

The goal of this library is to provide a starting point for users in metrology and related areas who deal with time-dependent i.e., dynamic, measurements. The initial version of this software was developed as part of a joint research project of the national metrology institutes from Germany and the UK, i.e. Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt and the National Physical Laboratory.
Further development and explicit use of PyDynamic was part of the European research project EMPIR 17IND12 Met4FoF and the German research project FAMOUS. Since the end of these two projects, development of PyDynamic continues mostly based on feature requests and smaller collaborations.
## Table of content - [Quickstart](#quickstart) - [Features](#features) - [Module diagram](#module-diagram) - [Documentation](#documentation) - [Installation](#installation) - [Contributing](#contributing) - [Examples](#examples) - [Roadmap](#roadmap) - [Citation](#citation) - [Acknowledgement](#acknowledgement) - [Disclaimer](#disclaimer) - [License](#license) ## Quickstart To dive right into it, install PyDynamic and execute one of the examples: ```shell (my_PyDynamice_venv) $ pip install PyDynamic Collecting PyDynamic [...] Successfully installed PyDynamic-[...] (my_PyDynamice_venv) $ python Python 3.9.7 (default, Aug 31 2021, 13:28:12) [GCC 11.1.0] on linux Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. ``` ```python >>> from PyDynamic.examples.uncertainty_for_dft.deconv_DFT import DftDeconvolutionExample >>> DftDeconvolutionExample() Propagating uncertainty associated with measurement through DFT Propagating uncertainty associated with calibration data to real and imag part Propagating uncertainty through the inverse system Propagating uncertainty through the low-pass filter Propagating uncertainty associated with the estimate back to time domain ``` You will see a couple of plots opening up to observe the results. For further information just read on and visit our [tutorial section](#examples). ## Features PyDynamic offers propagation of *uncertainties* for - application of the discrete Fourier transform and its inverse - filtering with an FIR or IIR filter with uncertain coefficients - design of a FIR filter as the inverse of a frequency response with uncertain coefficients - design on an IIR filter as the inverse of a frequency response with uncertain coefficients - deconvolution in the frequency domain by division - multiplication in the frequency domain - transformation from amplitude and phase to a representation by real and imaginary parts - 1-dimensional interpolation For the validation of the propagation of uncertainties, the Monte-Carlo method can be applied using a memory-efficient implementation of Monte-Carlo for digital filtering. ## Module diagram The fundamental structure of PyDynamic is shown in the following figure. 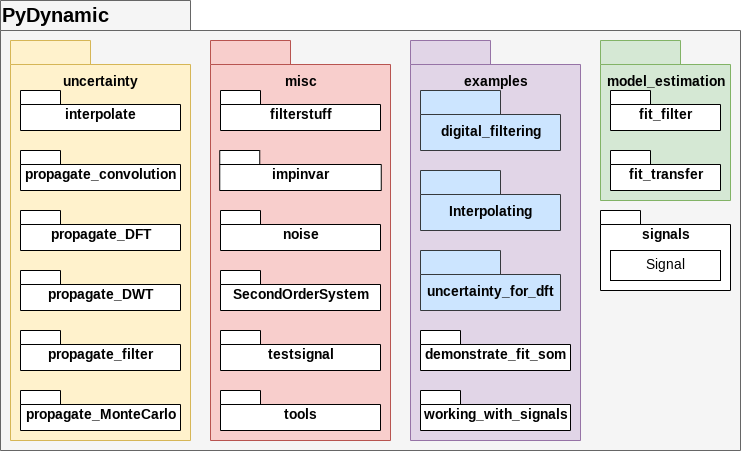 However, imports should generally be possible without explicitly naming all packages and modules in the path, so that for example the following import statements are all equivalent. ```python from PyDynamic.uncertainty.propagate_filter import FIRuncFilter from PyDynamic.uncertainty import FIRuncFilter from PyDynamic import FIRuncFilter ``` ## Documentation The documentation for PyDynamic can be found on [ReadTheDocs](http://pydynamic.readthedocs.io) ## Installation The installation of PyDynamic is as straightforward as the Python ecosystem suggests. Detailed instructions on different options to install PyDynamic you can find in the [installation section of the docs](https://pydynamic.readthedocs.io/en/latest/INSTALL.html). ## Contributing Whenever you are involved with PyDynamic, please respect our [Code of Conduct ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md). If you want to contribute back to the project, after reading our Code of Conduct, take a look at our open developments in the [project board ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/projects/1), [pull requests ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/pulls) and search [the issues ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/issues). If you find something similar to your ideas or troubles, let us know by leaving a comment or remark. If you have something new to tell us, feel free to open a feature request or bug report in the issues. If you want to contribute code or improve our documentation, please check our [contribution advices and tips](https://pydynamic.readthedocs.io/en/latest/CONTRIBUTING.html). If you have downloaded this software, we would be very thankful for letting us know. You may, for instance, drop an email to one of the [authors ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/graphs/contributors) (e.g. [Sascha Eichstädt](mailto:sascha.eichstaedt@ptb.de), [Björn Ludwig ](mailto:bjoern.ludwig@ptb.de) or [Maximilian Gruber ](mailto:maximilian.gruber@ptb.de)) ## Examples We have collected extended material for an easier introduction to PyDynamic in the package _examples_. Detailed assistance on getting started you can find in the corresponding sections of the docs: * [examples](https://pydynamic.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Examples.html) * [tutorials](https://pydynamic.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Tutorials.html) In various Jupyter Notebooks and scripts we demonstrate the use of the provided methods to aid the first steps in PyDynamic. New features are introduced with an example from the beginning if feasible. We are currently moving this supporting collection to an external repository on GitHub. They will be available at [github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic_tutorials](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic_tutorials) in the near future. ## Roadmap 1. Implementation of robust measurement (sensor) models 1. Extension to more complex noise and uncertainty models 1. Introducing uncertainty propagation for Kalman filters For a comprehensive overview of current development activities and upcoming tasks, take a look at the [project board](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/projects/1), [issues](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/issues) and [pull requests](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/pulls). ## Citation If you publish results obtained with the help of PyDynamic, please use the above linked [Zenodo DOI](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1489877) for the code itself or cite Sascha Eichstädt, Clemens Elster, Ian M. Smith, and Trevor J. Esward *Evaluation of dynamic measurement uncertainty – an open-source software package to bridge theory and practice* **J. Sens. Sens. Syst.**, 6, 97-105, 2017, DOI: [10.5194/jsss-6-97-2017 ](https://doi.org/10.5194/jsss-6-97-2017) ## Acknowledgement Part of this work is developed as part of the Joint Research Project [17IND12 Met4FoF ](http://met4fof.eu) of the European Metrology Programme for Innovation and Research (EMPIR). This work was part of the Joint Support for Impact project [14SIP08](https://www.euramet.org/research-innovation/search-research-projects/details/project/standards-and-software-to-maximise-end-user-uptake-of-nmi-calibrations-of-dynamic-force-torque-and/) of the European Metrology Programme for Innovation and Research (EMPIR). The [EMPIR](http://msu.euramet.org) is jointly funded by the EMPIR participating countries within EURAMET and the European Union. ## Disclaimer This software is developed at Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB). The software is made available "as is" free of cost. PTB assumes no responsibility whatsoever for its use by other parties, and makes no guarantees, expressed or implied, about its quality, reliability, safety, suitability or any other characteristic. In no event will PTB be liable for any direct, indirect or consequential damage arising in connection with the use of this software. ## License PyDynamic is distributed under the [LGPLv3 license ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/blob/main/licence.txt) except for the module [`impinvar.py` ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/blob/main/src/PyDynamic/misc/impinvar.py) in the package [`misc` ](https://pydynamic.readthedocs.io/en/main/PyDynamic.misc.html), which is distributed under the [GPLv3 license ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/blob/main/src/PyDynamic/misc/impinvar_license.txt). %package -n python3-PyDynamic Summary: A software package for the analysis of dynamic measurements Provides: python-PyDynamic BuildRequires: python3-devel BuildRequires: python3-setuptools BuildRequires: python3-pip %description -n python3-PyDynamicThe goal of this library is to provide a starting point for users in metrology and related areas who deal with time-dependent i.e., dynamic, measurements. The initial version of this software was developed as part of a joint research project of the national metrology institutes from Germany and the UK, i.e. Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt and the National Physical Laboratory.
Further development and explicit use of PyDynamic was part of the European research project EMPIR 17IND12 Met4FoF and the German research project FAMOUS. Since the end of these two projects, development of PyDynamic continues mostly based on feature requests and smaller collaborations.
## Table of content - [Quickstart](#quickstart) - [Features](#features) - [Module diagram](#module-diagram) - [Documentation](#documentation) - [Installation](#installation) - [Contributing](#contributing) - [Examples](#examples) - [Roadmap](#roadmap) - [Citation](#citation) - [Acknowledgement](#acknowledgement) - [Disclaimer](#disclaimer) - [License](#license) ## Quickstart To dive right into it, install PyDynamic and execute one of the examples: ```shell (my_PyDynamice_venv) $ pip install PyDynamic Collecting PyDynamic [...] Successfully installed PyDynamic-[...] (my_PyDynamice_venv) $ python Python 3.9.7 (default, Aug 31 2021, 13:28:12) [GCC 11.1.0] on linux Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. ``` ```python >>> from PyDynamic.examples.uncertainty_for_dft.deconv_DFT import DftDeconvolutionExample >>> DftDeconvolutionExample() Propagating uncertainty associated with measurement through DFT Propagating uncertainty associated with calibration data to real and imag part Propagating uncertainty through the inverse system Propagating uncertainty through the low-pass filter Propagating uncertainty associated with the estimate back to time domain ``` You will see a couple of plots opening up to observe the results. For further information just read on and visit our [tutorial section](#examples). ## Features PyDynamic offers propagation of *uncertainties* for - application of the discrete Fourier transform and its inverse - filtering with an FIR or IIR filter with uncertain coefficients - design of a FIR filter as the inverse of a frequency response with uncertain coefficients - design on an IIR filter as the inverse of a frequency response with uncertain coefficients - deconvolution in the frequency domain by division - multiplication in the frequency domain - transformation from amplitude and phase to a representation by real and imaginary parts - 1-dimensional interpolation For the validation of the propagation of uncertainties, the Monte-Carlo method can be applied using a memory-efficient implementation of Monte-Carlo for digital filtering. ## Module diagram The fundamental structure of PyDynamic is shown in the following figure.  However, imports should generally be possible without explicitly naming all packages and modules in the path, so that for example the following import statements are all equivalent. ```python from PyDynamic.uncertainty.propagate_filter import FIRuncFilter from PyDynamic.uncertainty import FIRuncFilter from PyDynamic import FIRuncFilter ``` ## Documentation The documentation for PyDynamic can be found on [ReadTheDocs](http://pydynamic.readthedocs.io) ## Installation The installation of PyDynamic is as straightforward as the Python ecosystem suggests. Detailed instructions on different options to install PyDynamic you can find in the [installation section of the docs](https://pydynamic.readthedocs.io/en/latest/INSTALL.html). ## Contributing Whenever you are involved with PyDynamic, please respect our [Code of Conduct ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md). If you want to contribute back to the project, after reading our Code of Conduct, take a look at our open developments in the [project board ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/projects/1), [pull requests ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/pulls) and search [the issues ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/issues). If you find something similar to your ideas or troubles, let us know by leaving a comment or remark. If you have something new to tell us, feel free to open a feature request or bug report in the issues. If you want to contribute code or improve our documentation, please check our [contribution advices and tips](https://pydynamic.readthedocs.io/en/latest/CONTRIBUTING.html). If you have downloaded this software, we would be very thankful for letting us know. You may, for instance, drop an email to one of the [authors ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/graphs/contributors) (e.g. [Sascha Eichstädt](mailto:sascha.eichstaedt@ptb.de), [Björn Ludwig ](mailto:bjoern.ludwig@ptb.de) or [Maximilian Gruber ](mailto:maximilian.gruber@ptb.de)) ## Examples We have collected extended material for an easier introduction to PyDynamic in the package _examples_. Detailed assistance on getting started you can find in the corresponding sections of the docs: * [examples](https://pydynamic.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Examples.html) * [tutorials](https://pydynamic.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Tutorials.html) In various Jupyter Notebooks and scripts we demonstrate the use of the provided methods to aid the first steps in PyDynamic. New features are introduced with an example from the beginning if feasible. We are currently moving this supporting collection to an external repository on GitHub. They will be available at [github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic_tutorials](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic_tutorials) in the near future. ## Roadmap 1. Implementation of robust measurement (sensor) models 1. Extension to more complex noise and uncertainty models 1. Introducing uncertainty propagation for Kalman filters For a comprehensive overview of current development activities and upcoming tasks, take a look at the [project board](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/projects/1), [issues](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/issues) and [pull requests](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/pulls). ## Citation If you publish results obtained with the help of PyDynamic, please use the above linked [Zenodo DOI](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1489877) for the code itself or cite Sascha Eichstädt, Clemens Elster, Ian M. Smith, and Trevor J. Esward *Evaluation of dynamic measurement uncertainty – an open-source software package to bridge theory and practice* **J. Sens. Sens. Syst.**, 6, 97-105, 2017, DOI: [10.5194/jsss-6-97-2017 ](https://doi.org/10.5194/jsss-6-97-2017) ## Acknowledgement Part of this work is developed as part of the Joint Research Project [17IND12 Met4FoF ](http://met4fof.eu) of the European Metrology Programme for Innovation and Research (EMPIR). This work was part of the Joint Support for Impact project [14SIP08](https://www.euramet.org/research-innovation/search-research-projects/details/project/standards-and-software-to-maximise-end-user-uptake-of-nmi-calibrations-of-dynamic-force-torque-and/) of the European Metrology Programme for Innovation and Research (EMPIR). The [EMPIR](http://msu.euramet.org) is jointly funded by the EMPIR participating countries within EURAMET and the European Union. ## Disclaimer This software is developed at Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB). The software is made available "as is" free of cost. PTB assumes no responsibility whatsoever for its use by other parties, and makes no guarantees, expressed or implied, about its quality, reliability, safety, suitability or any other characteristic. In no event will PTB be liable for any direct, indirect or consequential damage arising in connection with the use of this software. ## License PyDynamic is distributed under the [LGPLv3 license ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/blob/main/licence.txt) except for the module [`impinvar.py` ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/blob/main/src/PyDynamic/misc/impinvar.py) in the package [`misc` ](https://pydynamic.readthedocs.io/en/main/PyDynamic.misc.html), which is distributed under the [GPLv3 license ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/blob/main/src/PyDynamic/misc/impinvar_license.txt). %package help Summary: Development documents and examples for PyDynamic Provides: python3-PyDynamic-doc %description helpThe goal of this library is to provide a starting point for users in metrology and related areas who deal with time-dependent i.e., dynamic, measurements. The initial version of this software was developed as part of a joint research project of the national metrology institutes from Germany and the UK, i.e. Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt and the National Physical Laboratory.
Further development and explicit use of PyDynamic was part of the European research project EMPIR 17IND12 Met4FoF and the German research project FAMOUS. Since the end of these two projects, development of PyDynamic continues mostly based on feature requests and smaller collaborations.
## Table of content - [Quickstart](#quickstart) - [Features](#features) - [Module diagram](#module-diagram) - [Documentation](#documentation) - [Installation](#installation) - [Contributing](#contributing) - [Examples](#examples) - [Roadmap](#roadmap) - [Citation](#citation) - [Acknowledgement](#acknowledgement) - [Disclaimer](#disclaimer) - [License](#license) ## Quickstart To dive right into it, install PyDynamic and execute one of the examples: ```shell (my_PyDynamice_venv) $ pip install PyDynamic Collecting PyDynamic [...] Successfully installed PyDynamic-[...] (my_PyDynamice_venv) $ python Python 3.9.7 (default, Aug 31 2021, 13:28:12) [GCC 11.1.0] on linux Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information. ``` ```python >>> from PyDynamic.examples.uncertainty_for_dft.deconv_DFT import DftDeconvolutionExample >>> DftDeconvolutionExample() Propagating uncertainty associated with measurement through DFT Propagating uncertainty associated with calibration data to real and imag part Propagating uncertainty through the inverse system Propagating uncertainty through the low-pass filter Propagating uncertainty associated with the estimate back to time domain ``` You will see a couple of plots opening up to observe the results. For further information just read on and visit our [tutorial section](#examples). ## Features PyDynamic offers propagation of *uncertainties* for - application of the discrete Fourier transform and its inverse - filtering with an FIR or IIR filter with uncertain coefficients - design of a FIR filter as the inverse of a frequency response with uncertain coefficients - design on an IIR filter as the inverse of a frequency response with uncertain coefficients - deconvolution in the frequency domain by division - multiplication in the frequency domain - transformation from amplitude and phase to a representation by real and imaginary parts - 1-dimensional interpolation For the validation of the propagation of uncertainties, the Monte-Carlo method can be applied using a memory-efficient implementation of Monte-Carlo for digital filtering. ## Module diagram The fundamental structure of PyDynamic is shown in the following figure.  However, imports should generally be possible without explicitly naming all packages and modules in the path, so that for example the following import statements are all equivalent. ```python from PyDynamic.uncertainty.propagate_filter import FIRuncFilter from PyDynamic.uncertainty import FIRuncFilter from PyDynamic import FIRuncFilter ``` ## Documentation The documentation for PyDynamic can be found on [ReadTheDocs](http://pydynamic.readthedocs.io) ## Installation The installation of PyDynamic is as straightforward as the Python ecosystem suggests. Detailed instructions on different options to install PyDynamic you can find in the [installation section of the docs](https://pydynamic.readthedocs.io/en/latest/INSTALL.html). ## Contributing Whenever you are involved with PyDynamic, please respect our [Code of Conduct ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/blob/main/CODE_OF_CONDUCT.md). If you want to contribute back to the project, after reading our Code of Conduct, take a look at our open developments in the [project board ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/projects/1), [pull requests ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/pulls) and search [the issues ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/issues). If you find something similar to your ideas or troubles, let us know by leaving a comment or remark. If you have something new to tell us, feel free to open a feature request or bug report in the issues. If you want to contribute code or improve our documentation, please check our [contribution advices and tips](https://pydynamic.readthedocs.io/en/latest/CONTRIBUTING.html). If you have downloaded this software, we would be very thankful for letting us know. You may, for instance, drop an email to one of the [authors ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/graphs/contributors) (e.g. [Sascha Eichstädt](mailto:sascha.eichstaedt@ptb.de), [Björn Ludwig ](mailto:bjoern.ludwig@ptb.de) or [Maximilian Gruber ](mailto:maximilian.gruber@ptb.de)) ## Examples We have collected extended material for an easier introduction to PyDynamic in the package _examples_. Detailed assistance on getting started you can find in the corresponding sections of the docs: * [examples](https://pydynamic.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Examples.html) * [tutorials](https://pydynamic.readthedocs.io/en/latest/Tutorials.html) In various Jupyter Notebooks and scripts we demonstrate the use of the provided methods to aid the first steps in PyDynamic. New features are introduced with an example from the beginning if feasible. We are currently moving this supporting collection to an external repository on GitHub. They will be available at [github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic_tutorials](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic_tutorials) in the near future. ## Roadmap 1. Implementation of robust measurement (sensor) models 1. Extension to more complex noise and uncertainty models 1. Introducing uncertainty propagation for Kalman filters For a comprehensive overview of current development activities and upcoming tasks, take a look at the [project board](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/projects/1), [issues](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/issues) and [pull requests](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/pulls). ## Citation If you publish results obtained with the help of PyDynamic, please use the above linked [Zenodo DOI](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.1489877) for the code itself or cite Sascha Eichstädt, Clemens Elster, Ian M. Smith, and Trevor J. Esward *Evaluation of dynamic measurement uncertainty – an open-source software package to bridge theory and practice* **J. Sens. Sens. Syst.**, 6, 97-105, 2017, DOI: [10.5194/jsss-6-97-2017 ](https://doi.org/10.5194/jsss-6-97-2017) ## Acknowledgement Part of this work is developed as part of the Joint Research Project [17IND12 Met4FoF ](http://met4fof.eu) of the European Metrology Programme for Innovation and Research (EMPIR). This work was part of the Joint Support for Impact project [14SIP08](https://www.euramet.org/research-innovation/search-research-projects/details/project/standards-and-software-to-maximise-end-user-uptake-of-nmi-calibrations-of-dynamic-force-torque-and/) of the European Metrology Programme for Innovation and Research (EMPIR). The [EMPIR](http://msu.euramet.org) is jointly funded by the EMPIR participating countries within EURAMET and the European Union. ## Disclaimer This software is developed at Physikalisch-Technische Bundesanstalt (PTB). The software is made available "as is" free of cost. PTB assumes no responsibility whatsoever for its use by other parties, and makes no guarantees, expressed or implied, about its quality, reliability, safety, suitability or any other characteristic. In no event will PTB be liable for any direct, indirect or consequential damage arising in connection with the use of this software. ## License PyDynamic is distributed under the [LGPLv3 license ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/blob/main/licence.txt) except for the module [`impinvar.py` ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/blob/main/src/PyDynamic/misc/impinvar.py) in the package [`misc` ](https://pydynamic.readthedocs.io/en/main/PyDynamic.misc.html), which is distributed under the [GPLv3 license ](https://github.com/PTB-M4D/PyDynamic/blob/main/src/PyDynamic/misc/impinvar_license.txt). %prep %autosetup -n PyDynamic-2.4.0 %build %py3_build %install %py3_install install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir} if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi pushd %{buildroot} if [ -d usr/lib ]; then find usr/lib -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst fi if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst fi if [ -d usr/bin ]; then find usr/bin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst fi if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then find usr/sbin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst fi touch doclist.lst if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then find usr/share/man -type f -printf "/%h/%f.gz\n" >> doclist.lst fi popd mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst . mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst . %files -n python3-PyDynamic -f filelist.lst %dir %{python3_sitelib}/* %files help -f doclist.lst %{_docdir}/* %changelog * Fri May 05 2023 Python_Bot