1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
252
253
254
255
256
257
258
259
260
261
262
263
264
265
266
267
268
269
270
271
272
273
274
275
276
277
278
279
280
281
282
283
284
285
286
287
288
289
290
291
292
293
294
295
296
297
298
299
300
301
302
303
304
305
306
307
308
309
310
311
312
313
314
315
316
317
318
319
320
321
322
323
324
325
326
327
328
329
330
331
332
333
334
335
336
337
338
339
340
341
342
343
344
345
346
347
348
349
350
351
352
353
354
355
356
357
358
359
360
361
362
363
364
365
366
367
368
369
370
371
372
373
374
375
376
377
378
379
380
381
382
383
384
385
386
387
388
389
390
391
392
393
394
395
396
397
398
399
400
401
402
403
404
405
406
407
408
409
410
411
412
413
414
415
416
417
418
419
420
421
422
423
424
425
426
427
428
429
430
431
432
433
434
435
436
437
438
439
440
441
442
443
444
445
446
447
448
449
450
451
452
453
454
455
456
457
458
459
460
461
462
463
464
465
466
467
468
469
470
471
472
473
474
475
476
477
478
479
480
481
482
483
484
485
486
487
488
489
490
491
492
493
494
495
496
497
498
499
500
501
502
503
504
505
506
507
508
509
510
511
512
513
514
515
516
517
518
519
520
521
522
523
524
525
526
527
528
529
530
531
532
533
534
535
536
537
538
539
540
541
542
543
544
545
546
547
548
549
550
551
552
553
554
555
556
557
558
559
560
561
562
563
564
565
566
567
568
569
570
571
572
573
574
575
576
577
578
579
580
581
582
583
584
585
586
587
588
589
590
591
592
593
594
595
596
597
598
599
600
601
602
603
604
605
606
607
608
609
610
611
612
613
614
615
616
617
618
619
620
621
622
623
624
625
626
627
628
629
630
631
632
633
634
635
636
637
638
639
640
641
642
643
644
645
646
647
648
649
650
651
652
653
654
655
656
657
658
659
660
661
662
663
664
665
666
667
668
669
670
671
672
673
674
|
%global _empty_manifest_terminate_build 0
Name: python-hic2cool
Version: 0.8.3
Release: 1
Summary: Converter between hic files (from juicer) and single-resolution or multi-resolution cool files (for cooler). Both hic and cool files describe Hi-C contact matrices. Intended to be lightweight, this can be used as an imported package or a stand-alone Python tool for command line conversion.
License: MIT
URL: https://github.com/4dn-dcic/hic2cool
Source0: https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/web/packages/06/ea/b8af3388997d0955b25444da2fc09dbd7230fe40aa154083c060bf049a52/hic2cool-0.8.3.tar.gz
BuildArch: noarch
Requires: python3-h5py
Requires: python3-numpy
Requires: python3-scipy
Requires: python3-pandas
Requires: python3-cooler
%description
# hic2cool #
[](https://travis-ci.org/4dn-dcic/hic2cool)
Converter between hic files (from juicer) and single-resolution or multi-resolution cool files (for cooler). Both hic and cool files describe Hi-C contact matrices. Intended to be lightweight, this can be used as an imported package or a stand-alone Python tool for command line conversion
The hic parsing code is based off the [straw project](https://github.com/theaidenlab/straw) by Neva C. Durand and Yue Wu. The hdf5-based structure used for cooler file writing is based off code from the [cooler repository](https://github.com/mirnylab/cooler).
## Important
* Starting from version 0.8.0, hic2cool no longer supports Python 2.7.
* If you converted a hic file using a version of hic2cool lower than 0.5.0, please update your cooler file with the [new update function](#updating-hic2cool-coolers).
## Using the Python package
```
$ pip install hic2cool
```
You can also download the code directly and run the setup yourself.
```
# setuptools >=42 is recommended
$ python setup.py install
```
Once the package is installed, the main method is hic2cool_convert. It takes the same parameters as hic2cool.py, described in the next section. Example usage in a Python script is shown below or in test.py.
```
from hic2cool import hic2cool_convert
hic2cool_convert(<infile>, <outfile>, <resolution (optional)>, <nproc (optional)>, <warnings (optional)>, <silent (optional)>)
```
## Converting files using the command line
The main use of hic2cool is converting between filetypes using `hic2cool convert`. If you install hic2cool itself using pip, you use it on the command line with:
```
$ hic2cool convert <infile> <outfile> -r <resolution> -p <nproc>
```
### Arguments for hic2cool convert
**infile** is a .hic input file.
**outfile** is a .cool output file.
**-r**, or --resolution, is an integer bp resolution supported by the hic file. *Please note* that only resolutions contained within the original hic file can be used. If 0 is given, will use all resolutions to build a multi-resolution file. Default is 0.
**-p**, or --nproc, is the number of processes to use. Default 1. The multiprocessing is not very efficient and would slightly improve speed only for large high-resolution matrices.
**-w**, or --warnings, causes warnings to be explicitly printed to the console. This is false by default, though there are a few cases in which hic2cool will exit with an error based on the input hic file.
**-s**, or --silent, run in silent mode and hide console output from the program. Default false.
**-v**, or --version, print out hic2cool package version and exit.
**-h**, or --help, print out help about the package/specific run mode and exit.
Running hic2cool from the command line will cause some helpful information about the hic file to be printed to stdout unless the `-s` flag is used.
## Output file structure
If you elect to use all resolutions, a multi-resolution .mcool file will be produced. This changes the hdf5 structure of the file from a typical .cool file. Namely, all of the information needed for a complete cooler file is stored in separate hdf5 groups named by the individual resolutions. The hdf5 hierarchy is organized as such:
File --> 'resolutions' --> '###' (where ### is the resolution in bp).
For example, see the code below that generates a multi-res file and then accesses the specific resolution of 10000 bp.
```
from hic2cool import hic2cool_convert
import cooler
### using 0 triggers a multi-res output
hic2cool_convert('my_hic.hic', 'my_cool.cool', 0)
### will give you the cooler object with resolution = 10000 bp
my_cooler = cooler.Cooler('my_cool.cool::resolutions/10000')
```
When using only one resolution, the .cool file produced stores all the necessary information at the top level. Thus, organization in the multi-res format is not needed. The code below produces a file with one resolution, 10000 bp, and opens it with a cooler object.
```
from hic2cool import hic2cool_convert
import cooler
### giving a specific resolution below (e.g. 10000) triggers a single-res output
hic2cool_convert('my_hic.hic', 'my_cool.cool', 10000)
h5file = h5py.File('my_cool.cool', 'r')
### will give you the cooler object with resolution = 10000 bp
my_cooler = cooler.Cooler(h5file)
```
## higlass
Multi-resolution coolers produced by hi2cool can be visualized using [higlass](http://higlass.io/). Please note that single resolution coolers are NOT higlass compatible (created when using a non-zero value for `-r`). If you created a cooler before hic2cool version 0.5.0 that you want to view in higlass, it is highly recommended that you upgrade it before viewing on higlass to ensure correct normalization behavior.
To apply the hic normalization transformations in higlass, right click on the tileset and do the following:
`"<name of tileset>" --> "Configure Series" --> "Transforms" --> "<norm>"`
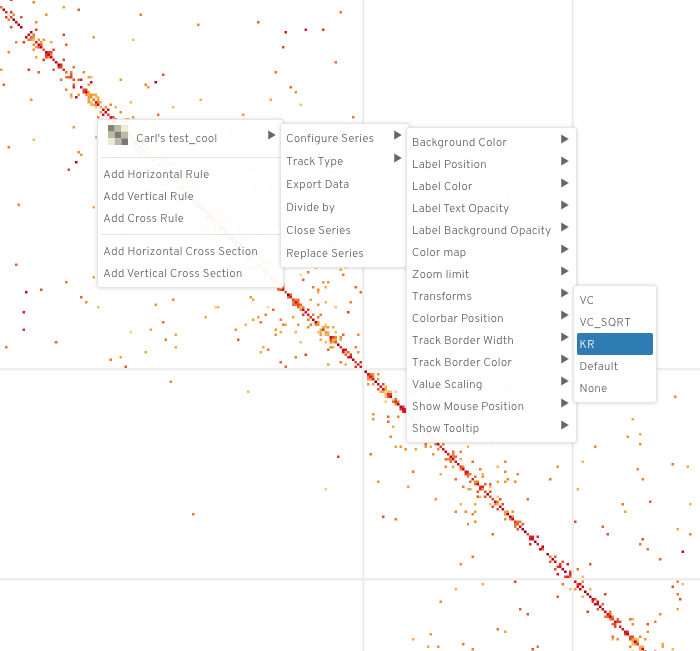
## Updating hic2cool coolers
As of hic2cool version 0.5.0, there was a critical change in how hic normalization vectors are handled in the resulting cooler files. Prior to 0.5.0, hic normalization vectors were inverted by hic2cool. The rationale for doing this is that hic uses divisive normalization values, whereas cooler uses multiplicative values. However, higlass and the 4DN analysis pipelines specifically handled the divisive normalization values, so hic2cool now handles them the same way.
In the near future, there will be a `cooler` package release to correctly handle divisive hic normalization values when balancing.
To update a hic2cool cooler, simply run:
```
hic2cool update <infile> <outfile (optional)>
```
If you only provide the `infile` argument, then the cooler will be updated directly. If you provide an optional `outfile` file path, then a new cooler updated cooler file will be created and the original file will remain unchanged.
## Extracting hic normalization values
As of hic2cool 0.5.0, you can easily extract hic normalization vectors to an existing cooler file. This will only work if the specified cooler file shares the resolutions found in the hic file. To do this, simply run:
```
hic2cool extract-norms <hic file> <cooler file>
```
You may also provide the optional `-e` flag, which will cause the mitchondrial chromosome to automatically be omitted from the extraction. This is found by name; the code specifically looks for one of `['M', 'MT', 'chrM', 'chrMT']` (in a case-insensitive way). Just like with `hic2cool convert`, you can also provide `-s` and `-w` [arguments](#arguments-for-hic2cool-convert).
## Changelog
### 0.8.2
* loosened version for `numpy`, `scipy` and `pandas`.
### 0.8.1
* `setup.py` takes dependencies directly from `requirements.txt` (`requirements.txt` updated to match `setup.py`)
### 0.8.0
* multiprocessing support for convert
* change in usage of convert API due to the addition of the `nproc` option
* Python 2.7 is deprecated.
### 0.7.3
* Pinned `pandas==0.24.2` since newer versions deprecate python 2
### 0.7.2
* Warning from `hic2cool_utils.parse_hic` will now output chromsome names, not indices
### 0.7.1
* Add `format` and `format-version` to `/` collection for multi-resolution coolers written by hic2cool
* Run `hic2cool_update` to add these attributes to mcool files generated with previous hic2cool versions
* Fixed issue where datetime-derived metadata was written as bytestring when using python 2
### 0.7.0
* Fixed package issues associated with python 2
* Fixed issue where some cooler metadata was written as non-unicode when using python 2
### 0.6.1
* Fixed input issue with `hic2cool update` when using python 2
### 0.6.0
* Added `format-version` and `storage-type` to attributes of output cooler to get up-to-date with cooler schema v3
* Run `hic2cool update` to add these attributes to files generated with previous hic2cool versions
### 0.5.1
Fixed packaging issue by adding MANIFEST.in and made some documentation/pypi edits
### 0.5.0
Large release that changes how hic2cool is run
* hic2cool is now executed with `hic2cool <mode>`, where mode is one of: `[convert, update, extract-norms]`
* Added two new modes: `update` (update coolers made by hic2cool based on version) and `extract-norms` (extract hic normalization vectors to pre-existing cooler file)
* Removed old hic2cool_extractnorms script (this is now run with `hic2cool extract-norms`)
* hic normalization vectors are NO LONGER INVERTED when added to output cooler for consistency with the 4DN omics processing pipeline and higlass
* Missing hic normalization vectors are now represented by vectors of `NaN` (used to be vectors of zeros)
* Improvement of help messages when running hic2cool and change around arguments for running the program
* Test updates
### 0.4.2
* Fixed issue where hic files could not be converted if they were missing normalization vectors
### 0.4.1
* Fixed error in reading counts from hic files of version 6
* Chromosome names are now directly taken from hic file (with exception of 'all')
### 0.4.0
Large patch, should fix most memory issues and improve runtimes:
* Changed run parameters. Removed -n and -e; added -v (--version) and -w (--warnings)
* Improved memory usage
* Improved runtime (many thanks to Nezar Abdennur)
* hic2cool now does a 'direct' conversion of files and does not fail on missing chr-chr contacts or missing normalization vectors. Finding these issues will cause warnings to be printed (controlled by -w flag)
* No longer uses the 'weights' column, which is reserved for cooler
* No longer takes a normalization type argument. All normalization vectors from the hic file are automatically added to the bins table in the output .cool
* Many other minor bug fixes/code improvement
### 0.3.7
Fixed issue with bin1_offset not containing final entry (should be length nbins + 1).
### 0.3.6
Simple release to fix pip execution.
### 0.3.5
README updates, switched cooler syntax in test, and added helpful printing of hic file header info when using the command line tool.
### 0.3.4
Fixed issue where chromosome name was not getting properly set for 'All' vs 'all'.
### 0.3.3
Removed rounding fix. For now, allow py2 and py3 weights to have different number of significant figures (they're very close).
### 0.3.2
Changed output file structure for single resolution file. Resolved an issue where rounding for weights was different between python 2 and 3.
### 0.3.1
Added .travis.yml for automated testing. Changed command line running scheme. Python3 fix in hic2cool_utils.
### 0.3.0
Added multi-resolution format to output cool files. Setup argparse. Improved speed. Added tests for new resolutions format.
## Contributors
Written by Carl Vitzthum (1), Nezar Abdennur (2), Soo Lee (1), and Peter Kerpedjiev (3).
(1) Park lab, Harvard Medical School DBMI
(2) Mirny lab, MIT
(3) Gehlenborg lab, Harvard Medical School DBMI
Originally published 1/26/17.
%package -n python3-hic2cool
Summary: Converter between hic files (from juicer) and single-resolution or multi-resolution cool files (for cooler). Both hic and cool files describe Hi-C contact matrices. Intended to be lightweight, this can be used as an imported package or a stand-alone Python tool for command line conversion.
Provides: python-hic2cool
BuildRequires: python3-devel
BuildRequires: python3-setuptools
BuildRequires: python3-pip
%description -n python3-hic2cool
# hic2cool #
[](https://travis-ci.org/4dn-dcic/hic2cool)
Converter between hic files (from juicer) and single-resolution or multi-resolution cool files (for cooler). Both hic and cool files describe Hi-C contact matrices. Intended to be lightweight, this can be used as an imported package or a stand-alone Python tool for command line conversion
The hic parsing code is based off the [straw project](https://github.com/theaidenlab/straw) by Neva C. Durand and Yue Wu. The hdf5-based structure used for cooler file writing is based off code from the [cooler repository](https://github.com/mirnylab/cooler).
## Important
* Starting from version 0.8.0, hic2cool no longer supports Python 2.7.
* If you converted a hic file using a version of hic2cool lower than 0.5.0, please update your cooler file with the [new update function](#updating-hic2cool-coolers).
## Using the Python package
```
$ pip install hic2cool
```
You can also download the code directly and run the setup yourself.
```
# setuptools >=42 is recommended
$ python setup.py install
```
Once the package is installed, the main method is hic2cool_convert. It takes the same parameters as hic2cool.py, described in the next section. Example usage in a Python script is shown below or in test.py.
```
from hic2cool import hic2cool_convert
hic2cool_convert(<infile>, <outfile>, <resolution (optional)>, <nproc (optional)>, <warnings (optional)>, <silent (optional)>)
```
## Converting files using the command line
The main use of hic2cool is converting between filetypes using `hic2cool convert`. If you install hic2cool itself using pip, you use it on the command line with:
```
$ hic2cool convert <infile> <outfile> -r <resolution> -p <nproc>
```
### Arguments for hic2cool convert
**infile** is a .hic input file.
**outfile** is a .cool output file.
**-r**, or --resolution, is an integer bp resolution supported by the hic file. *Please note* that only resolutions contained within the original hic file can be used. If 0 is given, will use all resolutions to build a multi-resolution file. Default is 0.
**-p**, or --nproc, is the number of processes to use. Default 1. The multiprocessing is not very efficient and would slightly improve speed only for large high-resolution matrices.
**-w**, or --warnings, causes warnings to be explicitly printed to the console. This is false by default, though there are a few cases in which hic2cool will exit with an error based on the input hic file.
**-s**, or --silent, run in silent mode and hide console output from the program. Default false.
**-v**, or --version, print out hic2cool package version and exit.
**-h**, or --help, print out help about the package/specific run mode and exit.
Running hic2cool from the command line will cause some helpful information about the hic file to be printed to stdout unless the `-s` flag is used.
## Output file structure
If you elect to use all resolutions, a multi-resolution .mcool file will be produced. This changes the hdf5 structure of the file from a typical .cool file. Namely, all of the information needed for a complete cooler file is stored in separate hdf5 groups named by the individual resolutions. The hdf5 hierarchy is organized as such:
File --> 'resolutions' --> '###' (where ### is the resolution in bp).
For example, see the code below that generates a multi-res file and then accesses the specific resolution of 10000 bp.
```
from hic2cool import hic2cool_convert
import cooler
### using 0 triggers a multi-res output
hic2cool_convert('my_hic.hic', 'my_cool.cool', 0)
### will give you the cooler object with resolution = 10000 bp
my_cooler = cooler.Cooler('my_cool.cool::resolutions/10000')
```
When using only one resolution, the .cool file produced stores all the necessary information at the top level. Thus, organization in the multi-res format is not needed. The code below produces a file with one resolution, 10000 bp, and opens it with a cooler object.
```
from hic2cool import hic2cool_convert
import cooler
### giving a specific resolution below (e.g. 10000) triggers a single-res output
hic2cool_convert('my_hic.hic', 'my_cool.cool', 10000)
h5file = h5py.File('my_cool.cool', 'r')
### will give you the cooler object with resolution = 10000 bp
my_cooler = cooler.Cooler(h5file)
```
## higlass
Multi-resolution coolers produced by hi2cool can be visualized using [higlass](http://higlass.io/). Please note that single resolution coolers are NOT higlass compatible (created when using a non-zero value for `-r`). If you created a cooler before hic2cool version 0.5.0 that you want to view in higlass, it is highly recommended that you upgrade it before viewing on higlass to ensure correct normalization behavior.
To apply the hic normalization transformations in higlass, right click on the tileset and do the following:
`"<name of tileset>" --> "Configure Series" --> "Transforms" --> "<norm>"`

## Updating hic2cool coolers
As of hic2cool version 0.5.0, there was a critical change in how hic normalization vectors are handled in the resulting cooler files. Prior to 0.5.0, hic normalization vectors were inverted by hic2cool. The rationale for doing this is that hic uses divisive normalization values, whereas cooler uses multiplicative values. However, higlass and the 4DN analysis pipelines specifically handled the divisive normalization values, so hic2cool now handles them the same way.
In the near future, there will be a `cooler` package release to correctly handle divisive hic normalization values when balancing.
To update a hic2cool cooler, simply run:
```
hic2cool update <infile> <outfile (optional)>
```
If you only provide the `infile` argument, then the cooler will be updated directly. If you provide an optional `outfile` file path, then a new cooler updated cooler file will be created and the original file will remain unchanged.
## Extracting hic normalization values
As of hic2cool 0.5.0, you can easily extract hic normalization vectors to an existing cooler file. This will only work if the specified cooler file shares the resolutions found in the hic file. To do this, simply run:
```
hic2cool extract-norms <hic file> <cooler file>
```
You may also provide the optional `-e` flag, which will cause the mitchondrial chromosome to automatically be omitted from the extraction. This is found by name; the code specifically looks for one of `['M', 'MT', 'chrM', 'chrMT']` (in a case-insensitive way). Just like with `hic2cool convert`, you can also provide `-s` and `-w` [arguments](#arguments-for-hic2cool-convert).
## Changelog
### 0.8.2
* loosened version for `numpy`, `scipy` and `pandas`.
### 0.8.1
* `setup.py` takes dependencies directly from `requirements.txt` (`requirements.txt` updated to match `setup.py`)
### 0.8.0
* multiprocessing support for convert
* change in usage of convert API due to the addition of the `nproc` option
* Python 2.7 is deprecated.
### 0.7.3
* Pinned `pandas==0.24.2` since newer versions deprecate python 2
### 0.7.2
* Warning from `hic2cool_utils.parse_hic` will now output chromsome names, not indices
### 0.7.1
* Add `format` and `format-version` to `/` collection for multi-resolution coolers written by hic2cool
* Run `hic2cool_update` to add these attributes to mcool files generated with previous hic2cool versions
* Fixed issue where datetime-derived metadata was written as bytestring when using python 2
### 0.7.0
* Fixed package issues associated with python 2
* Fixed issue where some cooler metadata was written as non-unicode when using python 2
### 0.6.1
* Fixed input issue with `hic2cool update` when using python 2
### 0.6.0
* Added `format-version` and `storage-type` to attributes of output cooler to get up-to-date with cooler schema v3
* Run `hic2cool update` to add these attributes to files generated with previous hic2cool versions
### 0.5.1
Fixed packaging issue by adding MANIFEST.in and made some documentation/pypi edits
### 0.5.0
Large release that changes how hic2cool is run
* hic2cool is now executed with `hic2cool <mode>`, where mode is one of: `[convert, update, extract-norms]`
* Added two new modes: `update` (update coolers made by hic2cool based on version) and `extract-norms` (extract hic normalization vectors to pre-existing cooler file)
* Removed old hic2cool_extractnorms script (this is now run with `hic2cool extract-norms`)
* hic normalization vectors are NO LONGER INVERTED when added to output cooler for consistency with the 4DN omics processing pipeline and higlass
* Missing hic normalization vectors are now represented by vectors of `NaN` (used to be vectors of zeros)
* Improvement of help messages when running hic2cool and change around arguments for running the program
* Test updates
### 0.4.2
* Fixed issue where hic files could not be converted if they were missing normalization vectors
### 0.4.1
* Fixed error in reading counts from hic files of version 6
* Chromosome names are now directly taken from hic file (with exception of 'all')
### 0.4.0
Large patch, should fix most memory issues and improve runtimes:
* Changed run parameters. Removed -n and -e; added -v (--version) and -w (--warnings)
* Improved memory usage
* Improved runtime (many thanks to Nezar Abdennur)
* hic2cool now does a 'direct' conversion of files and does not fail on missing chr-chr contacts or missing normalization vectors. Finding these issues will cause warnings to be printed (controlled by -w flag)
* No longer uses the 'weights' column, which is reserved for cooler
* No longer takes a normalization type argument. All normalization vectors from the hic file are automatically added to the bins table in the output .cool
* Many other minor bug fixes/code improvement
### 0.3.7
Fixed issue with bin1_offset not containing final entry (should be length nbins + 1).
### 0.3.6
Simple release to fix pip execution.
### 0.3.5
README updates, switched cooler syntax in test, and added helpful printing of hic file header info when using the command line tool.
### 0.3.4
Fixed issue where chromosome name was not getting properly set for 'All' vs 'all'.
### 0.3.3
Removed rounding fix. For now, allow py2 and py3 weights to have different number of significant figures (they're very close).
### 0.3.2
Changed output file structure for single resolution file. Resolved an issue where rounding for weights was different between python 2 and 3.
### 0.3.1
Added .travis.yml for automated testing. Changed command line running scheme. Python3 fix in hic2cool_utils.
### 0.3.0
Added multi-resolution format to output cool files. Setup argparse. Improved speed. Added tests for new resolutions format.
## Contributors
Written by Carl Vitzthum (1), Nezar Abdennur (2), Soo Lee (1), and Peter Kerpedjiev (3).
(1) Park lab, Harvard Medical School DBMI
(2) Mirny lab, MIT
(3) Gehlenborg lab, Harvard Medical School DBMI
Originally published 1/26/17.
%package help
Summary: Development documents and examples for hic2cool
Provides: python3-hic2cool-doc
%description help
# hic2cool #
[](https://travis-ci.org/4dn-dcic/hic2cool)
Converter between hic files (from juicer) and single-resolution or multi-resolution cool files (for cooler). Both hic and cool files describe Hi-C contact matrices. Intended to be lightweight, this can be used as an imported package or a stand-alone Python tool for command line conversion
The hic parsing code is based off the [straw project](https://github.com/theaidenlab/straw) by Neva C. Durand and Yue Wu. The hdf5-based structure used for cooler file writing is based off code from the [cooler repository](https://github.com/mirnylab/cooler).
## Important
* Starting from version 0.8.0, hic2cool no longer supports Python 2.7.
* If you converted a hic file using a version of hic2cool lower than 0.5.0, please update your cooler file with the [new update function](#updating-hic2cool-coolers).
## Using the Python package
```
$ pip install hic2cool
```
You can also download the code directly and run the setup yourself.
```
# setuptools >=42 is recommended
$ python setup.py install
```
Once the package is installed, the main method is hic2cool_convert. It takes the same parameters as hic2cool.py, described in the next section. Example usage in a Python script is shown below or in test.py.
```
from hic2cool import hic2cool_convert
hic2cool_convert(<infile>, <outfile>, <resolution (optional)>, <nproc (optional)>, <warnings (optional)>, <silent (optional)>)
```
## Converting files using the command line
The main use of hic2cool is converting between filetypes using `hic2cool convert`. If you install hic2cool itself using pip, you use it on the command line with:
```
$ hic2cool convert <infile> <outfile> -r <resolution> -p <nproc>
```
### Arguments for hic2cool convert
**infile** is a .hic input file.
**outfile** is a .cool output file.
**-r**, or --resolution, is an integer bp resolution supported by the hic file. *Please note* that only resolutions contained within the original hic file can be used. If 0 is given, will use all resolutions to build a multi-resolution file. Default is 0.
**-p**, or --nproc, is the number of processes to use. Default 1. The multiprocessing is not very efficient and would slightly improve speed only for large high-resolution matrices.
**-w**, or --warnings, causes warnings to be explicitly printed to the console. This is false by default, though there are a few cases in which hic2cool will exit with an error based on the input hic file.
**-s**, or --silent, run in silent mode and hide console output from the program. Default false.
**-v**, or --version, print out hic2cool package version and exit.
**-h**, or --help, print out help about the package/specific run mode and exit.
Running hic2cool from the command line will cause some helpful information about the hic file to be printed to stdout unless the `-s` flag is used.
## Output file structure
If you elect to use all resolutions, a multi-resolution .mcool file will be produced. This changes the hdf5 structure of the file from a typical .cool file. Namely, all of the information needed for a complete cooler file is stored in separate hdf5 groups named by the individual resolutions. The hdf5 hierarchy is organized as such:
File --> 'resolutions' --> '###' (where ### is the resolution in bp).
For example, see the code below that generates a multi-res file and then accesses the specific resolution of 10000 bp.
```
from hic2cool import hic2cool_convert
import cooler
### using 0 triggers a multi-res output
hic2cool_convert('my_hic.hic', 'my_cool.cool', 0)
### will give you the cooler object with resolution = 10000 bp
my_cooler = cooler.Cooler('my_cool.cool::resolutions/10000')
```
When using only one resolution, the .cool file produced stores all the necessary information at the top level. Thus, organization in the multi-res format is not needed. The code below produces a file with one resolution, 10000 bp, and opens it with a cooler object.
```
from hic2cool import hic2cool_convert
import cooler
### giving a specific resolution below (e.g. 10000) triggers a single-res output
hic2cool_convert('my_hic.hic', 'my_cool.cool', 10000)
h5file = h5py.File('my_cool.cool', 'r')
### will give you the cooler object with resolution = 10000 bp
my_cooler = cooler.Cooler(h5file)
```
## higlass
Multi-resolution coolers produced by hi2cool can be visualized using [higlass](http://higlass.io/). Please note that single resolution coolers are NOT higlass compatible (created when using a non-zero value for `-r`). If you created a cooler before hic2cool version 0.5.0 that you want to view in higlass, it is highly recommended that you upgrade it before viewing on higlass to ensure correct normalization behavior.
To apply the hic normalization transformations in higlass, right click on the tileset and do the following:
`"<name of tileset>" --> "Configure Series" --> "Transforms" --> "<norm>"`

## Updating hic2cool coolers
As of hic2cool version 0.5.0, there was a critical change in how hic normalization vectors are handled in the resulting cooler files. Prior to 0.5.0, hic normalization vectors were inverted by hic2cool. The rationale for doing this is that hic uses divisive normalization values, whereas cooler uses multiplicative values. However, higlass and the 4DN analysis pipelines specifically handled the divisive normalization values, so hic2cool now handles them the same way.
In the near future, there will be a `cooler` package release to correctly handle divisive hic normalization values when balancing.
To update a hic2cool cooler, simply run:
```
hic2cool update <infile> <outfile (optional)>
```
If you only provide the `infile` argument, then the cooler will be updated directly. If you provide an optional `outfile` file path, then a new cooler updated cooler file will be created and the original file will remain unchanged.
## Extracting hic normalization values
As of hic2cool 0.5.0, you can easily extract hic normalization vectors to an existing cooler file. This will only work if the specified cooler file shares the resolutions found in the hic file. To do this, simply run:
```
hic2cool extract-norms <hic file> <cooler file>
```
You may also provide the optional `-e` flag, which will cause the mitchondrial chromosome to automatically be omitted from the extraction. This is found by name; the code specifically looks for one of `['M', 'MT', 'chrM', 'chrMT']` (in a case-insensitive way). Just like with `hic2cool convert`, you can also provide `-s` and `-w` [arguments](#arguments-for-hic2cool-convert).
## Changelog
### 0.8.2
* loosened version for `numpy`, `scipy` and `pandas`.
### 0.8.1
* `setup.py` takes dependencies directly from `requirements.txt` (`requirements.txt` updated to match `setup.py`)
### 0.8.0
* multiprocessing support for convert
* change in usage of convert API due to the addition of the `nproc` option
* Python 2.7 is deprecated.
### 0.7.3
* Pinned `pandas==0.24.2` since newer versions deprecate python 2
### 0.7.2
* Warning from `hic2cool_utils.parse_hic` will now output chromsome names, not indices
### 0.7.1
* Add `format` and `format-version` to `/` collection for multi-resolution coolers written by hic2cool
* Run `hic2cool_update` to add these attributes to mcool files generated with previous hic2cool versions
* Fixed issue where datetime-derived metadata was written as bytestring when using python 2
### 0.7.0
* Fixed package issues associated with python 2
* Fixed issue where some cooler metadata was written as non-unicode when using python 2
### 0.6.1
* Fixed input issue with `hic2cool update` when using python 2
### 0.6.0
* Added `format-version` and `storage-type` to attributes of output cooler to get up-to-date with cooler schema v3
* Run `hic2cool update` to add these attributes to files generated with previous hic2cool versions
### 0.5.1
Fixed packaging issue by adding MANIFEST.in and made some documentation/pypi edits
### 0.5.0
Large release that changes how hic2cool is run
* hic2cool is now executed with `hic2cool <mode>`, where mode is one of: `[convert, update, extract-norms]`
* Added two new modes: `update` (update coolers made by hic2cool based on version) and `extract-norms` (extract hic normalization vectors to pre-existing cooler file)
* Removed old hic2cool_extractnorms script (this is now run with `hic2cool extract-norms`)
* hic normalization vectors are NO LONGER INVERTED when added to output cooler for consistency with the 4DN omics processing pipeline and higlass
* Missing hic normalization vectors are now represented by vectors of `NaN` (used to be vectors of zeros)
* Improvement of help messages when running hic2cool and change around arguments for running the program
* Test updates
### 0.4.2
* Fixed issue where hic files could not be converted if they were missing normalization vectors
### 0.4.1
* Fixed error in reading counts from hic files of version 6
* Chromosome names are now directly taken from hic file (with exception of 'all')
### 0.4.0
Large patch, should fix most memory issues and improve runtimes:
* Changed run parameters. Removed -n and -e; added -v (--version) and -w (--warnings)
* Improved memory usage
* Improved runtime (many thanks to Nezar Abdennur)
* hic2cool now does a 'direct' conversion of files and does not fail on missing chr-chr contacts or missing normalization vectors. Finding these issues will cause warnings to be printed (controlled by -w flag)
* No longer uses the 'weights' column, which is reserved for cooler
* No longer takes a normalization type argument. All normalization vectors from the hic file are automatically added to the bins table in the output .cool
* Many other minor bug fixes/code improvement
### 0.3.7
Fixed issue with bin1_offset not containing final entry (should be length nbins + 1).
### 0.3.6
Simple release to fix pip execution.
### 0.3.5
README updates, switched cooler syntax in test, and added helpful printing of hic file header info when using the command line tool.
### 0.3.4
Fixed issue where chromosome name was not getting properly set for 'All' vs 'all'.
### 0.3.3
Removed rounding fix. For now, allow py2 and py3 weights to have different number of significant figures (they're very close).
### 0.3.2
Changed output file structure for single resolution file. Resolved an issue where rounding for weights was different between python 2 and 3.
### 0.3.1
Added .travis.yml for automated testing. Changed command line running scheme. Python3 fix in hic2cool_utils.
### 0.3.0
Added multi-resolution format to output cool files. Setup argparse. Improved speed. Added tests for new resolutions format.
## Contributors
Written by Carl Vitzthum (1), Nezar Abdennur (2), Soo Lee (1), and Peter Kerpedjiev (3).
(1) Park lab, Harvard Medical School DBMI
(2) Mirny lab, MIT
(3) Gehlenborg lab, Harvard Medical School DBMI
Originally published 1/26/17.
%prep
%autosetup -n hic2cool-0.8.3
%build
%py3_build
%install
%py3_install
install -d -m755 %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}
if [ -d doc ]; then cp -arf doc %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d docs ]; then cp -arf docs %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d example ]; then cp -arf example %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
if [ -d examples ]; then cp -arf examples %{buildroot}/%{_pkgdocdir}; fi
pushd %{buildroot}
if [ -d usr/lib ]; then
find usr/lib -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/lib64 ]; then
find usr/lib64 -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/bin ]; then
find usr/bin -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
if [ -d usr/sbin ]; then
find usr/sbin -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f\"\n" >> filelist.lst
fi
touch doclist.lst
if [ -d usr/share/man ]; then
find usr/share/man -type f -printf "\"/%h/%f.gz\"\n" >> doclist.lst
fi
popd
mv %{buildroot}/filelist.lst .
mv %{buildroot}/doclist.lst .
%files -n python3-hic2cool -f filelist.lst
%dir %{python3_sitelib}/*
%files help -f doclist.lst
%{_docdir}/*
%changelog
* Fri Jun 09 2023 Python_Bot <Python_Bot@openeuler.org> - 0.8.3-1
- Package Spec generated
|
