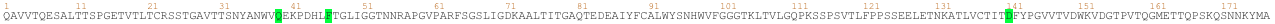%global _empty_manifest_terminate_build 0
Name: python-bio-transformers
Version: 0.1.17
Release: 1
Summary: Wrapper on top of ESM/Protbert model in order to easily work with protein embedding
License: Apache-2.0
URL: https://pypi.org/project/bio-transformers/
Source0: https://mirrors.nju.edu.cn/pypi/web/packages/34/5a/086fd5c388c4a6c0fb5f0e541b6ec922187a09d85f829789a4ff72f34295/bio-transformers-0.1.17.tar.gz
BuildArch: noarch
Requires: python3-biopython
Requires: python3-fair-esm
Requires: python3-numpy
Requires: python3-pandas
Requires: python3-pytorch-lightning
Requires: python3-ray
Requires: python3-scikit-learn
Requires: python3-torch
Requires: python3-torchmetrics
Requires: python3-tqdm
Requires: python3-transformers
%description
 
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/Apache-2.0)
[](https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-360/)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)

[](https://bio-transformers.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/delfosseaurelien/bio-transformers)

[](https://opensource.org/licenses/Apache-2.0)
[](https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-360/)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)

[](https://bio-transformers.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/delfosseaurelien/bio-transformers)
Table of contents
- [Description](#bio-transformers)
- [Installation](#Installation)
- [Usage](#usage)
- [Quick Start](#quickstart)
- [Compute embeddings](#embeddings)
- [Pseudo-Loglikelihood](#pseudo-loglikelihood)
- [Roadmap](#roadmap)
- [Citations](#citations)
- [License](#license)
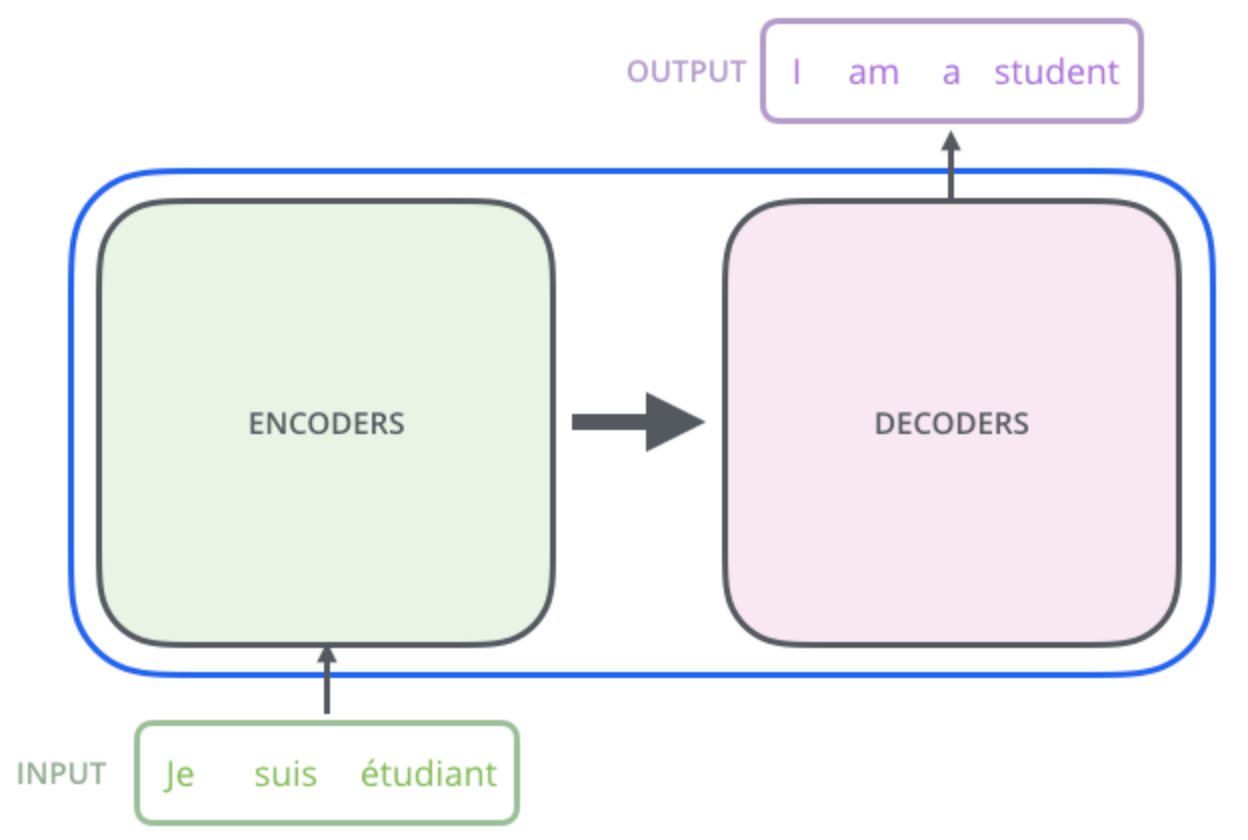
### Why transformers for protein ?
Proteins are molecules that perform critical functions in all living beings. It consists of one or more strings of amino acids. There are only 20 different amino acids and the different combinations of them have resulted in thousands of functional proteins in humans. If we consider amino acids as words that constitute proteins, which are the sentences, then we could use transformers to understand the language of proteins. When trained with the billions of protein sequences identified so far across multiple species, a transformer is capable of understanding what sequences of amino acids make sense from a language perspective and can propose new combinations.
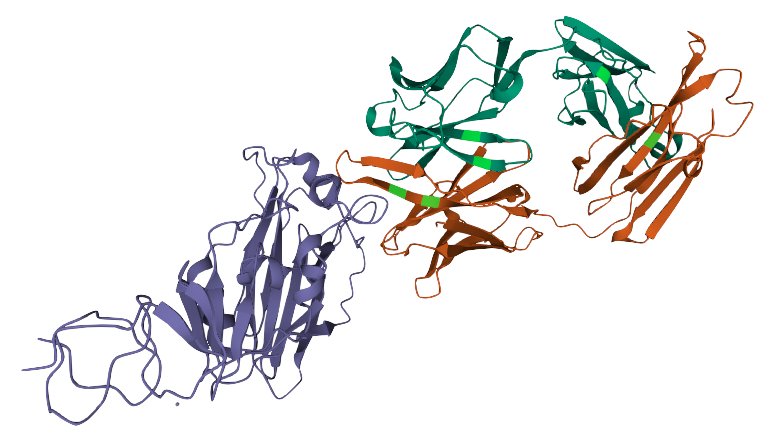
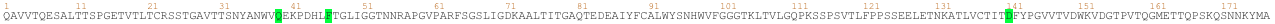
Querying a transformer trained in the language of proteins on a particular sequence provides a wealth of information about the protein. As seen in the above example, the transformer can tell you which amino acids might be key and need to be present at the protein of interest from a language perspective. This information is of particular interest when trying to understand amino acid regions that might be essential to protein function or stability.
## Getting started
## Installation
It is recommended to work with conda environments in order to manage the specific dependencies of this package.
The `bio-transformers` package can be found on [pypi](https://pypi.org/project/bio-transformers/).
Please note that you are suppose to have a correct cuda/torch installation before installing this library.
### Work with conda environment
1. Install [Miniconda](https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html) or [Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/products/individual)
2. Create a virtual environment and activate it.
```bash
conda create --name bio-transformers python=3.7 -y && conda activate bio-transformers
```
3. Install the package in environment.
```bash
pip install bio-transformers
```
### Environment for developing
Conda:
1. Clone this git repo via HTTPS or SSH:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/DeepChainBio/bio-transformers
cd bio-transformers
```
2. Create developement environment based on the yaml file.
```bash
conda env create -f environment_dev.yaml
conda activate bio-transformers-dev
```
3. Install package and pre-commit hooks.
```
pip install -e .
pre-commit install
```
Docker:
You can directly use a docker image for using bio-transformers or for development. The image is based on cuda11.1, be sure to use it on GPU.
1. Build the image:
```
docker build --tag instadeep/biotransformers-dev .
```
2. Run interactively with GPUs:
```
docker run --d -it --gpus all -v /home/bio-transformers:/app/bio-transformers instadeep/biotransformers-dev /bin/bash
```
# Usage
## Quick start
The main class ```BioTranformers``` allows developers to use Protbert and ESM backends
```python
> from biotransformers import BioTransformers
> BioTransformers.list_backend()
```
```python
>>
Use backend in this list :
* esm1_t34_670M_UR100
* esm1_t6_43M_UR50S
* esm1b_t33_650M_UR50S
* esm_msa1_t12_100M_UR50S
* protbert
* protbert_bfd
```
## Embeddings
The embedding of a an object is a representation of the object in a lower dimensional space. In this lower space, it is easier to manipulate, visualize, and apply mathematical functions on proteins' projection. Embeddings model will take a sequence of amino acids in input (string) and return a vector of lower dimension.
You can choose a backend and pass a list of sequences of Amino acids to compute the embeddings.
By default, the ```compute_embeddings``` function returns the `````` token embeddings.
You can add a ```pool_mode``` in addition, so you can compute the mean of the tokens embeddings.
```python
from biotransformers import BioTransformers
sequences = [
"MKTVRQERLKSIVRILERSKEPVSGAQLAEELSVSRQVIVQDIAYLRSLGYNIVATPRGYVLAGG",
"KALTARQQEVFDLIRDHISQTGMPPTRAEIAQRLGFRSPNAAEEHLKALARKGVIEIVSGASRGIRLLQEE",
]
bio_trans = BioTransformers(backend="protbert")
embeddings = bio_trans.compute_embeddings(sequences, pool_mode=('cls','mean'),batch_size=2)
cls_emb = embeddings['cls']
mean_emb = embeddings['mean']
```
### Multi-gpu
If you have access to multiple GPUs, you can specify the ```num_gpus``` option to speed-up the inference. Please refer to this [section](https://bio-transformers.readthedocs.io/en/develop/documentation/multi_gpus.html) to have a full understanding.
This option relies on `Ray` since version 0.0.11 (```torch.nn.DataParallel``` and `multi_gpu` option deprecated.)
```python
import ray
ray.init()
bio_trans = BioTransformers(backend="protbert",num_gpus=2)
embeddings = bio_trans.compute_embeddings(sequences, pool_mode=('cls','mean'), batch_size=2)
```
## Pseudo-Loglikelihood
The protein loglikelihood is a metric that estimates the joint probability of observing a given sequence of amino acids. The idea behind such an estimator is to approximate the probability that a mutated protein will be “natural”, and can effectively be produced by a cell.
These metrics rely on transformers language models. These models are trained to predict a “masked” amino acid in a sequence. As a consequence, they can provide us with an estimate of the probability of observing an amino acid given the “context” (the surrounding amino acids). By multiplying individual probabilities computed for a given amino-acid given its context, we obtain a pseudo-likelihood, which can be a candidate estimator to approximate sequence stability.
```python
from biotransformers import BioTransformers
import ray
sequences = [
"MKTVRQERLKSIVRILERSKEPVSGAQLAEELSVSRQVIVQDIAYLRSLGYNIVATPRGYVLAGG",
"KALTARQQEVFDLIRDHISQTGMPPTRAEIAQRLGFRSPNAAEEHLKALARKGVIEIVSGASRGIRLLQEE",
]
bio_trans = BioTransformers(backend="protbert",num_gpus=1)
loglikelihood = bio_trans.compute_loglikelihood(sequences)
```
## Finetune pre-trained transformers on your dataset
You can use the `finetune` function to finetune your backend on your dataset. The model is automatically scaled on the available GPUs. More information on the [documentation](https://bio-transformers.readthedocs.io/en/main/getting_started/quick_start.html#display-available-backend)
```python
import biodatasets
import numpy as np
from biotransformers import BioTransformers
import ray
data = biodatasets.load_dataset("swissProt")
X, y = data.to_npy_arrays(input_names=["sequence"])
X = X[0]
# Train on small sequences
length = np.array(list(map(len, X))) < 200
train_seq = X[length][:15000]
ray.init()
bio_trans = BioTransformers("esm1_t6_43M_UR50S", num_gpus=2)
bio_trans.finetune(
train_seq,
lr=1.0e-5,
warmup_init_lr=1e-7,
toks_per_batch=2000,
epochs=20,
batch_size=16,
acc_batch_size=256,
warmup_updates=1024,
accelerator="ddp",
checkpoint=None,
save_last_checkpoint=False,
)
```
# Roadmap:
- support MSA transformers
# ✏️ Citations
Here some papers on interest on the subject.
The excellent ProtBert work can be found at [(biorxiv preprint)](https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.07.12.199554v3.full.pdf):
```bibtex
@article{protTrans2021,
author={Ahmed Elnaggar and Michael Heinzinger, Christian Dallago1,Ghalia Rihawi, Yu Wang, Llion Jones, Tom Gibbs, Tamas Feher, Christoph Angerer,Debsindhu Bhowmik and Burkhard Rost},
title={ProtTrans: Towards Cracking the Language of Life’s Code Through Self-Supervised Deep Learning and High Performance Computing},
year={2019},
doi={10.1101/2020.07.12.199554},
url={https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.07.12.199554v3.full.pdf},
journal={bioRxiv}
}
```
For the ESM model, see [(biorxiv preprint)](https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/622803v4):
```bibtex
@article{rives2019biological,
author={Rives, Alexander and Meier, Joshua and Sercu, Tom and Goyal, Siddharth and Lin, Zeming and Liu, Jason and Guo, Demi and Ott, Myle and Zitnick, C. Lawrence and Ma, Jerry and Fergus, Rob},
title={Biological Structure and Function Emerge from Scaling Unsupervised Learning to 250 Million Protein Sequences},
year={2019},
doi={10.1101/622803},
url={https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/622803v4},
journal={bioRxiv}
}
```
For the self-attention contact prediction, see [the following paper (biorxiv preprint)](https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.12.15.422761v1):
```bibtex
@article{rao2020transformer,
author = {Rao, Roshan M and Meier, Joshua and Sercu, Tom and Ovchinnikov, Sergey and Rives, Alexander},
title={Transformer protein language models are unsupervised structure learners},
year={2020},
doi={10.1101/2020.12.15.422761},
url={https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.12.15.422761v1},
journal={bioRxiv}
}
```
For the MSA Transformer, see [the following paper (biorxiv preprint)](https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.12.430858):
```bibtex
@article{rao2021msa,
author = {Rao, Roshan and Liu, Jason and Verkuil, Robert and Meier, Joshua and Canny, John F. and Abbeel, Pieter and Sercu, Tom and Rives, Alexander},
title={MSA Transformer},
year={2021},
doi={10.1101/2021.02.12.430858},
url={https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.02.12.430858v1},
journal={bioRxiv}
}
```
# 📘 License
This source code is licensed under the **Apache 2** license found in the `LICENSE` file in the root directory.
%package -n python3-bio-transformers
Summary: Wrapper on top of ESM/Protbert model in order to easily work with protein embedding
Provides: python-bio-transformers
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3-setuptools
BuildRequires: python3-pip
%description -n python3-bio-transformers
 
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/Apache-2.0)
[](https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-360/)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)

[](https://bio-transformers.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/delfosseaurelien/bio-transformers)

[](https://opensource.org/licenses/Apache-2.0)
[](https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-360/)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)

[](https://bio-transformers.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/delfosseaurelien/bio-transformers)
Table of contents
- [Description](#bio-transformers)
- [Installation](#Installation)
- [Usage](#usage)
- [Quick Start](#quickstart)
- [Compute embeddings](#embeddings)
- [Pseudo-Loglikelihood](#pseudo-loglikelihood)
- [Roadmap](#roadmap)
- [Citations](#citations)
- [License](#license)

### Why transformers for protein ?
Proteins are molecules that perform critical functions in all living beings. It consists of one or more strings of amino acids. There are only 20 different amino acids and the different combinations of them have resulted in thousands of functional proteins in humans. If we consider amino acids as words that constitute proteins, which are the sentences, then we could use transformers to understand the language of proteins. When trained with the billions of protein sequences identified so far across multiple species, a transformer is capable of understanding what sequences of amino acids make sense from a language perspective and can propose new combinations.

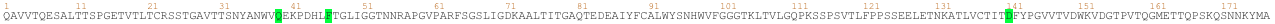
Querying a transformer trained in the language of proteins on a particular sequence provides a wealth of information about the protein. As seen in the above example, the transformer can tell you which amino acids might be key and need to be present at the protein of interest from a language perspective. This information is of particular interest when trying to understand amino acid regions that might be essential to protein function or stability.
## Getting started
## Installation
It is recommended to work with conda environments in order to manage the specific dependencies of this package.
The `bio-transformers` package can be found on [pypi](https://pypi.org/project/bio-transformers/).
Please note that you are suppose to have a correct cuda/torch installation before installing this library.
### Work with conda environment
1. Install [Miniconda](https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html) or [Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/products/individual)
2. Create a virtual environment and activate it.
```bash
conda create --name bio-transformers python=3.7 -y && conda activate bio-transformers
```
3. Install the package in environment.
```bash
pip install bio-transformers
```
### Environment for developing
Conda:
1. Clone this git repo via HTTPS or SSH:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/DeepChainBio/bio-transformers
cd bio-transformers
```
2. Create developement environment based on the yaml file.
```bash
conda env create -f environment_dev.yaml
conda activate bio-transformers-dev
```
3. Install package and pre-commit hooks.
```
pip install -e .
pre-commit install
```
Docker:
You can directly use a docker image for using bio-transformers or for development. The image is based on cuda11.1, be sure to use it on GPU.
1. Build the image:
```
docker build --tag instadeep/biotransformers-dev .
```
2. Run interactively with GPUs:
```
docker run --d -it --gpus all -v /home/bio-transformers:/app/bio-transformers instadeep/biotransformers-dev /bin/bash
```
# Usage
## Quick start
The main class ```BioTranformers``` allows developers to use Protbert and ESM backends
```python
> from biotransformers import BioTransformers
> BioTransformers.list_backend()
```
```python
>>
Use backend in this list :
* esm1_t34_670M_UR100
* esm1_t6_43M_UR50S
* esm1b_t33_650M_UR50S
* esm_msa1_t12_100M_UR50S
* protbert
* protbert_bfd
```
## Embeddings
The embedding of a an object is a representation of the object in a lower dimensional space. In this lower space, it is easier to manipulate, visualize, and apply mathematical functions on proteins' projection. Embeddings model will take a sequence of amino acids in input (string) and return a vector of lower dimension.
You can choose a backend and pass a list of sequences of Amino acids to compute the embeddings.
By default, the ```compute_embeddings``` function returns the `````` token embeddings.
You can add a ```pool_mode``` in addition, so you can compute the mean of the tokens embeddings.
```python
from biotransformers import BioTransformers
sequences = [
"MKTVRQERLKSIVRILERSKEPVSGAQLAEELSVSRQVIVQDIAYLRSLGYNIVATPRGYVLAGG",
"KALTARQQEVFDLIRDHISQTGMPPTRAEIAQRLGFRSPNAAEEHLKALARKGVIEIVSGASRGIRLLQEE",
]
bio_trans = BioTransformers(backend="protbert")
embeddings = bio_trans.compute_embeddings(sequences, pool_mode=('cls','mean'),batch_size=2)
cls_emb = embeddings['cls']
mean_emb = embeddings['mean']
```
### Multi-gpu
If you have access to multiple GPUs, you can specify the ```num_gpus``` option to speed-up the inference. Please refer to this [section](https://bio-transformers.readthedocs.io/en/develop/documentation/multi_gpus.html) to have a full understanding.
This option relies on `Ray` since version 0.0.11 (```torch.nn.DataParallel``` and `multi_gpu` option deprecated.)
```python
import ray
ray.init()
bio_trans = BioTransformers(backend="protbert",num_gpus=2)
embeddings = bio_trans.compute_embeddings(sequences, pool_mode=('cls','mean'), batch_size=2)
```
## Pseudo-Loglikelihood
The protein loglikelihood is a metric that estimates the joint probability of observing a given sequence of amino acids. The idea behind such an estimator is to approximate the probability that a mutated protein will be “natural”, and can effectively be produced by a cell.
These metrics rely on transformers language models. These models are trained to predict a “masked” amino acid in a sequence. As a consequence, they can provide us with an estimate of the probability of observing an amino acid given the “context” (the surrounding amino acids). By multiplying individual probabilities computed for a given amino-acid given its context, we obtain a pseudo-likelihood, which can be a candidate estimator to approximate sequence stability.
```python
from biotransformers import BioTransformers
import ray
sequences = [
"MKTVRQERLKSIVRILERSKEPVSGAQLAEELSVSRQVIVQDIAYLRSLGYNIVATPRGYVLAGG",
"KALTARQQEVFDLIRDHISQTGMPPTRAEIAQRLGFRSPNAAEEHLKALARKGVIEIVSGASRGIRLLQEE",
]
bio_trans = BioTransformers(backend="protbert",num_gpus=1)
loglikelihood = bio_trans.compute_loglikelihood(sequences)
```
## Finetune pre-trained transformers on your dataset
You can use the `finetune` function to finetune your backend on your dataset. The model is automatically scaled on the available GPUs. More information on the [documentation](https://bio-transformers.readthedocs.io/en/main/getting_started/quick_start.html#display-available-backend)
```python
import biodatasets
import numpy as np
from biotransformers import BioTransformers
import ray
data = biodatasets.load_dataset("swissProt")
X, y = data.to_npy_arrays(input_names=["sequence"])
X = X[0]
# Train on small sequences
length = np.array(list(map(len, X))) < 200
train_seq = X[length][:15000]
ray.init()
bio_trans = BioTransformers("esm1_t6_43M_UR50S", num_gpus=2)
bio_trans.finetune(
train_seq,
lr=1.0e-5,
warmup_init_lr=1e-7,
toks_per_batch=2000,
epochs=20,
batch_size=16,
acc_batch_size=256,
warmup_updates=1024,
accelerator="ddp",
checkpoint=None,
save_last_checkpoint=False,
)
```
# Roadmap:
- support MSA transformers
# ✏️ Citations
Here some papers on interest on the subject.
The excellent ProtBert work can be found at [(biorxiv preprint)](https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.07.12.199554v3.full.pdf):
```bibtex
@article{protTrans2021,
author={Ahmed Elnaggar and Michael Heinzinger, Christian Dallago1,Ghalia Rihawi, Yu Wang, Llion Jones, Tom Gibbs, Tamas Feher, Christoph Angerer,Debsindhu Bhowmik and Burkhard Rost},
title={ProtTrans: Towards Cracking the Language of Life’s Code Through Self-Supervised Deep Learning and High Performance Computing},
year={2019},
doi={10.1101/2020.07.12.199554},
url={https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.07.12.199554v3.full.pdf},
journal={bioRxiv}
}
```
For the ESM model, see [(biorxiv preprint)](https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/622803v4):
```bibtex
@article{rives2019biological,
author={Rives, Alexander and Meier, Joshua and Sercu, Tom and Goyal, Siddharth and Lin, Zeming and Liu, Jason and Guo, Demi and Ott, Myle and Zitnick, C. Lawrence and Ma, Jerry and Fergus, Rob},
title={Biological Structure and Function Emerge from Scaling Unsupervised Learning to 250 Million Protein Sequences},
year={2019},
doi={10.1101/622803},
url={https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/622803v4},
journal={bioRxiv}
}
```
For the self-attention contact prediction, see [the following paper (biorxiv preprint)](https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.12.15.422761v1):
```bibtex
@article{rao2020transformer,
author = {Rao, Roshan M and Meier, Joshua and Sercu, Tom and Ovchinnikov, Sergey and Rives, Alexander},
title={Transformer protein language models are unsupervised structure learners},
year={2020},
doi={10.1101/2020.12.15.422761},
url={https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.12.15.422761v1},
journal={bioRxiv}
}
```
For the MSA Transformer, see [the following paper (biorxiv preprint)](https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.12.430858):
```bibtex
@article{rao2021msa,
author = {Rao, Roshan and Liu, Jason and Verkuil, Robert and Meier, Joshua and Canny, John F. and Abbeel, Pieter and Sercu, Tom and Rives, Alexander},
title={MSA Transformer},
year={2021},
doi={10.1101/2021.02.12.430858},
url={https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.02.12.430858v1},
journal={bioRxiv}
}
```
# 📘 License
This source code is licensed under the **Apache 2** license found in the `LICENSE` file in the root directory.
%package help
Summary: Development documents and examples for bio-transformers
Provides: python3-bio-transformers-doc
%description help
 
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/Apache-2.0)
[](https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-360/)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)

[](https://bio-transformers.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/delfosseaurelien/bio-transformers)

[](https://opensource.org/licenses/Apache-2.0)
[](https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-360/)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)

[](https://bio-transformers.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/delfosseaurelien/bio-transformers)
Table of contents
- [Description](#bio-transformers)
- [Installation](#Installation)
- [Usage](#usage)
- [Quick Start](#quickstart)
- [Compute embeddings](#embeddings)
- [Pseudo-Loglikelihood](#pseudo-loglikelihood)
- [Roadmap](#roadmap)
- [Citations](#citations)
- [License](#license)

### Why transformers for protein ?
Proteins are molecules that perform critical functions in all living beings. It consists of one or more strings of amino acids. There are only 20 different amino acids and the different combinations of them have resulted in thousands of functional proteins in humans. If we consider amino acids as words that constitute proteins, which are the sentences, then we could use transformers to understand the language of proteins. When trained with the billions of protein sequences identified so far across multiple species, a transformer is capable of understanding what sequences of amino acids make sense from a language perspective and can propose new combinations.

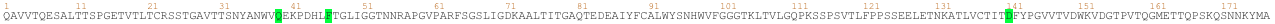
Querying a transformer trained in the language of proteins on a particular sequence provides a wealth of information about the protein. As seen in the above example, the transformer can tell you which amino acids might be key and need to be present at the protein of interest from a language perspective. This information is of particular interest when trying to understand amino acid regions that might be essential to protein function or stability.
## Getting started
## Installation
It is recommended to work with conda environments in order to manage the specific dependencies of this package.
The `bio-transformers` package can be found on [pypi](https://pypi.org/project/bio-transformers/).
Please note that you are suppose to have a correct cuda/torch installation before installing this library.
### Work with conda environment
1. Install [Miniconda](https://docs.conda.io/en/latest/miniconda.html) or [Anaconda](https://www.anaconda.com/products/individual)
2. Create a virtual environment and activate it.
```bash
conda create --name bio-transformers python=3.7 -y && conda activate bio-transformers
```
3. Install the package in environment.
```bash
pip install bio-transformers
```
### Environment for developing
Conda:
1. Clone this git repo via HTTPS or SSH:
```bash
git clone https://github.com/DeepChainBio/bio-transformers
cd bio-transformers
```
2. Create developement environment based on the yaml file.
```bash
conda env create -f environment_dev.yaml
conda activate bio-transformers-dev
```
3. Install package and pre-commit hooks.
```
pip install -e .
pre-commit install
```
Docker:
You can directly use a docker image for using bio-transformers or for development. The image is based on cuda11.1, be sure to use it on GPU.
1. Build the image:
```
docker build --tag instadeep/biotransformers-dev .
```
2. Run interactively with GPUs:
```
docker run --d -it --gpus all -v /home/bio-transformers:/app/bio-transformers instadeep/biotransformers-dev /bin/bash
```
# Usage
## Quick start
The main class ```BioTranformers``` allows developers to use Protbert and ESM backends
```python
> from biotransformers import BioTransformers
> BioTransformers.list_backend()
```
```python
>>
Use backend in this list :
* esm1_t34_670M_UR100
* esm1_t6_43M_UR50S
* esm1b_t33_650M_UR50S
* esm_msa1_t12_100M_UR50S
* protbert
* protbert_bfd
```
## Embeddings
The embedding of a an object is a representation of the object in a lower dimensional space. In this lower space, it is easier to manipulate, visualize, and apply mathematical functions on proteins' projection. Embeddings model will take a sequence of amino acids in input (string) and return a vector of lower dimension.
You can choose a backend and pass a list of sequences of Amino acids to compute the embeddings.
By default, the ```compute_embeddings``` function returns the `````` token embeddings.
You can add a ```pool_mode``` in addition, so you can compute the mean of the tokens embeddings.
```python
from biotransformers import BioTransformers
sequences = [
"MKTVRQERLKSIVRILERSKEPVSGAQLAEELSVSRQVIVQDIAYLRSLGYNIVATPRGYVLAGG",
"KALTARQQEVFDLIRDHISQTGMPPTRAEIAQRLGFRSPNAAEEHLKALARKGVIEIVSGASRGIRLLQEE",
]
bio_trans = BioTransformers(backend="protbert")
embeddings = bio_trans.compute_embeddings(sequences, pool_mode=('cls','mean'),batch_size=2)
cls_emb = embeddings['cls']
mean_emb = embeddings['mean']
```
### Multi-gpu
If you have access to multiple GPUs, you can specify the ```num_gpus``` option to speed-up the inference. Please refer to this [section](https://bio-transformers.readthedocs.io/en/develop/documentation/multi_gpus.html) to have a full understanding.
This option relies on `Ray` since version 0.0.11 (```torch.nn.DataParallel``` and `multi_gpu` option deprecated.)
```python
import ray
ray.init()
bio_trans = BioTransformers(backend="protbert",num_gpus=2)
embeddings = bio_trans.compute_embeddings(sequences, pool_mode=('cls','mean'), batch_size=2)
```
## Pseudo-Loglikelihood
The protein loglikelihood is a metric that estimates the joint probability of observing a given sequence of amino acids. The idea behind such an estimator is to approximate the probability that a mutated protein will be “natural”, and can effectively be produced by a cell.
These metrics rely on transformers language models. These models are trained to predict a “masked” amino acid in a sequence. As a consequence, they can provide us with an estimate of the probability of observing an amino acid given the “context” (the surrounding amino acids). By multiplying individual probabilities computed for a given amino-acid given its context, we obtain a pseudo-likelihood, which can be a candidate estimator to approximate sequence stability.
```python
from biotransformers import BioTransformers
import ray
sequences = [
"MKTVRQERLKSIVRILERSKEPVSGAQLAEELSVSRQVIVQDIAYLRSLGYNIVATPRGYVLAGG",
"KALTARQQEVFDLIRDHISQTGMPPTRAEIAQRLGFRSPNAAEEHLKALARKGVIEIVSGASRGIRLLQEE",
]
bio_trans = BioTransformers(backend="protbert",num_gpus=1)
loglikelihood = bio_trans.compute_loglikelihood(sequences)
```
## Finetune pre-trained transformers on your dataset
You can use the `finetune` function to finetune your backend on your dataset. The model is automatically scaled on the available GPUs. More information on the [documentation](https://bio-transformers.readthedocs.io/en/main/getting_started/quick_start.html#display-available-backend)
```python
import biodatasets
import numpy as np
from biotransformers import BioTransformers
import ray
data = biodatasets.load_dataset("swissProt")
X, y = data.to_npy_arrays(input_names=["sequence"])
X = X[0]
# Train on small sequences
length = np.array(list(map(len, X))) < 200
train_seq = X[length][:15000]
ray.init()
bio_trans = BioTransformers("esm1_t6_43M_UR50S", num_gpus=2)
bio_trans.finetune(
train_seq,
lr=1.0e-5,
warmup_init_lr=1e-7,
toks_per_batch=2000,
epochs=20,
batch_size=16,
acc_batch_size=256,
warmup_updates=1024,
accelerator="ddp",
checkpoint=None,
save_last_checkpoint=False,
)
```
# Roadmap:
- support MSA transformers
# ✏️ Citations
Here some papers on interest on the subject.
The excellent ProtBert work can be found at [(biorxiv preprint)](https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.07.12.199554v3.full.pdf):
```bibtex
@article{protTrans2021,
author={Ahmed Elnaggar and Michael Heinzinger, Christian Dallago1,Ghalia Rihawi, Yu Wang, Llion Jones, Tom Gibbs, Tamas Feher, Christoph Angerer,Debsindhu Bhowmik and Burkhard Rost},
title={ProtTrans: Towards Cracking the Language of Life’s Code Through Self-Supervised Deep Learning and High Performance Computing},
year={2019},
doi={10.1101/2020.07.12.199554},
url={https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.07.12.199554v3.full.pdf},
journal={bioRxiv}
}
```
For the ESM model, see [(biorxiv preprint)](https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/622803v4):
```bibtex
@article{rives2019biological,
author={Rives, Alexander and Meier, Joshua and Sercu, Tom and Goyal, Siddharth and Lin, Zeming and Liu, Jason and Guo, Demi and Ott, Myle and Zitnick, C. Lawrence and Ma, Jerry and Fergus, Rob},
title={Biological Structure and Function Emerge from Scaling Unsupervised Learning to 250 Million Protein Sequences},
year={2019},
doi={10.1101/622803},
url={https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/622803v4},
journal={bioRxiv}
}
```
For the self-attention contact prediction, see [the following paper (biorxiv preprint)](https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.12.15.422761v1):
```bibtex
@article{rao2020transformer,
author = {Rao, Roshan M and Meier, Joshua and Sercu, Tom and Ovchinnikov, Sergey and Rives, Alexander},
title={Transformer protein language models are unsupervised structure learners},
year={2020},
doi={10.1101/2020.12.15.422761},
url={https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2020.12.15.422761v1},
journal={bioRxiv}
}
```
For the MSA Transformer, see [the following paper (biorxiv preprint)](https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.02.12.430858):
```bibtex
@article{rao2021msa,
author = {Rao, Roshan and Liu, Jason and Verkuil, Robert and Meier, Joshua and Canny, John F. and Abbeel, Pieter and Sercu, Tom and Rives, Alexander},
title={MSA Transformer},
year={2021},
doi={10.1101/2021.02.12.430858},
url={https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2021.02.12.430858v1},
journal={bioRxiv}
}
```
# 📘 License
This source code is licensed under the **Apache 2** license found in the `LICENSE` file in the root directory.
%prep
%autosetup -n bio-transformers-0.1.17
%build
%py3_build
%install
%py3_install
install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}
if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
pushd %{buildroot}
if [ -d usr/lib ]; then
find usr/lib -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then
find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/bin ]; then
find usr/bin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then
find usr/sbin -type f -printf "/%h/%f\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
touch doclist.lst
if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then
find usr/share/man -type f -printf "/%h/%f.gz\n" >> doclist.lst
fi
popd
mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst .
mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst .
%files -n python3-bio-transformers -f filelist.lst
%dir %{python3_sitelib}/*
%files help -f doclist.lst
%{_docdir}/*
%changelog
* Tue May 30 2023 Python_Bot - 0.1.17-1
- Package Spec generated
 
[](https://opensource.org/licenses/Apache-2.0)
[](https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-360/)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)

[](https://bio-transformers.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/delfosseaurelien/bio-transformers)

[](https://opensource.org/licenses/Apache-2.0)
[](https://www.python.org/downloads/release/python-360/)
[](https://github.com/psf/black)

[](https://bio-transformers.readthedocs.io/en/latest/?badge=latest)
[](https://codecov.io/gh/delfosseaurelien/bio-transformers)