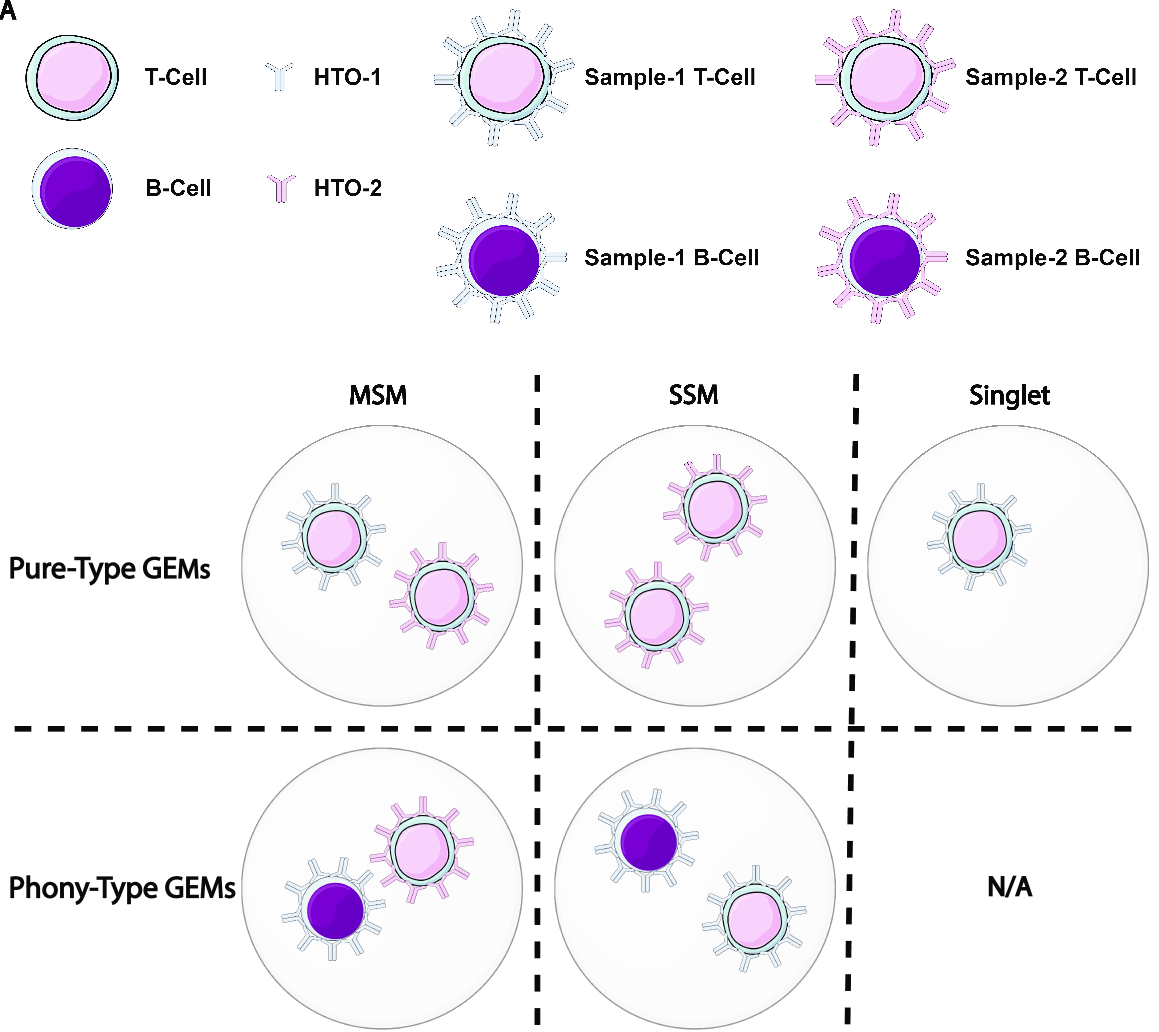
## Terminology
* **Singlet**: A droplet that contains a single cell.
* **MSM**: Multi-Sample Multiplet. A MSM is a multiplet that contains cells from different samples in sample barcoding. MSMs can be identified by GMM-Demux.
* **SSM**: Same-Sample Multiplet. A SSM is a multiplet that contains cells from a single sample in sample barcoding. SSMs cannot be separated from singlets by sample barcoding.
* **SSD**: Same-Sample Droplet. SSD is a combined category of both SSMs and singlets.
* **Pure type**: a pure type cell type is a real cell type that exist in the tissue.
* **Phony type**: a phony type cell type is an artificial cell type that is an artifact produced by multiplets.
* **Mixture type**: a mixture type cell type is a cluster of droplets in which there exist a non-trivial fraction of phony type droplets.
An illustration of the above terminologies in a PBMC dataset is provided in the figure below:
In the above figure, both the CD3+CD19+ and the CD4+CD8+ cell types are multiplet-induced fake cell types.
Phony type clusters have large percentages of MSMs, as above figure shows. Both phony type clusters have large MSM percentages.
Percentages of MSMs are used as key features by GMM-Demux to classify GEM clusters.
## Terminology
* **Singlet**: A droplet that contains a single cell.
* **MSM**: Multi-Sample Multiplet. A MSM is a multiplet that contains cells from different samples in sample barcoding. MSMs can be identified by GMM-Demux.
* **SSM**: Same-Sample Multiplet. A SSM is a multiplet that contains cells from a single sample in sample barcoding. SSMs cannot be separated from singlets by sample barcoding.
* **SSD**: Same-Sample Droplet. SSD is a combined category of both SSMs and singlets.
* **Pure type**: a pure type cell type is a real cell type that exist in the tissue.
* **Phony type**: a phony type cell type is an artificial cell type that is an artifact produced by multiplets.
* **Mixture type**: a mixture type cell type is a cluster of droplets in which there exist a non-trivial fraction of phony type droplets.
An illustration of the above terminologies in a PBMC dataset is provided in the figure below:
 ## Features
* Remove cell-hashing-identifiable multiplets (i.e., MSMs) from the dataset.
* Estimate the fraction of cell-hashing-unidentifiable multiplets (SSMs) in the remaining dataset (the RSSM percentage).
* Test if a putative cell type is a pure (real) cell type or is it a phony (fake) cell type.
## Example Dataset
* An example cell hashing dataset is provided in the *example_input* folder. It contains the per-drop HTO count matrix of a 4-sample cell hashing library prep. The input folder has the same file format with the CellRanger v3 output.
# Authors
Hongyi Xin, Qi Yan, Yale Jiang, Jiadi Luo, Carla Erb, Richard Duerr, Kong Chen* and Wei Chen*
# Maintainer
Hongyi Xin
## Requirement
GMM-Demux requires python3 (>3.5).
## Install
GMM-Demux can be directly installed from PyPi. Or it can be built and installed locally.
### Install GMM-Demux from PyPi.
```bash
pip3 install --user GMM_Demux
```
In some OS, the `pip3` is linked to `pip` by default. For these OS, the installation command is simply:
```bash
pip install --user GMM_Demux
```
Check if `pip3` is linked to `pip` with `pip -V`.
If one chooses to install GMM-Demux from PyPi, it is unnecessary to download GMM-Demux from github. However, we still recommend downloading the example dataset to try out GMM-Demux.
### Install GMM-Demux locally using [setuptools](https://packaging.python.org/tutorials/installing-packages/) and pip3.
You may choose to install GMM-Demux locally after cloning the github repository. However, **this is for advanced users only and support is not gauranteed**.
The command is provided below:
```bash
cd
python3 setup.py sdist bdist_wheel
pip3 install --user .
```
### Post installation processes
If this is the first time you install a python3 software through pip, make sure you add the pip binary folder to your `PATH` variable.
Typically, the pip binary folder is located at ```~/.local/bin```.
The pip binary folder might locate at a different location if the user uses virtual enviroment. Pay attention to the pip installation output.
Here is an example installation output. The path of the pip binary folder is highlighted:
## Features
* Remove cell-hashing-identifiable multiplets (i.e., MSMs) from the dataset.
* Estimate the fraction of cell-hashing-unidentifiable multiplets (SSMs) in the remaining dataset (the RSSM percentage).
* Test if a putative cell type is a pure (real) cell type or is it a phony (fake) cell type.
## Example Dataset
* An example cell hashing dataset is provided in the *example_input* folder. It contains the per-drop HTO count matrix of a 4-sample cell hashing library prep. The input folder has the same file format with the CellRanger v3 output.
# Authors
Hongyi Xin, Qi Yan, Yale Jiang, Jiadi Luo, Carla Erb, Richard Duerr, Kong Chen* and Wei Chen*
# Maintainer
Hongyi Xin
## Requirement
GMM-Demux requires python3 (>3.5).
## Install
GMM-Demux can be directly installed from PyPi. Or it can be built and installed locally.
### Install GMM-Demux from PyPi.
```bash
pip3 install --user GMM_Demux
```
In some OS, the `pip3` is linked to `pip` by default. For these OS, the installation command is simply:
```bash
pip install --user GMM_Demux
```
Check if `pip3` is linked to `pip` with `pip -V`.
If one chooses to install GMM-Demux from PyPi, it is unnecessary to download GMM-Demux from github. However, we still recommend downloading the example dataset to try out GMM-Demux.
### Install GMM-Demux locally using [setuptools](https://packaging.python.org/tutorials/installing-packages/) and pip3.
You may choose to install GMM-Demux locally after cloning the github repository. However, **this is for advanced users only and support is not gauranteed**.
The command is provided below:
```bash
cd
python3 setup.py sdist bdist_wheel
pip3 install --user .
```
### Post installation processes
If this is the first time you install a python3 software through pip, make sure you add the pip binary folder to your `PATH` variable.
Typically, the pip binary folder is located at ```~/.local/bin```.
The pip binary folder might locate at a different location if the user uses virtual enviroment. Pay attention to the pip installation output.
Here is an example installation output. The path of the pip binary folder is highlighted:
 To temporarily add the pip binary folder, run the following command:
```bash
export PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
To permenantly add the pip library folder to your `PATH` variable, append the following line to your `.bashrc` file (assuming bash is the default shell).
```bash
PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
## Content
The source code of GMM-Demux is supplied in the ```GMM_Demux``` folder.
An example cell hashing dataset is also provided, located in the ```example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix``` folder.
An example set of hand-curated putative cell types of the above dataset are provided in the ```example_cell_types``` folder. Cell types are annotated through manual gating using surface marker expression data.
An example csv format of the above cell hashing dataset is provided as the ```example_hto.csv``` file.
## Usage
### Case 1: Basic Usage, Remove MSMs
Once installed, GMM-Demux is directly accessible with the ```GMM-demux``` command.
```bash
GMM-demux
```
`````` is a list of sample tags (HTOs) separated by ',' without whitespace.
For example, there are four sample barcoding tags in the example cell hashing dataset.
They are **HTO_1**, **HTO_2**, **HTO_3**, **HTO_4**. The `````` variable therefore is ```HTO_1,HTO_2,_HTO_3,HTO_4```.
The non-MSM droplets (SSDs) of the dataset are stored in the *GMM_Demux_mtx* folder under the current directory by default.
The output path can also be specified through the `-o` flag.
#### Example Command
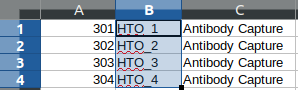
An example cell hashing data is provided in the *example_input* folder. can be obtained from the features.tsv file.
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4
```
are included in the features.tsv file. The content of the feature.tsv file is shown below.
#### Output
The default content in the output folder are the non-MSM droplets (SSDs), stored in MTX format. The output shares the same format with CellRanger 3.0. By default, the output is stored in `SSD_mtx` folder. The output location can be overwritten with the `-o` flag.
### Case 2: Compute the MSM and SSM rates
To compute the MSM and SSM rates, GMM-Demux requires the `-u` flag:
* -u SUMMARY, --summary SUMMARY Generate the statstic summary of the dataset. Requires an estimated total number of cells in the assay as input.
The `-u` flag requires an additional argument, which is the estimated total count of cells in the single cell assay.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685
```
#### Output
Below is an example report:

* RSSM denotes the percentage of SSMs among the remaining SSDs (after removing all MSMs). RSSM **measures the quality of the final cell hashing dataset after removing MSMs**.
### Case 3: Verify if a cell type exists
GMM-Demux verifies if a putative cell type exists with the `-e` flag:
* -e EXAMINE, --examine EXAMINE Provide the cell list. Requires a file argument. Only executes if -u is set.
The `-e` flag requires a file name, which stores the list of droplet barcodes of the putative cell type.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685 -e example_cell_types/CD19+.txt
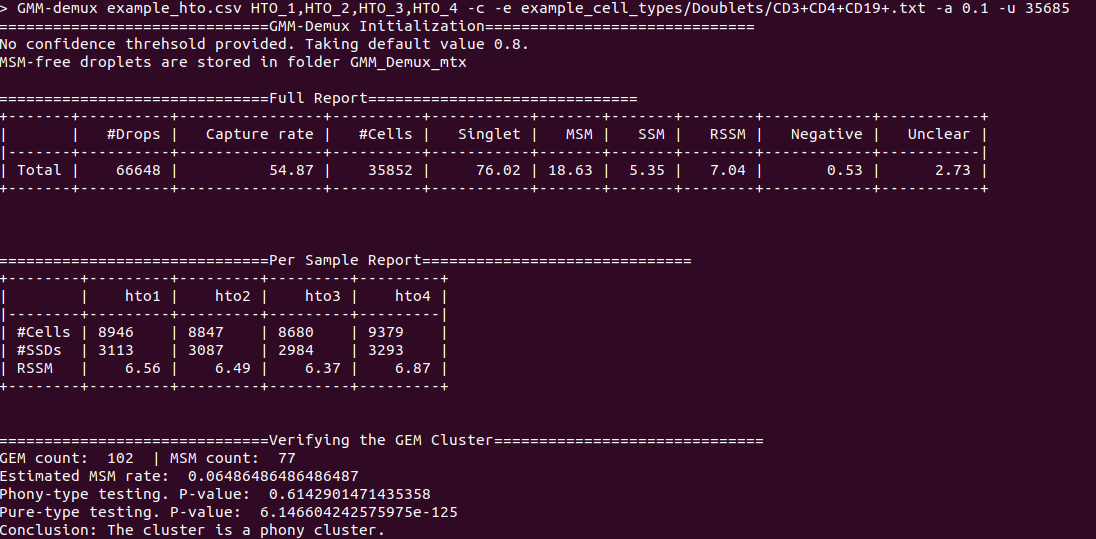
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685 -e example_cell_types/Doublets/CD3+CD4+CD19+.txt
```
#### Output
An example output of a pure cell type:
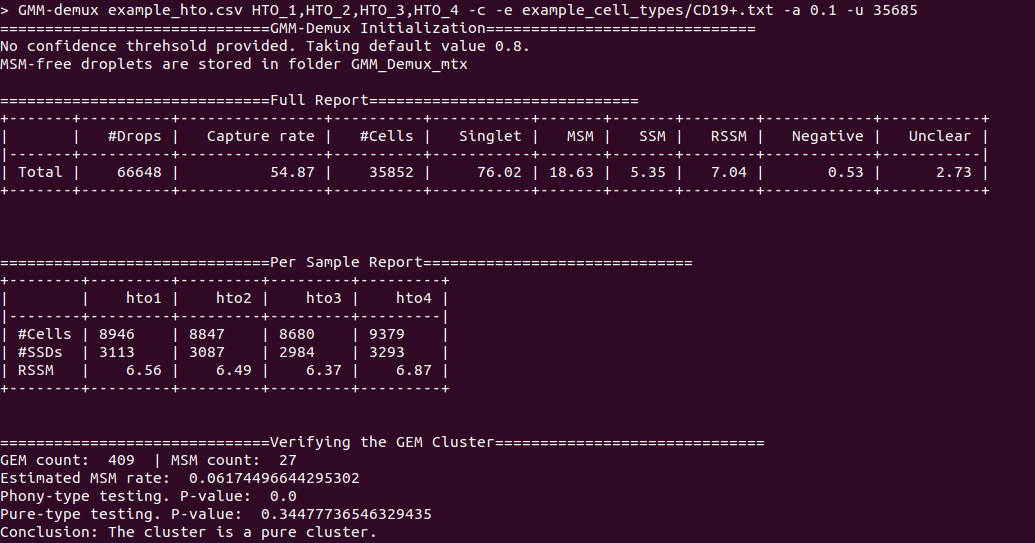
An example output of a phony cell type:
### Case 4: Use the csv file format as input, instead of the mtx format
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux -c example_hto.csv HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685
```
### Case 5: Extract droplets that are labeled by a combination of sample tags
Extract droplets that are labeled by multiple sample barcoding tags, with the `-x` flag:
* -x EXTRACT, --extract EXTRACT Names of the sample barcoding tag(s) to extract, separated by ','. Joint tags are linked with '+'.
**When `-x` is set, other functions of GMM-Demux will be turned off.**
#### *Case 5a: Extract a single HTO sample*
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO_1
```
#### *Case 5b: Extract a single HTO sample that are jointly defined by multiple HTO tags*
Use `+` to specify the joint HTO tags.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO_1+HTO_2
```
#### *Case 5c: Extract multiple HTO samples*
Use `,` to separate sample tags. Single tag samples can be merged with joint-tag samples.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO3,HTO_1+HTO_2,HTO_1+HTO_4+HTO_2
```
## Optional Arguments
* -h: show help information.
* -f FULL, --full FULL Generate the full classification report. Require a path argument.
* -s SIMPLIFIED, --simplified SIMPLIFIED Generate the simplified classification report. Require a path argument.
* -o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT The path for storing the Same-Sample-Droplets (SSDs). SSDs are stored in mtx format. Requires a path argument. Default path: SSD_mtx.
* -r REPORT, --report REPORT Specify the file to store summary report. Require a file argument.
* -c CSV, --csv Take input in csv format, instead of mmx format.
* -s SKIP, --skip FULL\_REPORT Load a full classification report and skip the mtx folder as input. Require a path argument.
* -a AMBIGUOUS, --ambiguous AMBIGUOUS The estimated chance of having a phony GEM getting included in a pure type GEM cluster by the clustering algorithm. Requires a float in (0, 1). Default value: 0.05. Only executes if -e executes.
* -t THRESHOLD, --threshold THRESHOLD Provide the confidence threshold value. Requires a float in (0,1). Default value: 0.8.
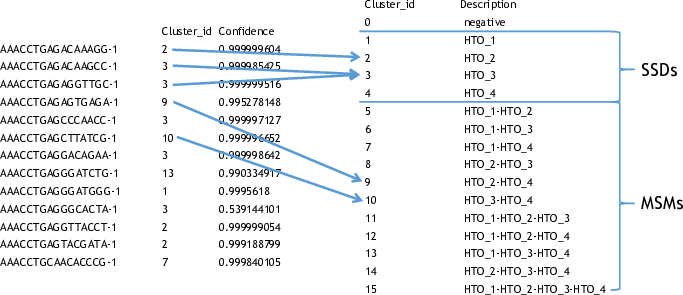
## Parsing the Classification Output
There are two files in a classification output folder. A config file (ending with .config) and a classification file (ending with .csv).
The classification file contains the label of each droplet as well as the probability of the classification. The classification is represented with numbers which are explained in the config file.
Below shows the classification output of the example data:
To temporarily add the pip binary folder, run the following command:
```bash
export PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
To permenantly add the pip library folder to your `PATH` variable, append the following line to your `.bashrc` file (assuming bash is the default shell).
```bash
PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
## Content
The source code of GMM-Demux is supplied in the ```GMM_Demux``` folder.
An example cell hashing dataset is also provided, located in the ```example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix``` folder.
An example set of hand-curated putative cell types of the above dataset are provided in the ```example_cell_types``` folder. Cell types are annotated through manual gating using surface marker expression data.
An example csv format of the above cell hashing dataset is provided as the ```example_hto.csv``` file.
## Usage
### Case 1: Basic Usage, Remove MSMs
Once installed, GMM-Demux is directly accessible with the ```GMM-demux``` command.
```bash
GMM-demux
```
`````` is a list of sample tags (HTOs) separated by ',' without whitespace.
For example, there are four sample barcoding tags in the example cell hashing dataset.
They are **HTO_1**, **HTO_2**, **HTO_3**, **HTO_4**. The `````` variable therefore is ```HTO_1,HTO_2,_HTO_3,HTO_4```.
The non-MSM droplets (SSDs) of the dataset are stored in the *GMM_Demux_mtx* folder under the current directory by default.
The output path can also be specified through the `-o` flag.
#### Example Command
An example cell hashing data is provided in the *example_input* folder. can be obtained from the features.tsv file.
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4
```
are included in the features.tsv file. The content of the feature.tsv file is shown below.

#### Output
The default content in the output folder are the non-MSM droplets (SSDs), stored in MTX format. The output shares the same format with CellRanger 3.0. By default, the output is stored in `SSD_mtx` folder. The output location can be overwritten with the `-o` flag.
### Case 2: Compute the MSM and SSM rates
To compute the MSM and SSM rates, GMM-Demux requires the `-u` flag:
* -u SUMMARY, --summary SUMMARY Generate the statstic summary of the dataset. Requires an estimated total number of cells in the assay as input.
The `-u` flag requires an additional argument, which is the estimated total count of cells in the single cell assay.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685
```
#### Output
Below is an example report:

* RSSM denotes the percentage of SSMs among the remaining SSDs (after removing all MSMs). RSSM **measures the quality of the final cell hashing dataset after removing MSMs**.
### Case 3: Verify if a cell type exists
GMM-Demux verifies if a putative cell type exists with the `-e` flag:
* -e EXAMINE, --examine EXAMINE Provide the cell list. Requires a file argument. Only executes if -u is set.
The `-e` flag requires a file name, which stores the list of droplet barcodes of the putative cell type.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685 -e example_cell_types/CD19+.txt
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685 -e example_cell_types/Doublets/CD3+CD4+CD19+.txt
```
#### Output
An example output of a pure cell type:

An example output of a phony cell type:

### Case 4: Use the csv file format as input, instead of the mtx format
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux -c example_hto.csv HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685
```
### Case 5: Extract droplets that are labeled by a combination of sample tags
Extract droplets that are labeled by multiple sample barcoding tags, with the `-x` flag:
* -x EXTRACT, --extract EXTRACT Names of the sample barcoding tag(s) to extract, separated by ','. Joint tags are linked with '+'.
**When `-x` is set, other functions of GMM-Demux will be turned off.**
#### *Case 5a: Extract a single HTO sample*
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO_1
```
#### *Case 5b: Extract a single HTO sample that are jointly defined by multiple HTO tags*
Use `+` to specify the joint HTO tags.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO_1+HTO_2
```
#### *Case 5c: Extract multiple HTO samples*
Use `,` to separate sample tags. Single tag samples can be merged with joint-tag samples.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO3,HTO_1+HTO_2,HTO_1+HTO_4+HTO_2
```
## Optional Arguments
* -h: show help information.
* -f FULL, --full FULL Generate the full classification report. Require a path argument.
* -s SIMPLIFIED, --simplified SIMPLIFIED Generate the simplified classification report. Require a path argument.
* -o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT The path for storing the Same-Sample-Droplets (SSDs). SSDs are stored in mtx format. Requires a path argument. Default path: SSD_mtx.
* -r REPORT, --report REPORT Specify the file to store summary report. Require a file argument.
* -c CSV, --csv Take input in csv format, instead of mmx format.
* -s SKIP, --skip FULL\_REPORT Load a full classification report and skip the mtx folder as input. Require a path argument.
* -a AMBIGUOUS, --ambiguous AMBIGUOUS The estimated chance of having a phony GEM getting included in a pure type GEM cluster by the clustering algorithm. Requires a float in (0, 1). Default value: 0.05. Only executes if -e executes.
* -t THRESHOLD, --threshold THRESHOLD Provide the confidence threshold value. Requires a float in (0,1). Default value: 0.8.
## Parsing the Classification Output
There are two files in a classification output folder. A config file (ending with .config) and a classification file (ending with .csv).
The classification file contains the label of each droplet as well as the probability of the classification. The classification is represented with numbers which are explained in the config file.
Below shows the classification output of the example data:
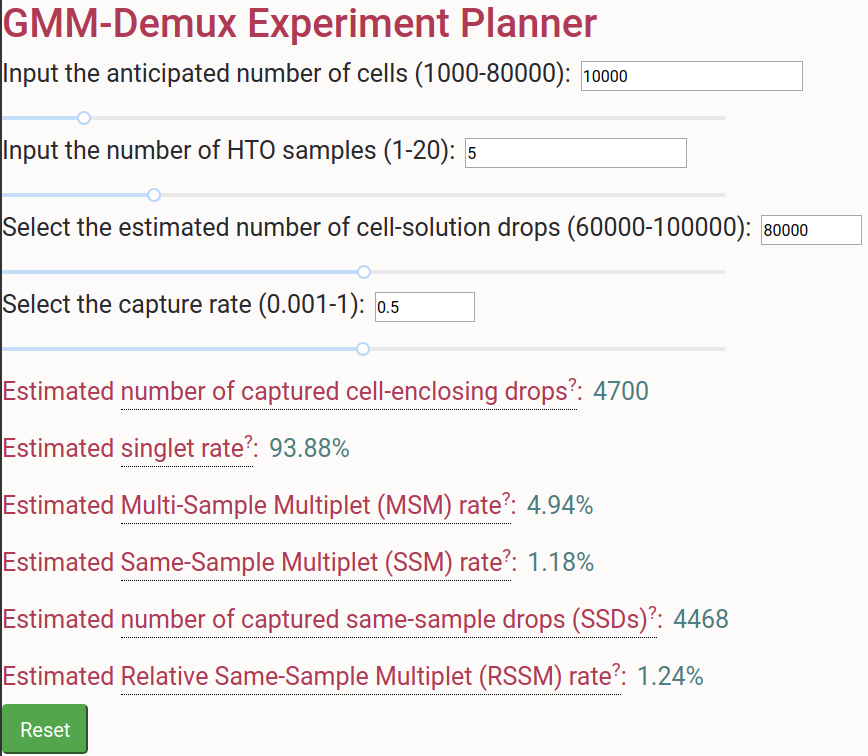
 ## Online Cell Hashing Experiment Planner
A GMM-Demux based online cell hashing experiment planner is publically accessible at [here](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html).
[
## Online Cell Hashing Experiment Planner
A GMM-Demux based online cell hashing experiment planner is publically accessible at [here](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html).
[ ](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html)
## Citation
If you find this code useful in your research, please consider citing:
@article{xin2019sample,
title={Sample demultiplexing, multiplet detection, experiment planning and novel cell type verification in single cell sequencing},
author={Xin, Hongyi and Yan, Qi and Jiang, Yale and Lian, Qiuyu and Luo, Jiadi and Erb, Carla and Duerr, Richard and Chen, Kong and Chen, Wei},
journal={bioRxiv},
pages={828483},
year={2019},
publisher={Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}
}
## Acknowledgement
Special thank to Zhongli Xu for testing GMM-Demux!
%package -n python3-GMM-Demux
Summary: A multiplet removal tool for processing cell hashing data
Provides: python-GMM-Demux
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3-setuptools
BuildRequires: python3-pip
%description -n python3-GMM-Demux
# GMM-Demux
GMM-Demux is a Gaussian-Mixture-Model-based software for processing sample barcoding data (cell hashing and MULTI-seq).
GMM-Demux identifies Multi-Sample Multiplets (MSMs) in a sample barcoding dataset. Below shows an example distribution of MSMs in a PBMC scRNA-seq dataset. Orange dots in the scatter plot are MSMs.
](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html)
## Citation
If you find this code useful in your research, please consider citing:
@article{xin2019sample,
title={Sample demultiplexing, multiplet detection, experiment planning and novel cell type verification in single cell sequencing},
author={Xin, Hongyi and Yan, Qi and Jiang, Yale and Lian, Qiuyu and Luo, Jiadi and Erb, Carla and Duerr, Richard and Chen, Kong and Chen, Wei},
journal={bioRxiv},
pages={828483},
year={2019},
publisher={Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}
}
## Acknowledgement
Special thank to Zhongli Xu for testing GMM-Demux!
%package -n python3-GMM-Demux
Summary: A multiplet removal tool for processing cell hashing data
Provides: python-GMM-Demux
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3-setuptools
BuildRequires: python3-pip
%description -n python3-GMM-Demux
# GMM-Demux
GMM-Demux is a Gaussian-Mixture-Model-based software for processing sample barcoding data (cell hashing and MULTI-seq).
GMM-Demux identifies Multi-Sample Multiplets (MSMs) in a sample barcoding dataset. Below shows an example distribution of MSMs in a PBMC scRNA-seq dataset. Orange dots in the scatter plot are MSMs.
 ## Description
GMM-Demux removes Multi-Sample-Multiplets (MSMs) in a cell hashing dataset and estimates the percentages of Same-Sample-Multiplets (SSMs) and singlets in the remaining dataset.
GMM-Demux also verifies if a putative cell type exists, or is it merely an artifact induced by multiplets.
Multiplet-induced fake cell types are called "phony cell types".
Examples of phony cell types in a PBMC CITE-seq dataset is provided in the figure below:
## Description
GMM-Demux removes Multi-Sample-Multiplets (MSMs) in a cell hashing dataset and estimates the percentages of Same-Sample-Multiplets (SSMs) and singlets in the remaining dataset.
GMM-Demux also verifies if a putative cell type exists, or is it merely an artifact induced by multiplets.
Multiplet-induced fake cell types are called "phony cell types".
Examples of phony cell types in a PBMC CITE-seq dataset is provided in the figure below:
 In the above figure, both the CD3+CD19+ and the CD4+CD8+ cell types are multiplet-induced fake cell types.
Phony type clusters have large percentages of MSMs, as above figure shows. Both phony type clusters have large MSM percentages.
Percentages of MSMs are used as key features by GMM-Demux to classify GEM clusters.
## Terminology
* **Singlet**: A droplet that contains a single cell.
* **MSM**: Multi-Sample Multiplet. A MSM is a multiplet that contains cells from different samples in sample barcoding. MSMs can be identified by GMM-Demux.
* **SSM**: Same-Sample Multiplet. A SSM is a multiplet that contains cells from a single sample in sample barcoding. SSMs cannot be separated from singlets by sample barcoding.
* **SSD**: Same-Sample Droplet. SSD is a combined category of both SSMs and singlets.
* **Pure type**: a pure type cell type is a real cell type that exist in the tissue.
* **Phony type**: a phony type cell type is an artificial cell type that is an artifact produced by multiplets.
* **Mixture type**: a mixture type cell type is a cluster of droplets in which there exist a non-trivial fraction of phony type droplets.
An illustration of the above terminologies in a PBMC dataset is provided in the figure below:
In the above figure, both the CD3+CD19+ and the CD4+CD8+ cell types are multiplet-induced fake cell types.
Phony type clusters have large percentages of MSMs, as above figure shows. Both phony type clusters have large MSM percentages.
Percentages of MSMs are used as key features by GMM-Demux to classify GEM clusters.
## Terminology
* **Singlet**: A droplet that contains a single cell.
* **MSM**: Multi-Sample Multiplet. A MSM is a multiplet that contains cells from different samples in sample barcoding. MSMs can be identified by GMM-Demux.
* **SSM**: Same-Sample Multiplet. A SSM is a multiplet that contains cells from a single sample in sample barcoding. SSMs cannot be separated from singlets by sample barcoding.
* **SSD**: Same-Sample Droplet. SSD is a combined category of both SSMs and singlets.
* **Pure type**: a pure type cell type is a real cell type that exist in the tissue.
* **Phony type**: a phony type cell type is an artificial cell type that is an artifact produced by multiplets.
* **Mixture type**: a mixture type cell type is a cluster of droplets in which there exist a non-trivial fraction of phony type droplets.
An illustration of the above terminologies in a PBMC dataset is provided in the figure below:
 ## Features
* Remove cell-hashing-identifiable multiplets (i.e., MSMs) from the dataset.
* Estimate the fraction of cell-hashing-unidentifiable multiplets (SSMs) in the remaining dataset (the RSSM percentage).
* Test if a putative cell type is a pure (real) cell type or is it a phony (fake) cell type.
## Example Dataset
* An example cell hashing dataset is provided in the *example_input* folder. It contains the per-drop HTO count matrix of a 4-sample cell hashing library prep. The input folder has the same file format with the CellRanger v3 output.
# Authors
Hongyi Xin, Qi Yan, Yale Jiang, Jiadi Luo, Carla Erb, Richard Duerr, Kong Chen* and Wei Chen*
# Maintainer
Hongyi Xin
## Requirement
GMM-Demux requires python3 (>3.5).
## Install
GMM-Demux can be directly installed from PyPi. Or it can be built and installed locally.
### Install GMM-Demux from PyPi.
```bash
pip3 install --user GMM_Demux
```
In some OS, the `pip3` is linked to `pip` by default. For these OS, the installation command is simply:
```bash
pip install --user GMM_Demux
```
Check if `pip3` is linked to `pip` with `pip -V`.
If one chooses to install GMM-Demux from PyPi, it is unnecessary to download GMM-Demux from github. However, we still recommend downloading the example dataset to try out GMM-Demux.
### Install GMM-Demux locally using [setuptools](https://packaging.python.org/tutorials/installing-packages/) and pip3.
You may choose to install GMM-Demux locally after cloning the github repository. However, **this is for advanced users only and support is not gauranteed**.
The command is provided below:
```bash
cd
python3 setup.py sdist bdist_wheel
pip3 install --user .
```
### Post installation processes
If this is the first time you install a python3 software through pip, make sure you add the pip binary folder to your `PATH` variable.
Typically, the pip binary folder is located at ```~/.local/bin```.
The pip binary folder might locate at a different location if the user uses virtual enviroment. Pay attention to the pip installation output.
Here is an example installation output. The path of the pip binary folder is highlighted:
## Features
* Remove cell-hashing-identifiable multiplets (i.e., MSMs) from the dataset.
* Estimate the fraction of cell-hashing-unidentifiable multiplets (SSMs) in the remaining dataset (the RSSM percentage).
* Test if a putative cell type is a pure (real) cell type or is it a phony (fake) cell type.
## Example Dataset
* An example cell hashing dataset is provided in the *example_input* folder. It contains the per-drop HTO count matrix of a 4-sample cell hashing library prep. The input folder has the same file format with the CellRanger v3 output.
# Authors
Hongyi Xin, Qi Yan, Yale Jiang, Jiadi Luo, Carla Erb, Richard Duerr, Kong Chen* and Wei Chen*
# Maintainer
Hongyi Xin
## Requirement
GMM-Demux requires python3 (>3.5).
## Install
GMM-Demux can be directly installed from PyPi. Or it can be built and installed locally.
### Install GMM-Demux from PyPi.
```bash
pip3 install --user GMM_Demux
```
In some OS, the `pip3` is linked to `pip` by default. For these OS, the installation command is simply:
```bash
pip install --user GMM_Demux
```
Check if `pip3` is linked to `pip` with `pip -V`.
If one chooses to install GMM-Demux from PyPi, it is unnecessary to download GMM-Demux from github. However, we still recommend downloading the example dataset to try out GMM-Demux.
### Install GMM-Demux locally using [setuptools](https://packaging.python.org/tutorials/installing-packages/) and pip3.
You may choose to install GMM-Demux locally after cloning the github repository. However, **this is for advanced users only and support is not gauranteed**.
The command is provided below:
```bash
cd
python3 setup.py sdist bdist_wheel
pip3 install --user .
```
### Post installation processes
If this is the first time you install a python3 software through pip, make sure you add the pip binary folder to your `PATH` variable.
Typically, the pip binary folder is located at ```~/.local/bin```.
The pip binary folder might locate at a different location if the user uses virtual enviroment. Pay attention to the pip installation output.
Here is an example installation output. The path of the pip binary folder is highlighted:
 To temporarily add the pip binary folder, run the following command:
```bash
export PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
To permenantly add the pip library folder to your `PATH` variable, append the following line to your `.bashrc` file (assuming bash is the default shell).
```bash
PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
## Content
The source code of GMM-Demux is supplied in the ```GMM_Demux``` folder.
An example cell hashing dataset is also provided, located in the ```example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix``` folder.
An example set of hand-curated putative cell types of the above dataset are provided in the ```example_cell_types``` folder. Cell types are annotated through manual gating using surface marker expression data.
An example csv format of the above cell hashing dataset is provided as the ```example_hto.csv``` file.
## Usage
### Case 1: Basic Usage, Remove MSMs
Once installed, GMM-Demux is directly accessible with the ```GMM-demux``` command.
```bash
GMM-demux
```
`````` is a list of sample tags (HTOs) separated by ',' without whitespace.
For example, there are four sample barcoding tags in the example cell hashing dataset.
They are **HTO_1**, **HTO_2**, **HTO_3**, **HTO_4**. The `````` variable therefore is ```HTO_1,HTO_2,_HTO_3,HTO_4```.
The non-MSM droplets (SSDs) of the dataset are stored in the *GMM_Demux_mtx* folder under the current directory by default.
The output path can also be specified through the `-o` flag.
#### Example Command
An example cell hashing data is provided in the *example_input* folder. can be obtained from the features.tsv file.
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4
```
are included in the features.tsv file. The content of the feature.tsv file is shown below.

#### Output
The default content in the output folder are the non-MSM droplets (SSDs), stored in MTX format. The output shares the same format with CellRanger 3.0. By default, the output is stored in `SSD_mtx` folder. The output location can be overwritten with the `-o` flag.
### Case 2: Compute the MSM and SSM rates
To compute the MSM and SSM rates, GMM-Demux requires the `-u` flag:
* -u SUMMARY, --summary SUMMARY Generate the statstic summary of the dataset. Requires an estimated total number of cells in the assay as input.
The `-u` flag requires an additional argument, which is the estimated total count of cells in the single cell assay.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685
```
#### Output
Below is an example report:

* RSSM denotes the percentage of SSMs among the remaining SSDs (after removing all MSMs). RSSM **measures the quality of the final cell hashing dataset after removing MSMs**.
### Case 3: Verify if a cell type exists
GMM-Demux verifies if a putative cell type exists with the `-e` flag:
* -e EXAMINE, --examine EXAMINE Provide the cell list. Requires a file argument. Only executes if -u is set.
The `-e` flag requires a file name, which stores the list of droplet barcodes of the putative cell type.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685 -e example_cell_types/CD19+.txt
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685 -e example_cell_types/Doublets/CD3+CD4+CD19+.txt
```
#### Output
An example output of a pure cell type:

An example output of a phony cell type:

### Case 4: Use the csv file format as input, instead of the mtx format
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux -c example_hto.csv HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685
```
### Case 5: Extract droplets that are labeled by a combination of sample tags
Extract droplets that are labeled by multiple sample barcoding tags, with the `-x` flag:
* -x EXTRACT, --extract EXTRACT Names of the sample barcoding tag(s) to extract, separated by ','. Joint tags are linked with '+'.
**When `-x` is set, other functions of GMM-Demux will be turned off.**
#### *Case 5a: Extract a single HTO sample*
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO_1
```
#### *Case 5b: Extract a single HTO sample that are jointly defined by multiple HTO tags*
Use `+` to specify the joint HTO tags.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO_1+HTO_2
```
#### *Case 5c: Extract multiple HTO samples*
Use `,` to separate sample tags. Single tag samples can be merged with joint-tag samples.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO3,HTO_1+HTO_2,HTO_1+HTO_4+HTO_2
```
## Optional Arguments
* -h: show help information.
* -f FULL, --full FULL Generate the full classification report. Require a path argument.
* -s SIMPLIFIED, --simplified SIMPLIFIED Generate the simplified classification report. Require a path argument.
* -o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT The path for storing the Same-Sample-Droplets (SSDs). SSDs are stored in mtx format. Requires a path argument. Default path: SSD_mtx.
* -r REPORT, --report REPORT Specify the file to store summary report. Require a file argument.
* -c CSV, --csv Take input in csv format, instead of mmx format.
* -s SKIP, --skip FULL\_REPORT Load a full classification report and skip the mtx folder as input. Require a path argument.
* -a AMBIGUOUS, --ambiguous AMBIGUOUS The estimated chance of having a phony GEM getting included in a pure type GEM cluster by the clustering algorithm. Requires a float in (0, 1). Default value: 0.05. Only executes if -e executes.
* -t THRESHOLD, --threshold THRESHOLD Provide the confidence threshold value. Requires a float in (0,1). Default value: 0.8.
## Parsing the Classification Output
There are two files in a classification output folder. A config file (ending with .config) and a classification file (ending with .csv).
The classification file contains the label of each droplet as well as the probability of the classification. The classification is represented with numbers which are explained in the config file.
Below shows the classification output of the example data:
To temporarily add the pip binary folder, run the following command:
```bash
export PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
To permenantly add the pip library folder to your `PATH` variable, append the following line to your `.bashrc` file (assuming bash is the default shell).
```bash
PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
## Content
The source code of GMM-Demux is supplied in the ```GMM_Demux``` folder.
An example cell hashing dataset is also provided, located in the ```example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix``` folder.
An example set of hand-curated putative cell types of the above dataset are provided in the ```example_cell_types``` folder. Cell types are annotated through manual gating using surface marker expression data.
An example csv format of the above cell hashing dataset is provided as the ```example_hto.csv``` file.
## Usage
### Case 1: Basic Usage, Remove MSMs
Once installed, GMM-Demux is directly accessible with the ```GMM-demux``` command.
```bash
GMM-demux
```
`````` is a list of sample tags (HTOs) separated by ',' without whitespace.
For example, there are four sample barcoding tags in the example cell hashing dataset.
They are **HTO_1**, **HTO_2**, **HTO_3**, **HTO_4**. The `````` variable therefore is ```HTO_1,HTO_2,_HTO_3,HTO_4```.
The non-MSM droplets (SSDs) of the dataset are stored in the *GMM_Demux_mtx* folder under the current directory by default.
The output path can also be specified through the `-o` flag.
#### Example Command
An example cell hashing data is provided in the *example_input* folder. can be obtained from the features.tsv file.
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4
```
are included in the features.tsv file. The content of the feature.tsv file is shown below.

#### Output
The default content in the output folder are the non-MSM droplets (SSDs), stored in MTX format. The output shares the same format with CellRanger 3.0. By default, the output is stored in `SSD_mtx` folder. The output location can be overwritten with the `-o` flag.
### Case 2: Compute the MSM and SSM rates
To compute the MSM and SSM rates, GMM-Demux requires the `-u` flag:
* -u SUMMARY, --summary SUMMARY Generate the statstic summary of the dataset. Requires an estimated total number of cells in the assay as input.
The `-u` flag requires an additional argument, which is the estimated total count of cells in the single cell assay.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685
```
#### Output
Below is an example report:

* RSSM denotes the percentage of SSMs among the remaining SSDs (after removing all MSMs). RSSM **measures the quality of the final cell hashing dataset after removing MSMs**.
### Case 3: Verify if a cell type exists
GMM-Demux verifies if a putative cell type exists with the `-e` flag:
* -e EXAMINE, --examine EXAMINE Provide the cell list. Requires a file argument. Only executes if -u is set.
The `-e` flag requires a file name, which stores the list of droplet barcodes of the putative cell type.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685 -e example_cell_types/CD19+.txt
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685 -e example_cell_types/Doublets/CD3+CD4+CD19+.txt
```
#### Output
An example output of a pure cell type:

An example output of a phony cell type:

### Case 4: Use the csv file format as input, instead of the mtx format
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux -c example_hto.csv HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685
```
### Case 5: Extract droplets that are labeled by a combination of sample tags
Extract droplets that are labeled by multiple sample barcoding tags, with the `-x` flag:
* -x EXTRACT, --extract EXTRACT Names of the sample barcoding tag(s) to extract, separated by ','. Joint tags are linked with '+'.
**When `-x` is set, other functions of GMM-Demux will be turned off.**
#### *Case 5a: Extract a single HTO sample*
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO_1
```
#### *Case 5b: Extract a single HTO sample that are jointly defined by multiple HTO tags*
Use `+` to specify the joint HTO tags.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO_1+HTO_2
```
#### *Case 5c: Extract multiple HTO samples*
Use `,` to separate sample tags. Single tag samples can be merged with joint-tag samples.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO3,HTO_1+HTO_2,HTO_1+HTO_4+HTO_2
```
## Optional Arguments
* -h: show help information.
* -f FULL, --full FULL Generate the full classification report. Require a path argument.
* -s SIMPLIFIED, --simplified SIMPLIFIED Generate the simplified classification report. Require a path argument.
* -o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT The path for storing the Same-Sample-Droplets (SSDs). SSDs are stored in mtx format. Requires a path argument. Default path: SSD_mtx.
* -r REPORT, --report REPORT Specify the file to store summary report. Require a file argument.
* -c CSV, --csv Take input in csv format, instead of mmx format.
* -s SKIP, --skip FULL\_REPORT Load a full classification report and skip the mtx folder as input. Require a path argument.
* -a AMBIGUOUS, --ambiguous AMBIGUOUS The estimated chance of having a phony GEM getting included in a pure type GEM cluster by the clustering algorithm. Requires a float in (0, 1). Default value: 0.05. Only executes if -e executes.
* -t THRESHOLD, --threshold THRESHOLD Provide the confidence threshold value. Requires a float in (0,1). Default value: 0.8.
## Parsing the Classification Output
There are two files in a classification output folder. A config file (ending with .config) and a classification file (ending with .csv).
The classification file contains the label of each droplet as well as the probability of the classification. The classification is represented with numbers which are explained in the config file.
Below shows the classification output of the example data:
 ## Online Cell Hashing Experiment Planner
A GMM-Demux based online cell hashing experiment planner is publically accessible at [here](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html).
[
## Online Cell Hashing Experiment Planner
A GMM-Demux based online cell hashing experiment planner is publically accessible at [here](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html).
[ ](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html)
## Citation
If you find this code useful in your research, please consider citing:
@article{xin2019sample,
title={Sample demultiplexing, multiplet detection, experiment planning and novel cell type verification in single cell sequencing},
author={Xin, Hongyi and Yan, Qi and Jiang, Yale and Lian, Qiuyu and Luo, Jiadi and Erb, Carla and Duerr, Richard and Chen, Kong and Chen, Wei},
journal={bioRxiv},
pages={828483},
year={2019},
publisher={Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}
}
## Acknowledgement
Special thank to Zhongli Xu for testing GMM-Demux!
%package help
Summary: Development documents and examples for GMM-Demux
Provides: python3-GMM-Demux-doc
%description help
# GMM-Demux
GMM-Demux is a Gaussian-Mixture-Model-based software for processing sample barcoding data (cell hashing and MULTI-seq).
GMM-Demux identifies Multi-Sample Multiplets (MSMs) in a sample barcoding dataset. Below shows an example distribution of MSMs in a PBMC scRNA-seq dataset. Orange dots in the scatter plot are MSMs.
](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html)
## Citation
If you find this code useful in your research, please consider citing:
@article{xin2019sample,
title={Sample demultiplexing, multiplet detection, experiment planning and novel cell type verification in single cell sequencing},
author={Xin, Hongyi and Yan, Qi and Jiang, Yale and Lian, Qiuyu and Luo, Jiadi and Erb, Carla and Duerr, Richard and Chen, Kong and Chen, Wei},
journal={bioRxiv},
pages={828483},
year={2019},
publisher={Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}
}
## Acknowledgement
Special thank to Zhongli Xu for testing GMM-Demux!
%package help
Summary: Development documents and examples for GMM-Demux
Provides: python3-GMM-Demux-doc
%description help
# GMM-Demux
GMM-Demux is a Gaussian-Mixture-Model-based software for processing sample barcoding data (cell hashing and MULTI-seq).
GMM-Demux identifies Multi-Sample Multiplets (MSMs) in a sample barcoding dataset. Below shows an example distribution of MSMs in a PBMC scRNA-seq dataset. Orange dots in the scatter plot are MSMs.
 ## Description
GMM-Demux removes Multi-Sample-Multiplets (MSMs) in a cell hashing dataset and estimates the percentages of Same-Sample-Multiplets (SSMs) and singlets in the remaining dataset.
GMM-Demux also verifies if a putative cell type exists, or is it merely an artifact induced by multiplets.
Multiplet-induced fake cell types are called "phony cell types".
Examples of phony cell types in a PBMC CITE-seq dataset is provided in the figure below:
## Description
GMM-Demux removes Multi-Sample-Multiplets (MSMs) in a cell hashing dataset and estimates the percentages of Same-Sample-Multiplets (SSMs) and singlets in the remaining dataset.
GMM-Demux also verifies if a putative cell type exists, or is it merely an artifact induced by multiplets.
Multiplet-induced fake cell types are called "phony cell types".
Examples of phony cell types in a PBMC CITE-seq dataset is provided in the figure below:
 In the above figure, both the CD3+CD19+ and the CD4+CD8+ cell types are multiplet-induced fake cell types.
Phony type clusters have large percentages of MSMs, as above figure shows. Both phony type clusters have large MSM percentages.
Percentages of MSMs are used as key features by GMM-Demux to classify GEM clusters.
## Terminology
* **Singlet**: A droplet that contains a single cell.
* **MSM**: Multi-Sample Multiplet. A MSM is a multiplet that contains cells from different samples in sample barcoding. MSMs can be identified by GMM-Demux.
* **SSM**: Same-Sample Multiplet. A SSM is a multiplet that contains cells from a single sample in sample barcoding. SSMs cannot be separated from singlets by sample barcoding.
* **SSD**: Same-Sample Droplet. SSD is a combined category of both SSMs and singlets.
* **Pure type**: a pure type cell type is a real cell type that exist in the tissue.
* **Phony type**: a phony type cell type is an artificial cell type that is an artifact produced by multiplets.
* **Mixture type**: a mixture type cell type is a cluster of droplets in which there exist a non-trivial fraction of phony type droplets.
An illustration of the above terminologies in a PBMC dataset is provided in the figure below:
In the above figure, both the CD3+CD19+ and the CD4+CD8+ cell types are multiplet-induced fake cell types.
Phony type clusters have large percentages of MSMs, as above figure shows. Both phony type clusters have large MSM percentages.
Percentages of MSMs are used as key features by GMM-Demux to classify GEM clusters.
## Terminology
* **Singlet**: A droplet that contains a single cell.
* **MSM**: Multi-Sample Multiplet. A MSM is a multiplet that contains cells from different samples in sample barcoding. MSMs can be identified by GMM-Demux.
* **SSM**: Same-Sample Multiplet. A SSM is a multiplet that contains cells from a single sample in sample barcoding. SSMs cannot be separated from singlets by sample barcoding.
* **SSD**: Same-Sample Droplet. SSD is a combined category of both SSMs and singlets.
* **Pure type**: a pure type cell type is a real cell type that exist in the tissue.
* **Phony type**: a phony type cell type is an artificial cell type that is an artifact produced by multiplets.
* **Mixture type**: a mixture type cell type is a cluster of droplets in which there exist a non-trivial fraction of phony type droplets.
An illustration of the above terminologies in a PBMC dataset is provided in the figure below:
 ## Features
* Remove cell-hashing-identifiable multiplets (i.e., MSMs) from the dataset.
* Estimate the fraction of cell-hashing-unidentifiable multiplets (SSMs) in the remaining dataset (the RSSM percentage).
* Test if a putative cell type is a pure (real) cell type or is it a phony (fake) cell type.
## Example Dataset
* An example cell hashing dataset is provided in the *example_input* folder. It contains the per-drop HTO count matrix of a 4-sample cell hashing library prep. The input folder has the same file format with the CellRanger v3 output.
# Authors
Hongyi Xin, Qi Yan, Yale Jiang, Jiadi Luo, Carla Erb, Richard Duerr, Kong Chen* and Wei Chen*
# Maintainer
Hongyi Xin
## Requirement
GMM-Demux requires python3 (>3.5).
## Install
GMM-Demux can be directly installed from PyPi. Or it can be built and installed locally.
### Install GMM-Demux from PyPi.
```bash
pip3 install --user GMM_Demux
```
In some OS, the `pip3` is linked to `pip` by default. For these OS, the installation command is simply:
```bash
pip install --user GMM_Demux
```
Check if `pip3` is linked to `pip` with `pip -V`.
If one chooses to install GMM-Demux from PyPi, it is unnecessary to download GMM-Demux from github. However, we still recommend downloading the example dataset to try out GMM-Demux.
### Install GMM-Demux locally using [setuptools](https://packaging.python.org/tutorials/installing-packages/) and pip3.
You may choose to install GMM-Demux locally after cloning the github repository. However, **this is for advanced users only and support is not gauranteed**.
The command is provided below:
```bash
cd
python3 setup.py sdist bdist_wheel
pip3 install --user .
```
### Post installation processes
If this is the first time you install a python3 software through pip, make sure you add the pip binary folder to your `PATH` variable.
Typically, the pip binary folder is located at ```~/.local/bin```.
The pip binary folder might locate at a different location if the user uses virtual enviroment. Pay attention to the pip installation output.
Here is an example installation output. The path of the pip binary folder is highlighted:
## Features
* Remove cell-hashing-identifiable multiplets (i.e., MSMs) from the dataset.
* Estimate the fraction of cell-hashing-unidentifiable multiplets (SSMs) in the remaining dataset (the RSSM percentage).
* Test if a putative cell type is a pure (real) cell type or is it a phony (fake) cell type.
## Example Dataset
* An example cell hashing dataset is provided in the *example_input* folder. It contains the per-drop HTO count matrix of a 4-sample cell hashing library prep. The input folder has the same file format with the CellRanger v3 output.
# Authors
Hongyi Xin, Qi Yan, Yale Jiang, Jiadi Luo, Carla Erb, Richard Duerr, Kong Chen* and Wei Chen*
# Maintainer
Hongyi Xin
## Requirement
GMM-Demux requires python3 (>3.5).
## Install
GMM-Demux can be directly installed from PyPi. Or it can be built and installed locally.
### Install GMM-Demux from PyPi.
```bash
pip3 install --user GMM_Demux
```
In some OS, the `pip3` is linked to `pip` by default. For these OS, the installation command is simply:
```bash
pip install --user GMM_Demux
```
Check if `pip3` is linked to `pip` with `pip -V`.
If one chooses to install GMM-Demux from PyPi, it is unnecessary to download GMM-Demux from github. However, we still recommend downloading the example dataset to try out GMM-Demux.
### Install GMM-Demux locally using [setuptools](https://packaging.python.org/tutorials/installing-packages/) and pip3.
You may choose to install GMM-Demux locally after cloning the github repository. However, **this is for advanced users only and support is not gauranteed**.
The command is provided below:
```bash
cd
python3 setup.py sdist bdist_wheel
pip3 install --user .
```
### Post installation processes
If this is the first time you install a python3 software through pip, make sure you add the pip binary folder to your `PATH` variable.
Typically, the pip binary folder is located at ```~/.local/bin```.
The pip binary folder might locate at a different location if the user uses virtual enviroment. Pay attention to the pip installation output.
Here is an example installation output. The path of the pip binary folder is highlighted:
 To temporarily add the pip binary folder, run the following command:
```bash
export PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
To permenantly add the pip library folder to your `PATH` variable, append the following line to your `.bashrc` file (assuming bash is the default shell).
```bash
PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
## Content
The source code of GMM-Demux is supplied in the ```GMM_Demux``` folder.
An example cell hashing dataset is also provided, located in the ```example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix``` folder.
An example set of hand-curated putative cell types of the above dataset are provided in the ```example_cell_types``` folder. Cell types are annotated through manual gating using surface marker expression data.
An example csv format of the above cell hashing dataset is provided as the ```example_hto.csv``` file.
## Usage
### Case 1: Basic Usage, Remove MSMs
Once installed, GMM-Demux is directly accessible with the ```GMM-demux``` command.
```bash
GMM-demux
```
`````` is a list of sample tags (HTOs) separated by ',' without whitespace.
For example, there are four sample barcoding tags in the example cell hashing dataset.
They are **HTO_1**, **HTO_2**, **HTO_3**, **HTO_4**. The `````` variable therefore is ```HTO_1,HTO_2,_HTO_3,HTO_4```.
The non-MSM droplets (SSDs) of the dataset are stored in the *GMM_Demux_mtx* folder under the current directory by default.
The output path can also be specified through the `-o` flag.
#### Example Command
An example cell hashing data is provided in the *example_input* folder. can be obtained from the features.tsv file.
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4
```
are included in the features.tsv file. The content of the feature.tsv file is shown below.

#### Output
The default content in the output folder are the non-MSM droplets (SSDs), stored in MTX format. The output shares the same format with CellRanger 3.0. By default, the output is stored in `SSD_mtx` folder. The output location can be overwritten with the `-o` flag.
### Case 2: Compute the MSM and SSM rates
To compute the MSM and SSM rates, GMM-Demux requires the `-u` flag:
* -u SUMMARY, --summary SUMMARY Generate the statstic summary of the dataset. Requires an estimated total number of cells in the assay as input.
The `-u` flag requires an additional argument, which is the estimated total count of cells in the single cell assay.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685
```
#### Output
Below is an example report:

* RSSM denotes the percentage of SSMs among the remaining SSDs (after removing all MSMs). RSSM **measures the quality of the final cell hashing dataset after removing MSMs**.
### Case 3: Verify if a cell type exists
GMM-Demux verifies if a putative cell type exists with the `-e` flag:
* -e EXAMINE, --examine EXAMINE Provide the cell list. Requires a file argument. Only executes if -u is set.
The `-e` flag requires a file name, which stores the list of droplet barcodes of the putative cell type.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685 -e example_cell_types/CD19+.txt
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685 -e example_cell_types/Doublets/CD3+CD4+CD19+.txt
```
#### Output
An example output of a pure cell type:

An example output of a phony cell type:

### Case 4: Use the csv file format as input, instead of the mtx format
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux -c example_hto.csv HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685
```
### Case 5: Extract droplets that are labeled by a combination of sample tags
Extract droplets that are labeled by multiple sample barcoding tags, with the `-x` flag:
* -x EXTRACT, --extract EXTRACT Names of the sample barcoding tag(s) to extract, separated by ','. Joint tags are linked with '+'.
**When `-x` is set, other functions of GMM-Demux will be turned off.**
#### *Case 5a: Extract a single HTO sample*
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO_1
```
#### *Case 5b: Extract a single HTO sample that are jointly defined by multiple HTO tags*
Use `+` to specify the joint HTO tags.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO_1+HTO_2
```
#### *Case 5c: Extract multiple HTO samples*
Use `,` to separate sample tags. Single tag samples can be merged with joint-tag samples.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO3,HTO_1+HTO_2,HTO_1+HTO_4+HTO_2
```
## Optional Arguments
* -h: show help information.
* -f FULL, --full FULL Generate the full classification report. Require a path argument.
* -s SIMPLIFIED, --simplified SIMPLIFIED Generate the simplified classification report. Require a path argument.
* -o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT The path for storing the Same-Sample-Droplets (SSDs). SSDs are stored in mtx format. Requires a path argument. Default path: SSD_mtx.
* -r REPORT, --report REPORT Specify the file to store summary report. Require a file argument.
* -c CSV, --csv Take input in csv format, instead of mmx format.
* -s SKIP, --skip FULL\_REPORT Load a full classification report and skip the mtx folder as input. Require a path argument.
* -a AMBIGUOUS, --ambiguous AMBIGUOUS The estimated chance of having a phony GEM getting included in a pure type GEM cluster by the clustering algorithm. Requires a float in (0, 1). Default value: 0.05. Only executes if -e executes.
* -t THRESHOLD, --threshold THRESHOLD Provide the confidence threshold value. Requires a float in (0,1). Default value: 0.8.
## Parsing the Classification Output
There are two files in a classification output folder. A config file (ending with .config) and a classification file (ending with .csv).
The classification file contains the label of each droplet as well as the probability of the classification. The classification is represented with numbers which are explained in the config file.
Below shows the classification output of the example data:
To temporarily add the pip binary folder, run the following command:
```bash
export PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
To permenantly add the pip library folder to your `PATH` variable, append the following line to your `.bashrc` file (assuming bash is the default shell).
```bash
PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
## Content
The source code of GMM-Demux is supplied in the ```GMM_Demux``` folder.
An example cell hashing dataset is also provided, located in the ```example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix``` folder.
An example set of hand-curated putative cell types of the above dataset are provided in the ```example_cell_types``` folder. Cell types are annotated through manual gating using surface marker expression data.
An example csv format of the above cell hashing dataset is provided as the ```example_hto.csv``` file.
## Usage
### Case 1: Basic Usage, Remove MSMs
Once installed, GMM-Demux is directly accessible with the ```GMM-demux``` command.
```bash
GMM-demux
```
`````` is a list of sample tags (HTOs) separated by ',' without whitespace.
For example, there are four sample barcoding tags in the example cell hashing dataset.
They are **HTO_1**, **HTO_2**, **HTO_3**, **HTO_4**. The `````` variable therefore is ```HTO_1,HTO_2,_HTO_3,HTO_4```.
The non-MSM droplets (SSDs) of the dataset are stored in the *GMM_Demux_mtx* folder under the current directory by default.
The output path can also be specified through the `-o` flag.
#### Example Command
An example cell hashing data is provided in the *example_input* folder. can be obtained from the features.tsv file.
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4
```
are included in the features.tsv file. The content of the feature.tsv file is shown below.

#### Output
The default content in the output folder are the non-MSM droplets (SSDs), stored in MTX format. The output shares the same format with CellRanger 3.0. By default, the output is stored in `SSD_mtx` folder. The output location can be overwritten with the `-o` flag.
### Case 2: Compute the MSM and SSM rates
To compute the MSM and SSM rates, GMM-Demux requires the `-u` flag:
* -u SUMMARY, --summary SUMMARY Generate the statstic summary of the dataset. Requires an estimated total number of cells in the assay as input.
The `-u` flag requires an additional argument, which is the estimated total count of cells in the single cell assay.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685
```
#### Output
Below is an example report:

* RSSM denotes the percentage of SSMs among the remaining SSDs (after removing all MSMs). RSSM **measures the quality of the final cell hashing dataset after removing MSMs**.
### Case 3: Verify if a cell type exists
GMM-Demux verifies if a putative cell type exists with the `-e` flag:
* -e EXAMINE, --examine EXAMINE Provide the cell list. Requires a file argument. Only executes if -u is set.
The `-e` flag requires a file name, which stores the list of droplet barcodes of the putative cell type.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685 -e example_cell_types/CD19+.txt
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685 -e example_cell_types/Doublets/CD3+CD4+CD19+.txt
```
#### Output
An example output of a pure cell type:

An example output of a phony cell type:

### Case 4: Use the csv file format as input, instead of the mtx format
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux -c example_hto.csv HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -u 35685
```
### Case 5: Extract droplets that are labeled by a combination of sample tags
Extract droplets that are labeled by multiple sample barcoding tags, with the `-x` flag:
* -x EXTRACT, --extract EXTRACT Names of the sample barcoding tag(s) to extract, separated by ','. Joint tags are linked with '+'.
**When `-x` is set, other functions of GMM-Demux will be turned off.**
#### *Case 5a: Extract a single HTO sample*
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO_1
```
#### *Case 5b: Extract a single HTO sample that are jointly defined by multiple HTO tags*
Use `+` to specify the joint HTO tags.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO_1+HTO_2
```
#### *Case 5c: Extract multiple HTO samples*
Use `,` to separate sample tags. Single tag samples can be merged with joint-tag samples.
#### Example Command
```bash
GMM-demux example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix HTO_1,HTO_2,HTO_3,HTO_4 -x HTO3,HTO_1+HTO_2,HTO_1+HTO_4+HTO_2
```
## Optional Arguments
* -h: show help information.
* -f FULL, --full FULL Generate the full classification report. Require a path argument.
* -s SIMPLIFIED, --simplified SIMPLIFIED Generate the simplified classification report. Require a path argument.
* -o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT The path for storing the Same-Sample-Droplets (SSDs). SSDs are stored in mtx format. Requires a path argument. Default path: SSD_mtx.
* -r REPORT, --report REPORT Specify the file to store summary report. Require a file argument.
* -c CSV, --csv Take input in csv format, instead of mmx format.
* -s SKIP, --skip FULL\_REPORT Load a full classification report and skip the mtx folder as input. Require a path argument.
* -a AMBIGUOUS, --ambiguous AMBIGUOUS The estimated chance of having a phony GEM getting included in a pure type GEM cluster by the clustering algorithm. Requires a float in (0, 1). Default value: 0.05. Only executes if -e executes.
* -t THRESHOLD, --threshold THRESHOLD Provide the confidence threshold value. Requires a float in (0,1). Default value: 0.8.
## Parsing the Classification Output
There are two files in a classification output folder. A config file (ending with .config) and a classification file (ending with .csv).
The classification file contains the label of each droplet as well as the probability of the classification. The classification is represented with numbers which are explained in the config file.
Below shows the classification output of the example data:
 ## Online Cell Hashing Experiment Planner
A GMM-Demux based online cell hashing experiment planner is publically accessible at [here](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html).
[
## Online Cell Hashing Experiment Planner
A GMM-Demux based online cell hashing experiment planner is publically accessible at [here](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html).
[ ](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html)
## Citation
If you find this code useful in your research, please consider citing:
@article{xin2019sample,
title={Sample demultiplexing, multiplet detection, experiment planning and novel cell type verification in single cell sequencing},
author={Xin, Hongyi and Yan, Qi and Jiang, Yale and Lian, Qiuyu and Luo, Jiadi and Erb, Carla and Duerr, Richard and Chen, Kong and Chen, Wei},
journal={bioRxiv},
pages={828483},
year={2019},
publisher={Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}
}
## Acknowledgement
Special thank to Zhongli Xu for testing GMM-Demux!
%prep
%autosetup -n GMM-Demux-0.2.1.3
%build
%py3_build
%install
%py3_install
install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}
if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
pushd %{buildroot}
if [ -d usr/lib ]; then
find usr/lib -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then
find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/bin ]; then
find usr/bin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then
find usr/sbin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
touch doclist.lst
if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then
find usr/share/man -type f -printf "/%h/%f.gz\n" >> doclist.lst
fi
popd
mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst .
mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst .
%files -n python3-GMM-Demux -f filelist.lst
%dir %{python3_sitelib}/*
%files help -f doclist.lst
%{_docdir}/*
%changelog
* Mon May 29 2023 Python_Bot - 0.2.1.3-1
- Package Spec generated
](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html)
## Citation
If you find this code useful in your research, please consider citing:
@article{xin2019sample,
title={Sample demultiplexing, multiplet detection, experiment planning and novel cell type verification in single cell sequencing},
author={Xin, Hongyi and Yan, Qi and Jiang, Yale and Lian, Qiuyu and Luo, Jiadi and Erb, Carla and Duerr, Richard and Chen, Kong and Chen, Wei},
journal={bioRxiv},
pages={828483},
year={2019},
publisher={Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}
}
## Acknowledgement
Special thank to Zhongli Xu for testing GMM-Demux!
%prep
%autosetup -n GMM-Demux-0.2.1.3
%build
%py3_build
%install
%py3_install
install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}
if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
pushd %{buildroot}
if [ -d usr/lib ]; then
find usr/lib -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then
find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/bin ]; then
find usr/bin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then
find usr/sbin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
touch doclist.lst
if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then
find usr/share/man -type f -printf "/%h/%f.gz\n" >> doclist.lst
fi
popd
mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst .
mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst .
%files -n python3-GMM-Demux -f filelist.lst
%dir %{python3_sitelib}/*
%files help -f doclist.lst
%{_docdir}/*
%changelog
* Mon May 29 2023 Python_Bot - 0.2.1.3-1
- Package Spec generated
 To temporarily add the pip binary folder, run the following command:
```bash
export PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
To permenantly add the pip library folder to your `PATH` variable, append the following line to your `.bashrc` file (assuming bash is the default shell).
```bash
PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
## Content
The source code of GMM-Demux is supplied in the ```GMM_Demux``` folder.
An example cell hashing dataset is also provided, located in the ```example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix``` folder.
An example set of hand-curated putative cell types of the above dataset are provided in the ```example_cell_types``` folder. Cell types are annotated through manual gating using surface marker expression data.
An example csv format of the above cell hashing dataset is provided as the ```example_hto.csv``` file.
## Usage
### Case 1: Basic Usage, Remove MSMs
Once installed, GMM-Demux is directly accessible with the ```GMM-demux``` command.
```bash
GMM-demux
To temporarily add the pip binary folder, run the following command:
```bash
export PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
To permenantly add the pip library folder to your `PATH` variable, append the following line to your `.bashrc` file (assuming bash is the default shell).
```bash
PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
## Content
The source code of GMM-Demux is supplied in the ```GMM_Demux``` folder.
An example cell hashing dataset is also provided, located in the ```example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix``` folder.
An example set of hand-curated putative cell types of the above dataset are provided in the ```example_cell_types``` folder. Cell types are annotated through manual gating using surface marker expression data.
An example csv format of the above cell hashing dataset is provided as the ```example_hto.csv``` file.
## Usage
### Case 1: Basic Usage, Remove MSMs
Once installed, GMM-Demux is directly accessible with the ```GMM-demux``` command.
```bash
GMM-demux  ## Online Cell Hashing Experiment Planner
A GMM-Demux based online cell hashing experiment planner is publically accessible at [here](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html).
[
## Online Cell Hashing Experiment Planner
A GMM-Demux based online cell hashing experiment planner is publically accessible at [here](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html).
[ ](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html)
## Citation
If you find this code useful in your research, please consider citing:
@article{xin2019sample,
title={Sample demultiplexing, multiplet detection, experiment planning and novel cell type verification in single cell sequencing},
author={Xin, Hongyi and Yan, Qi and Jiang, Yale and Lian, Qiuyu and Luo, Jiadi and Erb, Carla and Duerr, Richard and Chen, Kong and Chen, Wei},
journal={bioRxiv},
pages={828483},
year={2019},
publisher={Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}
}
## Acknowledgement
Special thank to Zhongli Xu for testing GMM-Demux!
%package -n python3-GMM-Demux
Summary: A multiplet removal tool for processing cell hashing data
Provides: python-GMM-Demux
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3-setuptools
BuildRequires: python3-pip
%description -n python3-GMM-Demux
# GMM-Demux
GMM-Demux is a Gaussian-Mixture-Model-based software for processing sample barcoding data (cell hashing and MULTI-seq).
GMM-Demux identifies Multi-Sample Multiplets (MSMs) in a sample barcoding dataset. Below shows an example distribution of MSMs in a PBMC scRNA-seq dataset. Orange dots in the scatter plot are MSMs.
](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html)
## Citation
If you find this code useful in your research, please consider citing:
@article{xin2019sample,
title={Sample demultiplexing, multiplet detection, experiment planning and novel cell type verification in single cell sequencing},
author={Xin, Hongyi and Yan, Qi and Jiang, Yale and Lian, Qiuyu and Luo, Jiadi and Erb, Carla and Duerr, Richard and Chen, Kong and Chen, Wei},
journal={bioRxiv},
pages={828483},
year={2019},
publisher={Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}
}
## Acknowledgement
Special thank to Zhongli Xu for testing GMM-Demux!
%package -n python3-GMM-Demux
Summary: A multiplet removal tool for processing cell hashing data
Provides: python-GMM-Demux
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3-setuptools
BuildRequires: python3-pip
%description -n python3-GMM-Demux
# GMM-Demux
GMM-Demux is a Gaussian-Mixture-Model-based software for processing sample barcoding data (cell hashing and MULTI-seq).
GMM-Demux identifies Multi-Sample Multiplets (MSMs) in a sample barcoding dataset. Below shows an example distribution of MSMs in a PBMC scRNA-seq dataset. Orange dots in the scatter plot are MSMs.
 ## Description
GMM-Demux removes Multi-Sample-Multiplets (MSMs) in a cell hashing dataset and estimates the percentages of Same-Sample-Multiplets (SSMs) and singlets in the remaining dataset.
GMM-Demux also verifies if a putative cell type exists, or is it merely an artifact induced by multiplets.
Multiplet-induced fake cell types are called "phony cell types".
Examples of phony cell types in a PBMC CITE-seq dataset is provided in the figure below:
## Description
GMM-Demux removes Multi-Sample-Multiplets (MSMs) in a cell hashing dataset and estimates the percentages of Same-Sample-Multiplets (SSMs) and singlets in the remaining dataset.
GMM-Demux also verifies if a putative cell type exists, or is it merely an artifact induced by multiplets.
Multiplet-induced fake cell types are called "phony cell types".
Examples of phony cell types in a PBMC CITE-seq dataset is provided in the figure below:
 In the above figure, both the CD3+CD19+ and the CD4+CD8+ cell types are multiplet-induced fake cell types.
Phony type clusters have large percentages of MSMs, as above figure shows. Both phony type clusters have large MSM percentages.
Percentages of MSMs are used as key features by GMM-Demux to classify GEM clusters.
## Terminology
* **Singlet**: A droplet that contains a single cell.
* **MSM**: Multi-Sample Multiplet. A MSM is a multiplet that contains cells from different samples in sample barcoding. MSMs can be identified by GMM-Demux.
* **SSM**: Same-Sample Multiplet. A SSM is a multiplet that contains cells from a single sample in sample barcoding. SSMs cannot be separated from singlets by sample barcoding.
* **SSD**: Same-Sample Droplet. SSD is a combined category of both SSMs and singlets.
* **Pure type**: a pure type cell type is a real cell type that exist in the tissue.
* **Phony type**: a phony type cell type is an artificial cell type that is an artifact produced by multiplets.
* **Mixture type**: a mixture type cell type is a cluster of droplets in which there exist a non-trivial fraction of phony type droplets.
An illustration of the above terminologies in a PBMC dataset is provided in the figure below:
In the above figure, both the CD3+CD19+ and the CD4+CD8+ cell types are multiplet-induced fake cell types.
Phony type clusters have large percentages of MSMs, as above figure shows. Both phony type clusters have large MSM percentages.
Percentages of MSMs are used as key features by GMM-Demux to classify GEM clusters.
## Terminology
* **Singlet**: A droplet that contains a single cell.
* **MSM**: Multi-Sample Multiplet. A MSM is a multiplet that contains cells from different samples in sample barcoding. MSMs can be identified by GMM-Demux.
* **SSM**: Same-Sample Multiplet. A SSM is a multiplet that contains cells from a single sample in sample barcoding. SSMs cannot be separated from singlets by sample barcoding.
* **SSD**: Same-Sample Droplet. SSD is a combined category of both SSMs and singlets.
* **Pure type**: a pure type cell type is a real cell type that exist in the tissue.
* **Phony type**: a phony type cell type is an artificial cell type that is an artifact produced by multiplets.
* **Mixture type**: a mixture type cell type is a cluster of droplets in which there exist a non-trivial fraction of phony type droplets.
An illustration of the above terminologies in a PBMC dataset is provided in the figure below:
 ## Features
* Remove cell-hashing-identifiable multiplets (i.e., MSMs) from the dataset.
* Estimate the fraction of cell-hashing-unidentifiable multiplets (SSMs) in the remaining dataset (the RSSM percentage).
* Test if a putative cell type is a pure (real) cell type or is it a phony (fake) cell type.
## Example Dataset
* An example cell hashing dataset is provided in the *example_input* folder. It contains the per-drop HTO count matrix of a 4-sample cell hashing library prep. The input folder has the same file format with the CellRanger v3 output.
# Authors
Hongyi Xin, Qi Yan, Yale Jiang, Jiadi Luo, Carla Erb, Richard Duerr, Kong Chen* and Wei Chen*
# Maintainer
Hongyi Xin
## Features
* Remove cell-hashing-identifiable multiplets (i.e., MSMs) from the dataset.
* Estimate the fraction of cell-hashing-unidentifiable multiplets (SSMs) in the remaining dataset (the RSSM percentage).
* Test if a putative cell type is a pure (real) cell type or is it a phony (fake) cell type.
## Example Dataset
* An example cell hashing dataset is provided in the *example_input* folder. It contains the per-drop HTO count matrix of a 4-sample cell hashing library prep. The input folder has the same file format with the CellRanger v3 output.
# Authors
Hongyi Xin, Qi Yan, Yale Jiang, Jiadi Luo, Carla Erb, Richard Duerr, Kong Chen* and Wei Chen*
# Maintainer
Hongyi Xin  To temporarily add the pip binary folder, run the following command:
```bash
export PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
To permenantly add the pip library folder to your `PATH` variable, append the following line to your `.bashrc` file (assuming bash is the default shell).
```bash
PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
## Content
The source code of GMM-Demux is supplied in the ```GMM_Demux``` folder.
An example cell hashing dataset is also provided, located in the ```example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix``` folder.
An example set of hand-curated putative cell types of the above dataset are provided in the ```example_cell_types``` folder. Cell types are annotated through manual gating using surface marker expression data.
An example csv format of the above cell hashing dataset is provided as the ```example_hto.csv``` file.
## Usage
### Case 1: Basic Usage, Remove MSMs
Once installed, GMM-Demux is directly accessible with the ```GMM-demux``` command.
```bash
GMM-demux
To temporarily add the pip binary folder, run the following command:
```bash
export PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
To permenantly add the pip library folder to your `PATH` variable, append the following line to your `.bashrc` file (assuming bash is the default shell).
```bash
PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
## Content
The source code of GMM-Demux is supplied in the ```GMM_Demux``` folder.
An example cell hashing dataset is also provided, located in the ```example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix``` folder.
An example set of hand-curated putative cell types of the above dataset are provided in the ```example_cell_types``` folder. Cell types are annotated through manual gating using surface marker expression data.
An example csv format of the above cell hashing dataset is provided as the ```example_hto.csv``` file.
## Usage
### Case 1: Basic Usage, Remove MSMs
Once installed, GMM-Demux is directly accessible with the ```GMM-demux``` command.
```bash
GMM-demux  ## Online Cell Hashing Experiment Planner
A GMM-Demux based online cell hashing experiment planner is publically accessible at [here](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html).
[
## Online Cell Hashing Experiment Planner
A GMM-Demux based online cell hashing experiment planner is publically accessible at [here](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html).
[ ](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html)
## Citation
If you find this code useful in your research, please consider citing:
@article{xin2019sample,
title={Sample demultiplexing, multiplet detection, experiment planning and novel cell type verification in single cell sequencing},
author={Xin, Hongyi and Yan, Qi and Jiang, Yale and Lian, Qiuyu and Luo, Jiadi and Erb, Carla and Duerr, Richard and Chen, Kong and Chen, Wei},
journal={bioRxiv},
pages={828483},
year={2019},
publisher={Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}
}
## Acknowledgement
Special thank to Zhongli Xu for testing GMM-Demux!
%package help
Summary: Development documents and examples for GMM-Demux
Provides: python3-GMM-Demux-doc
%description help
# GMM-Demux
GMM-Demux is a Gaussian-Mixture-Model-based software for processing sample barcoding data (cell hashing and MULTI-seq).
GMM-Demux identifies Multi-Sample Multiplets (MSMs) in a sample barcoding dataset. Below shows an example distribution of MSMs in a PBMC scRNA-seq dataset. Orange dots in the scatter plot are MSMs.
](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html)
## Citation
If you find this code useful in your research, please consider citing:
@article{xin2019sample,
title={Sample demultiplexing, multiplet detection, experiment planning and novel cell type verification in single cell sequencing},
author={Xin, Hongyi and Yan, Qi and Jiang, Yale and Lian, Qiuyu and Luo, Jiadi and Erb, Carla and Duerr, Richard and Chen, Kong and Chen, Wei},
journal={bioRxiv},
pages={828483},
year={2019},
publisher={Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}
}
## Acknowledgement
Special thank to Zhongli Xu for testing GMM-Demux!
%package help
Summary: Development documents and examples for GMM-Demux
Provides: python3-GMM-Demux-doc
%description help
# GMM-Demux
GMM-Demux is a Gaussian-Mixture-Model-based software for processing sample barcoding data (cell hashing and MULTI-seq).
GMM-Demux identifies Multi-Sample Multiplets (MSMs) in a sample barcoding dataset. Below shows an example distribution of MSMs in a PBMC scRNA-seq dataset. Orange dots in the scatter plot are MSMs.
 ## Description
GMM-Demux removes Multi-Sample-Multiplets (MSMs) in a cell hashing dataset and estimates the percentages of Same-Sample-Multiplets (SSMs) and singlets in the remaining dataset.
GMM-Demux also verifies if a putative cell type exists, or is it merely an artifact induced by multiplets.
Multiplet-induced fake cell types are called "phony cell types".
Examples of phony cell types in a PBMC CITE-seq dataset is provided in the figure below:
## Description
GMM-Demux removes Multi-Sample-Multiplets (MSMs) in a cell hashing dataset and estimates the percentages of Same-Sample-Multiplets (SSMs) and singlets in the remaining dataset.
GMM-Demux also verifies if a putative cell type exists, or is it merely an artifact induced by multiplets.
Multiplet-induced fake cell types are called "phony cell types".
Examples of phony cell types in a PBMC CITE-seq dataset is provided in the figure below:
 In the above figure, both the CD3+CD19+ and the CD4+CD8+ cell types are multiplet-induced fake cell types.
Phony type clusters have large percentages of MSMs, as above figure shows. Both phony type clusters have large MSM percentages.
Percentages of MSMs are used as key features by GMM-Demux to classify GEM clusters.
## Terminology
* **Singlet**: A droplet that contains a single cell.
* **MSM**: Multi-Sample Multiplet. A MSM is a multiplet that contains cells from different samples in sample barcoding. MSMs can be identified by GMM-Demux.
* **SSM**: Same-Sample Multiplet. A SSM is a multiplet that contains cells from a single sample in sample barcoding. SSMs cannot be separated from singlets by sample barcoding.
* **SSD**: Same-Sample Droplet. SSD is a combined category of both SSMs and singlets.
* **Pure type**: a pure type cell type is a real cell type that exist in the tissue.
* **Phony type**: a phony type cell type is an artificial cell type that is an artifact produced by multiplets.
* **Mixture type**: a mixture type cell type is a cluster of droplets in which there exist a non-trivial fraction of phony type droplets.
An illustration of the above terminologies in a PBMC dataset is provided in the figure below:
In the above figure, both the CD3+CD19+ and the CD4+CD8+ cell types are multiplet-induced fake cell types.
Phony type clusters have large percentages of MSMs, as above figure shows. Both phony type clusters have large MSM percentages.
Percentages of MSMs are used as key features by GMM-Demux to classify GEM clusters.
## Terminology
* **Singlet**: A droplet that contains a single cell.
* **MSM**: Multi-Sample Multiplet. A MSM is a multiplet that contains cells from different samples in sample barcoding. MSMs can be identified by GMM-Demux.
* **SSM**: Same-Sample Multiplet. A SSM is a multiplet that contains cells from a single sample in sample barcoding. SSMs cannot be separated from singlets by sample barcoding.
* **SSD**: Same-Sample Droplet. SSD is a combined category of both SSMs and singlets.
* **Pure type**: a pure type cell type is a real cell type that exist in the tissue.
* **Phony type**: a phony type cell type is an artificial cell type that is an artifact produced by multiplets.
* **Mixture type**: a mixture type cell type is a cluster of droplets in which there exist a non-trivial fraction of phony type droplets.
An illustration of the above terminologies in a PBMC dataset is provided in the figure below:
 ## Features
* Remove cell-hashing-identifiable multiplets (i.e., MSMs) from the dataset.
* Estimate the fraction of cell-hashing-unidentifiable multiplets (SSMs) in the remaining dataset (the RSSM percentage).
* Test if a putative cell type is a pure (real) cell type or is it a phony (fake) cell type.
## Example Dataset
* An example cell hashing dataset is provided in the *example_input* folder. It contains the per-drop HTO count matrix of a 4-sample cell hashing library prep. The input folder has the same file format with the CellRanger v3 output.
# Authors
Hongyi Xin, Qi Yan, Yale Jiang, Jiadi Luo, Carla Erb, Richard Duerr, Kong Chen* and Wei Chen*
# Maintainer
Hongyi Xin
## Features
* Remove cell-hashing-identifiable multiplets (i.e., MSMs) from the dataset.
* Estimate the fraction of cell-hashing-unidentifiable multiplets (SSMs) in the remaining dataset (the RSSM percentage).
* Test if a putative cell type is a pure (real) cell type or is it a phony (fake) cell type.
## Example Dataset
* An example cell hashing dataset is provided in the *example_input* folder. It contains the per-drop HTO count matrix of a 4-sample cell hashing library prep. The input folder has the same file format with the CellRanger v3 output.
# Authors
Hongyi Xin, Qi Yan, Yale Jiang, Jiadi Luo, Carla Erb, Richard Duerr, Kong Chen* and Wei Chen*
# Maintainer
Hongyi Xin  To temporarily add the pip binary folder, run the following command:
```bash
export PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
To permenantly add the pip library folder to your `PATH` variable, append the following line to your `.bashrc` file (assuming bash is the default shell).
```bash
PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
## Content
The source code of GMM-Demux is supplied in the ```GMM_Demux``` folder.
An example cell hashing dataset is also provided, located in the ```example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix``` folder.
An example set of hand-curated putative cell types of the above dataset are provided in the ```example_cell_types``` folder. Cell types are annotated through manual gating using surface marker expression data.
An example csv format of the above cell hashing dataset is provided as the ```example_hto.csv``` file.
## Usage
### Case 1: Basic Usage, Remove MSMs
Once installed, GMM-Demux is directly accessible with the ```GMM-demux``` command.
```bash
GMM-demux
To temporarily add the pip binary folder, run the following command:
```bash
export PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
To permenantly add the pip library folder to your `PATH` variable, append the following line to your `.bashrc` file (assuming bash is the default shell).
```bash
PATH=~/.local/bin:$PATH
```
## Content
The source code of GMM-Demux is supplied in the ```GMM_Demux``` folder.
An example cell hashing dataset is also provided, located in the ```example_input/outs/filtered_feature_bc_matrix``` folder.
An example set of hand-curated putative cell types of the above dataset are provided in the ```example_cell_types``` folder. Cell types are annotated through manual gating using surface marker expression data.
An example csv format of the above cell hashing dataset is provided as the ```example_hto.csv``` file.
## Usage
### Case 1: Basic Usage, Remove MSMs
Once installed, GMM-Demux is directly accessible with the ```GMM-demux``` command.
```bash
GMM-demux  ## Online Cell Hashing Experiment Planner
A GMM-Demux based online cell hashing experiment planner is publically accessible at [here](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html).
[
## Online Cell Hashing Experiment Planner
A GMM-Demux based online cell hashing experiment planner is publically accessible at [here](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html).
[ ](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html)
## Citation
If you find this code useful in your research, please consider citing:
@article{xin2019sample,
title={Sample demultiplexing, multiplet detection, experiment planning and novel cell type verification in single cell sequencing},
author={Xin, Hongyi and Yan, Qi and Jiang, Yale and Lian, Qiuyu and Luo, Jiadi and Erb, Carla and Duerr, Richard and Chen, Kong and Chen, Wei},
journal={bioRxiv},
pages={828483},
year={2019},
publisher={Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}
}
## Acknowledgement
Special thank to Zhongli Xu for testing GMM-Demux!
%prep
%autosetup -n GMM-Demux-0.2.1.3
%build
%py3_build
%install
%py3_install
install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}
if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
pushd %{buildroot}
if [ -d usr/lib ]; then
find usr/lib -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then
find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/bin ]; then
find usr/bin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then
find usr/sbin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
touch doclist.lst
if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then
find usr/share/man -type f -printf "/%h/%f.gz\n" >> doclist.lst
fi
popd
mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst .
mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst .
%files -n python3-GMM-Demux -f filelist.lst
%dir %{python3_sitelib}/*
%files help -f doclist.lst
%{_docdir}/*
%changelog
* Mon May 29 2023 Python_Bot
](https://www.pitt.edu/~wec47/gmmdemux.html)
## Citation
If you find this code useful in your research, please consider citing:
@article{xin2019sample,
title={Sample demultiplexing, multiplet detection, experiment planning and novel cell type verification in single cell sequencing},
author={Xin, Hongyi and Yan, Qi and Jiang, Yale and Lian, Qiuyu and Luo, Jiadi and Erb, Carla and Duerr, Richard and Chen, Kong and Chen, Wei},
journal={bioRxiv},
pages={828483},
year={2019},
publisher={Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory}
}
## Acknowledgement
Special thank to Zhongli Xu for testing GMM-Demux!
%prep
%autosetup -n GMM-Demux-0.2.1.3
%build
%py3_build
%install
%py3_install
install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}
if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
pushd %{buildroot}
if [ -d usr/lib ]; then
find usr/lib -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then
find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/bin ]; then
find usr/bin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then
find usr/sbin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
touch doclist.lst
if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then
find usr/share/man -type f -printf "/%h/%f.gz\n" >> doclist.lst
fi
popd
mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst .
mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst .
%files -n python3-GMM-Demux -f filelist.lst
%dir %{python3_sitelib}/*
%files help -f doclist.lst
%{_docdir}/*
%changelog
* Mon May 29 2023 Python_Bot